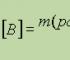Presentation on the topic of AIDS. Development of HIV infection Presentation on the topic of HIV and AIDS
Slide 1
Slide 2
 HIV can only infect cells of the human body that have the CD4 protein molecule on their shell: these are cells of the immune system (mainly blood cells called T-lymphocytes, or CD4-lymphocytes) and the central nervous system B - virus I - immunodeficiency virus H - human
HIV can only infect cells of the human body that have the CD4 protein molecule on their shell: these are cells of the immune system (mainly blood cells called T-lymphocytes, or CD4-lymphocytes) and the central nervous system B - virus I - immunodeficiency virus H - human
Slide 3
 HIV infection is an infectious disease of viral etiology with a long asymptomatic stage, characterized by a slowly progressive defect of the immune system, which leads to the death of the patient from secondary lesions, described as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).
HIV infection is an infectious disease of viral etiology with a long asymptomatic stage, characterized by a slowly progressive defect of the immune system, which leads to the death of the patient from secondary lesions, described as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).
Slide 4
 History of development Twenty-four years ago, most doctors did not know what HIV was. The first reports of a mysterious deadly disease appeared in the United States in 1978. In 1983, scientists managed to isolate the causative agent of the disease, called HIV. Over the years, 16 million people have died as a result of AIDS, the final stage of the disease caused by HIV.
History of development Twenty-four years ago, most doctors did not know what HIV was. The first reports of a mysterious deadly disease appeared in the United States in 1978. In 1983, scientists managed to isolate the causative agent of the disease, called HIV. Over the years, 16 million people have died as a result of AIDS, the final stage of the disease caused by HIV.
Slide 5
 Life with HIV Moment of infection end of life //___1___// _______________________2______________________//_______3____//_4_// “window” carriage of the AIDS virus terminal - from three weeks to 3–6 months or more: diagnosis of HIV infection is impossible due to the lack of antibodies , but a person is a source of infection from the moment of infection until the end of life - carrier of the virus - 7–15 years (without treatment): the person does not look or feel sick, retains ability to work and other social opportunities. Dispensary observation is necessary to make a decision on timely treatment - AIDS – 3–5 years (without treatment): the ability to work is gradually lost, the person looks and feels sick, treatment is required - terminal stage – 3–6 months: severe dying, outside care is required
Life with HIV Moment of infection end of life //___1___// _______________________2______________________//_______3____//_4_// “window” carriage of the AIDS virus terminal - from three weeks to 3–6 months or more: diagnosis of HIV infection is impossible due to the lack of antibodies , but a person is a source of infection from the moment of infection until the end of life - carrier of the virus - 7–15 years (without treatment): the person does not look or feel sick, retains ability to work and other social opportunities. Dispensary observation is necessary to make a decision on timely treatment - AIDS – 3–5 years (without treatment): the ability to work is gradually lost, the person looks and feels sick, treatment is required - terminal stage – 3–6 months: severe dying, outside care is required
Slide 6
 Remember!!! You can become infected with HIV without knowing it and unintentionally spread HIV to others. According to the criminal code, for deliberate infection - 5 years in prison.
Remember!!! You can become infected with HIV without knowing it and unintentionally spread HIV to others. According to the criminal code, for deliberate infection - 5 years in prison.
Slide 7
 Once in the body, the virus gradually destroys the immune system. Over time, she becomes weak. The development of numerous diseases: pneumonia, cancer, infectious diseases that do not usually occur in people with a healthy immune system. Sudden weight loss (10% or more) Increased body temperature Severe night sweats Chronic fatigue Enlarged lymph nodes Persistent cough Intestinal upset Eventually, there comes a time when the body's resistance is completely lost, and numerous diseases become so aggravated that the patient dies.
Once in the body, the virus gradually destroys the immune system. Over time, she becomes weak. The development of numerous diseases: pneumonia, cancer, infectious diseases that do not usually occur in people with a healthy immune system. Sudden weight loss (10% or more) Increased body temperature Severe night sweats Chronic fatigue Enlarged lymph nodes Persistent cough Intestinal upset Eventually, there comes a time when the body's resistance is completely lost, and numerous diseases become so aggravated that the patient dies.
Slide 8
 Routes of transmission of HIV infection The first way is sexual contact with an infected person. HIV can be transmitted from man to woman, from woman to man, from man to man and from woman to woman.
Routes of transmission of HIV infection The first way is sexual contact with an infected person. HIV can be transmitted from man to woman, from woman to man, from man to man and from woman to woman.
Slide 9
 The second way The second way is the entry of the blood of an HIV-infected or AIDS-infected person into the body of a healthy person. This can occur through blood transfusions from HIV-infected donors and through the use of non-sterile medical instruments. Blood used for medical purposes is tested for the presence of the virus, and the instruments, primarily syringes, are disposable.
The second way The second way is the entry of the blood of an HIV-infected or AIDS-infected person into the body of a healthy person. This can occur through blood transfusions from HIV-infected donors and through the use of non-sterile medical instruments. Blood used for medical purposes is tested for the presence of the virus, and the instruments, primarily syringes, are disposable.
Slide 10
 The third way The third way is the transmission of HIV from an infected or AIDS-sick mother to her child. This can happen during pregnancy. HIV passes through the placenta into the fetus. During the birth process, as the child passes through the mother’s birth canal, HIV, along with the blood, can enter the newborn’s body through easily vulnerable skin. BUT IN THE FIRST YEAR OF LIFE YOU CAN BE CURED.
The third way The third way is the transmission of HIV from an infected or AIDS-sick mother to her child. This can happen during pregnancy. HIV passes through the placenta into the fetus. During the birth process, as the child passes through the mother’s birth canal, HIV, along with the blood, can enter the newborn’s body through easily vulnerable skin. BUT IN THE FIRST YEAR OF LIFE YOU CAN BE CURED.
Slide 11
 Treatment -Currently, there is no vaccine that can prevent HIV infection and no medicine that can destroy HIV in the body.
Treatment -Currently, there is no vaccine that can prevent HIV infection and no medicine that can destroy HIV in the body.
Slide 12
 The spread of HIV/AIDS through blood can be prevented by: Testing donated blood People creating their own blood banks Sterilizing medical instruments and using disposable medical instruments Using personal equipment and instruments for manicure, pedicure, piercing, shaving Strict adherence to the rules of safe behavior and the use of personal protective equipment
The spread of HIV/AIDS through blood can be prevented by: Testing donated blood People creating their own blood banks Sterilizing medical instruments and using disposable medical instruments Using personal equipment and instruments for manicure, pedicure, piercing, shaving Strict adherence to the rules of safe behavior and the use of personal protective equipment
Slide 13
 The HIV virus is not transmitted through: bites of mosquitoes and other insects, air, a handshake (in the absence of open skin lesions), a kiss (any, but in the absence of bleeding lesions and cracks on the lips and mouth), dishes, clothes, use of the bathroom, toilet, swimming pool, etc.
The HIV virus is not transmitted through: bites of mosquitoes and other insects, air, a handshake (in the absence of open skin lesions), a kiss (any, but in the absence of bleeding lesions and cracks on the lips and mouth), dishes, clothes, use of the bathroom, toilet, swimming pool, etc.
Slide 14
 WHY DO YOU KNOW IF YOU HAVE HIV? - to stop the disease in time and prevent the development of AIDS; - to be more attentive to your health, because... Any disease caused by HIV infection is more severe and requires special treatment. This especially applies to hepatitis, tumors, tuberculosis; - so as not to infect your loved ones.
WHY DO YOU KNOW IF YOU HAVE HIV? - to stop the disease in time and prevent the development of AIDS; - to be more attentive to your health, because... Any disease caused by HIV infection is more severe and requires special treatment. This especially applies to hepatitis, tumors, tuberculosis; - so as not to infect your loved ones.
Slide 15
 7 rules for safe behavior regarding HIV/AIDS -I know how HIV is transmitted and how I can protect myself. -I never use drugs. -I do not use non-sterile instruments for ear piercing, tattooing, piercing, or shaving. -I always follow the rules of personal hygiene. -I will refuse medical services if I am not sure that the instruments are sterile. -For manicure or shaving I use only my personal tools. -If I have had/will be at risk of contracting HIV, I will get my blood tested.
7 rules for safe behavior regarding HIV/AIDS -I know how HIV is transmitted and how I can protect myself. -I never use drugs. -I do not use non-sterile instruments for ear piercing, tattooing, piercing, or shaving. -I always follow the rules of personal hygiene. -I will refuse medical services if I am not sure that the instruments are sterile. -For manicure or shaving I use only my personal tools. -If I have had/will be at risk of contracting HIV, I will get my blood tested.
1 slide

2 slide
C – syndrome. There are a large number of signs and symptoms associated with the disease. P – acquired. The disease is not caused by genetic predisposition, but is acquired in a specific way. And – immune. D – deficiency. At the same time, the immune system is suppressed and loses its ability to resist various infections.

3 slide
The first cases of AIDS were noted in the early eighties in the United States among drug addicts. The epidemic has now spread to about 190 countries around the world.

4 slide
Why can't the body defend itself? Virus T-lymphocyte T-lymphocyte with virus Damage to new T-lymphocytes Antibody Viruses in cells are in a form inaccessible to antibodies

5 slide
As a result of the disease, the human body becomes defenseless against infectious and tumor diseases, which the normal immune system copes with.

6 slide
Stages of AIDS disease. I. Infection with the HIV virus: weekly fever, swollen lymph nodes, rash. After a month, antibodies to the HIV virus are detected in the blood. II. Latent period: from several weeks to several years: ulcerations of the mucous membrane, fungal infections of the skin, weight loss, diarrhea, elevated body temperature. III. AIDS: pneumonia, tumors, sepsis and other infectious diseases.


8 slide
Routes of transmission of HIV infection. Through blood: during blood transfusion, organ and tissue transplantation. From mother to child: in utero, during childbirth, during breastfeeding. When using contaminated medical instruments, drug addicts use one syringe. Sexual – with a regular sexual partner (use condoms!) and homosexual relationships; with artificial insemination.

- decrease in the number of CD4 lymphocytes;
- various infections (opportunistic);
- tumor diseases of infectious and non-infectious nature.
AIDS is the final stage of infection.
What you should pay attention to?
- cough for more than a month;
- dermatitis;
- herpes;
- candidiasis;
- lymphadenopathy.
Symptoms (major)
- weight loss (more than 12% of the original);
- diarrhea (chronic);
- fever (constant or intermittent).
Stages of the disease
- Infection.
- Period of infection (latent).
- Laboratory signs of infection.
- Clinic (primary) of an acute viral infection is not a mandatory stage.
- AIDS in the clinic - immunodeficiency with the addition of disease indicators.
Routes of transmission
- Direct contact of mucous membranes or blood with liquids (containing the virus).
- Sexual contacts: anal, oral, vaginal sex.
- Blood transfusion.
- From mother to fetus.
Current status of infection
Today, HIV infection has become an epidemic. In 2008, the number of citizens infected with HIV was 34 million people. In Russia, more than 790,866 thousand people are living with HIV infection, including about 7,000 children under 15 years of age.
When did HIV originate?
Using the method of molecular phylogeny, it has been proven that the birthplace of this terrible disease is the region of West-Central Africa. This infection arose there at the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries. The symptoms of the disease were first described in 1981 in the USA. This was done by an organization called the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
How is HIV treated?
At present, no vaccine has been created. Treatment of this infection slows down the course of the disease, but does not eliminate the disease itself. Science and society know of one case of cure for HIV through a stem cell (modified) transplant. Antiviral therapy reduces mortality from the disease, but drugs against the disease are expensive. They are not available to citizens of all countries of the world.
Disease prevention
Due to the difficulty of treating HIV, doctors assign a special role to the prevention of HIV infection. It consists of disseminating information about protected sex and the use of disposable syringes.
What contacts do not spread the disease?
HIV is not dangerous during household contacts through salivary and tear fluid; in addition, it is not transmitted by airborne droplets, through moisture and food. An infected person's saliva can be potentially dangerous if it contains blood.
Should there be a day of remembrance for citizens who died of AIDS?
Notable people who died from this disease
Actor Cancer Hudson, singer Freddie Mercury, Rudolf Nureyev, Isaac Asimov (writer).
1. Incubation period (the period of seroconversion - before the appearance of detectable antibodies to HIV) - from 3 weeks to 3 months (according to other sources - from 2 weeks to 1 year). 2. Prodromal period - the stage of primary infection, up to 1 month. Clinical manifestations: low-grade fever, urticaria, stomatitis, inflammation of the lymph nodes - they become enlarged, soft and painful (passes under the guise of infectious mononucleosis). The maximum concentration of virus and antibodies appears only at the very end of the prodromal period. 3. The latent period is 5-10 years, the only manifestation is a persistent enlargement of the lymph nodes (dense, painless) - lymphadenopathy. 4. Pre-AIDS - duration 1-2 years - the beginning of suppression of cellular immunity. Often recurrent herpes - long-term non-healing ulcerations of the oral mucosa, genital organs, stomatitis. Leukoplakia of the tongue (proliferation of the papillary layer - “fibrous tongue”). Candidiasis - oral mucosa, genital organs. 5. Terminal stage - AIDS - 1-2 years.

Slide 2
HIV INFECTION -
This is a disease caused by the human immunodeficiency virus, characterized by a specific lesion of the immune system, leading to its slow and steady destruction until the formation of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).

Slide 3
RELEVANCE
A quarter of a century has passed since the first cases of AIDS were discovered. During this time, AIDS has radically changed our world: it has killed more than 25 million men and women, orphaned millions of children, increased poverty and misery, and in some countries even reversed human development efforts. Today, about 40 million people are living with HIV – half of them are women. What was initially reported as just a few cases of a mysterious disease has now become a pandemic that is one of the most serious threats to global progress in the 21st century.
Kofi A. Annan former UN Secretary-General From the Report on the global AIDS epidemic (UNAIDS, 2006)

Slide 4

Slide 5

Slide 6
AIDS = disease
HIV INFECTION = disease ending with AIDS!!!

Slide 7
Hypotheses for the origin of HIV
At the moment, the main hypothesis for the occurrence of HIV infection is the transmission of the virus to humans from primates.

Slide 8
History of HIV infection
1978 – the first detection of AIDS symptoms. 1983 – discovery of the human immunodeficiency virus. 1987 – the first case of HIV infection was registered in Russia. 1991 – Freddie Mercury, leader of the band Queen, died of AIDS.

Slide 9
1995 – 1,200 people with HIV infection were registered in Russia. 1996 - HIV spreads among drug addicts, the number of patients grows rapidly (6 times per year) 2001 - the beginning of an epidemic is declared in Russia, more than 150,000 cases of HIV infection are registered. 2009 – more than 100 people become infected with HIV every day in Russia.

Slide 10
Number of HIV-infected people in the Samara region
2009 – 40,500 people registered; Of the 100 thousand population of the Samara region, 730 people are HIV-infected.

Slide 11

Slide 12

Slide 13
With intravenous drug administration
Drug addicts often share syringes, so the risk of infection is very high. The first dose may be the last

Slide 14
For blood transfusions, organ and tissue transplants
From an infected donor

Slide 15
When using non-sterile medical instruments
for ear piercing, piercing, tattoo

Slide 16
From an infected mother
intrauterine infection during pregnancy; during childbirth; through the breast milk of an HIV-infected mother

Slide 17

Slide 18
HIV is not transmitted:
when touching and shaking hands; when kissing; when hugging; when drinking from one glass; when using shared clothing or bedding: for insect and animal bites.

Slide 19
Changes in the body during HIV infection (pathogenesis)
HIV primarily infects cells of the immune system - lymphocytes. Infected lymphocytes gradually die. When the number of cells reaches a critical level, the body becomes susceptible to various infections - AIDS develops, which ultimately causes death.

Slide 20
Course of HIV infection
Incubation stage From the moment of infection until the clinical manifestations of acute infection and/or the production of antibodies (on average from 3 weeks to 3 months). There are no clinical manifestations of the disease, antibodies to HIV are not detectable. But already during this period it is possible to detect the virus using PCR.

Slide 21
II. Stage of primary manifestations
2 "A" - asymptomatic. 2 “B” - acute HIV infection without secondary diseases. 2 “B” - acute HIV infection with secondary diseases (against the background of a temporary decrease in immunity, secondary diseases develop - sore throat, bacterial pneumonia, candidiasis, herpes). The duration of clinical manifestations of acute HIV infection is usually 2 - 3 weeks.

Slide 22
III. Latent stage.
Slow progression of immunodeficiency. The only clinical manifestation is enlarged lymph nodes, which may be absent. The duration of the latent stage is from 2 - 3 to 20 or more years, on average 6 - 7 years.

Slide 23
IV. Stage of secondary diseases
4 “A” - it is characterized by bacterial, fungal and viral lesions of the mucous membranes and skin, inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract. 4 "B" - more severe and long-lasting skin lesions, Kaposi's sarcoma, weight loss, damage to the peripheral nervous system and internal organs. 4 “B” - severe, life-threatening secondary diseases.

Slide 24
V. Terminal stage
cachexia (exhaustion) occurs; fever persists; intoxication is pronounced; the patient spends all the time in bed; dementia develops, the content of lymphocytes reaches critical values. the disease progresses and the patient dies.

Slide 25

Slide 26

Slide 27
PREVENTION OF HIV infection
THE ONLY WAY TO NOT get HIV infection IS TO PROTECT YOURSELF FROM THE POSSIBILITY OF INFECTION

Slide 28
How to prevent HIV infection through sexual contact?
Delay entering into sexual relations. If a person decides to engage in sexual relations, then safe sex should be practiced. You should use a condom during penetrative sexual intercourse, remembering the rules for quality purchase, storage and use of a condom:

Slide 29
buy condoms in pharmacies and good supermarkets, where the rules for storing condoms are observed; buy condoms from well-known European, American and Russian companies; pay attention to the expiration date indicated on the packaging so that it is not expired; it is necessary to use only water-based lubricants, since fat-based lubricants (vaseline, cream, lipstick, etc.) destroy latex and impair the reliability of the condom; Only latex or polyurethane condoms protect against HIV and other infections, which should be indicated on the packaging; the condom should be used only once; It is necessary to carefully open the condom package without damaging the condom itself with your nails; Birth control pills and suppositories only prevent pregnancy, but do not protect against HIV.

Slide 30
Safe sex is like self-love
Accepting your sexuality. Acceptance of sex without drugs and alcohol. Integrity. A high self-evaluation. Respect. Health concerns. Self confidence.
Despite all the differences, people who practice only safe sex, in most cases, have several common features:

Slide 31
How to prevent infection through blood, through injections?
Intact skin is a reliable barrier to the virus. Disposable and/or sterile instruments should be used. for medical and cosmetic services Refuse any use of drugs.

Slide 32
HIV infection is a disease of behavior
It is possible to avoid infection by following certain rules of safe behavior.

Slide 33
16 rules of safe behavior regarding HIV infection:
I do physical exercise or sports every day. I can cope with stress. I do not smoke. I know how HIV is transmitted and how I can protect myself. I keep a daily routine. I never use drugs. I do not use non-sterile instruments for ear piercing, tattooing, piercing, or shaving. I don't drink alcohol.

Slide 34
I strive to ensure that my diet is balanced. I always follow the rules of personal hygiene. I exclude casual sexual contacts. I will refuse medical services if I am not sure that the instruments are sterile. When having sexual intercourse, I use a condom. For manicure or shaving I use only my personal tools. If I have been/will be at risk of contracting HIV, I will get my blood tested. I will/have a regular sexual partner.

Slide 35
When should you get tested for HIV?
after having sex with a new partner without a condom after sexual assault if your sex partner has had sex with someone else if your current or past sex partner is HIV positive after sharing needles or syringes to inject drugs or other substances, and also for tattoos and piercings after any contact with the blood of an HIV-infected person if your partner shared needles with others or was exposed to any other risk of infection after the discovery of another sexually transmitted infection

Slide 36
If you are not sure of your safety and want to be tested for HIV infection, you can do this at the clinic at your place of residence. If you want to undergo an anonymous examination, you can contact the regional center for the prevention and control of AIDS at the address: Samara, st. L. Tolstoy, 142 tel. 242-69-38

Slide 37
Treatment of HIV infection
Currently, there is no vaccine that can prevent HIV infection and no medicine that can destroy HIV in the body. At the moment, drugs have been developed that make it possible to maintain the health of HIV-infected people for some time and delay the final stage of the disease.

Slide 38
Slide 40
Currently, there are many support centers for HIV-infected citizens, which provide social, medical and psychological assistance.
Samara Regional Center "Family" tel.: 958-32-90 District Center "Family", located at the place of residence Samara Regional Center for the Prevention and Control of AIDS, tel.: 332-36-57 Regional public organization "Unity" for the provision of support for HIV-infected women, tel.: 8-917-144-39-10 Mutual help groups for women living with HIV, Marina Vladimirovna Bogacheva, tel.: 8-917-105-65-33 “Medical Prevention Center” - organized 24/7 hotline telephone service. For all questions, please call: 337 – 49 – 49, 337 – 05 - 11