Why is nerve paralysis
Paralysis is a condition in which muscles are unable to perform their function because shrink. Paralysis itself is only a sign (symptom). This disease is not independent, but only develops secondarily due to some kind of ailment or a component of a condition, disorder, neoplasm, etc.
From the point of view of origin, there are two types of paralysis:
- peripheral (another name for it is sluggish);
- central (aka spastic).
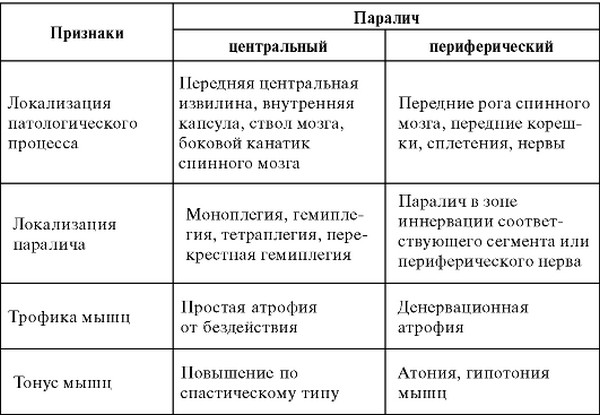
Peripheral is expressed by the destruction of motor neurons that innervate muscles, or nerves connected to muscles. In the course of the development of peripheral destruction, the tone of the paralyzed muscles decreases, they become thinner and depleted, which creates complete atrophy.
The central ones have their own distinctive ability - an increase in muscle activity in the paralyzed areas and damage to the area above the neuronal motility.
There is another classification of paralysis - in terms of the number of affected limbs:
- monoplegia - paralysis of one of the limbs;
- hemiplegia - lesion on only one side;
- paraplegia is a partial paralysis of the legs or arms (only the upper or lower limbs are affected);
- tetraplegia affects all limbs, it is paralysis of the legs and arms.
Causes
According to statistics, about 2% of the population experience discomfort in the lower extremities when moving. Every year, just over 1 million people injure their back to varying degrees. And these numbers are growing every year.
With the weakening of the capabilities of full-fledged motor skills, and not their complete loss, we can talk about paresis. Paresis and paralysis are similar in one thing - they occur when a person's nerve cells are damaged, when two parts of the motor system responsible for coordination are affected. Complete paralysis can be caused by the following factors:
- spinal and head injuries;
- intoxication with substances: heavy metals and their salts, poisons of various origins, alcohol, drugs, drugs, etc.;
- cancers;
- infectious diseases that entail negative consequences in the work of the whole organism;
- metabolic disorders in the body;
- botulism (manifested by a violation in the process of the respiratory system, gastrointestinal disorders, abdominal pain, slurred speech);
- poor diet, unhealthy lifestyle;
- alcohol and drug abuse;
- hereditary changes in the body, affecting the work of the nervous system and accompanied by poor coordination of movements.
People who have suffered a birth trauma can also suffer from paralysis. This, among other things, is a common cause of cerebral palsy.
There are several ailments of unknown origin (for example,), which are manifested by impaired motor skills, they have very negative consequences. There is a high probability that paralysis may be the result of neurosis and have a psychogenic nature of origin. Such patients definitely need psychological help from a professional.
Pathogenesis
A paralyzed person must be carefully examined in order to notice even the slightest changes in the body. If there are signs of changes in reflexes, then most likely the ailment is caused by organic causes. In this case, there is a risk of developing atrophy and a complete disorder of muscle tone. If the paralysis is temporary, there is no change in tendon reflexes or muscle tone.
Symptoms
Paralysis can be caused by various reasons, which is why its symptoms can be of a different nature and all kinds of localization. The most common changes occurring in the main structural component of the nervous system with paralysis can be:
- degeneration (nerve tissue dies and a new one does not form);
- destruction (in this case, the conduction of nerve impulses is disrupted);
- neuroinflammation;
- violation of vascular patency, plaque formation, risk of thrombus formation;
- the development of sclerosis;
- the appearance of demyelination - a pathological process of destruction of the myelin sheath of the nervous system.
With this disease, there are other symptoms: headaches, migraines, fever, lump in the throat, partial loss of vision, nausea and vomiting, increased fatigue, muscle pain or weakness, involuntary urination, inability to control bowel movements.
If we consider paralysis from the point of view of anatomy, then we can divide them into two forms: the first are caused by damage to the central nervous system (cerebral and spinal), the second -.
Central paralysis symptoms
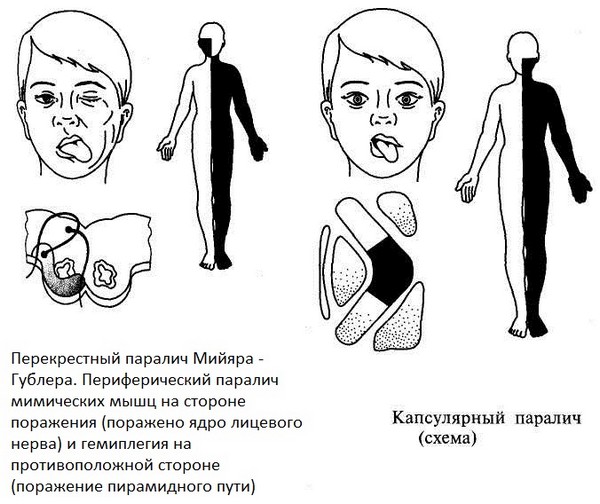
Symptoms of central paralysis are very diverse: some signs are detected immediately in their pure form, others are confused by their combination with some signs of peripheral paralysis. But both are accompanied by changes in sensing and atrophy, pathologies of vascular tone.
With the genesis of this type of ailment, the body is completely exposed to suffering, and not individual parts of the musculoskeletal system, for example, muscles.
Absolute tendon reflexes persist and may even increase; accelerated muscle spasm of the paralyzed limbs is noted. Abdominal reflexes - on the contrary: reduced or disappear on the paralyzed side.
Symptoms of Peripheral Paralysis
Paralysis of this form is formed when the nerve roots are destroyed, the muscles are weakened, the plexuses or the nerve itself are damaged. This form is usually characterized by vulnerability.
Symptoms of paralysis of the lower extremities
In the process of diagnosing paralysis of the lower extremities, a phenomenon may occur - in which a response is received to the dashed irritation of the outer edge of the sole - 1 toe of the foot unbends. In a paralyzed limb, there is a complete decrease in deep reflexes, there is a possibility of their complete absence. In the same case, clones are not detected. But abdominal reflexes can be noted, which remain intact.
First aid
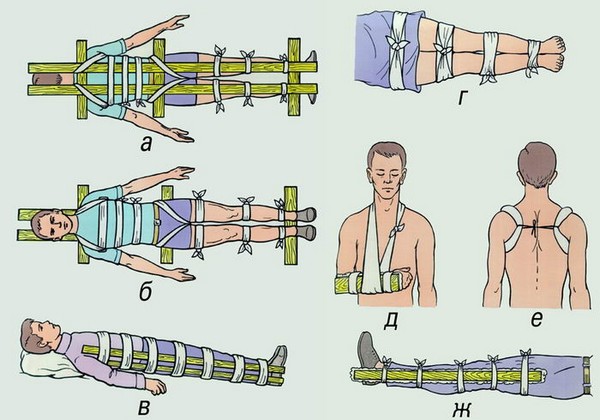
In case of a sudden lesion of the limbs, it is necessary to consult a doctor promptly. To do this, the first step is to call an ambulance. While waiting for the medical team, you can alleviate the patient's situation.
- If the head, neck or back is injured (or if there is suspicion of injury), the victim should never be moved. The exception is a deadly threat to life - fire, flood, natural disaster.
- Spinal fixation. To prevent further damage, it is necessary to position the victim's head in a straight line with the body, using available means.
- Do not give anything to drink. Under no pretext, water should be given before the arrival of specialists.
Diagnostics
- analysis of complaints, studying the patient's medical record, interviewing relatives about the patient's health status, about the medications taken;
- what signs preceded the onset of complaints and the first symptoms (for example, migraines, indigestion, changes in body temperature, etc.);
- is there a hereditary predisposition to the appearance of such an ailment;
- is there a connection between the paralysis and the victim's occupation, perhaps a problem in the place of residence or being in a room with salts of various heavy metals or organic solvents;
- examination of the patient by a neurologist to assess muscle mass, search for neurological symptoms necessary to further clarify the clinical picture (strabismus, atrophy, facial asymmetry, lack of swallowing reflex);
- a blood test to detect inflammatory processes, to determine the level of erythrocytes and leukocytes;
- exclusion or confirmation of intoxication;
- electroneuromyography - to assess the bioelectric muscle activity, the speed of the nerve impulse, reduce the amplitude of the M-response;
- electroencephalography - to determine if the electrical activity of various areas of the brain has changed and how much;
- MRI - examines the brain and spinal cord to study their structure, identify violations in their structure and exclude the likelihood of subsequent tumor formation or hemorrhage. They also examine the brain for the presence of abscesses and foci of decay of nervous tissue;
- MR-angiography - to assess the patency of the arteries in the cranial cavity, their integrity, as well as to detect tumor formations.
Treatment

The primary task that the attending physician sets himself is to eliminate the cause of the disease. In all cases, without exception, symptomatic drug treatment, exercise therapy, as well as therapeutic massage are carried out, which will help accelerate the recovery of motor reflexes. For each individual case, its own program is selected, including medicines and preventive gymnastics.
In the treatment of this dangerous ailment, the main emphasis is on physiotherapy exercises. In the process of training, it is very important to position the affected limb correctly so that contractures do not appear. Physical education includes vigorous and passive exercises aimed at restoring motor skills and healthy muscle tone. You need to do gymnastics carefully, in moderation, observing all the doctor's instructions.
Before a gymnastic complex of exercises with peripheral paralysis, it is necessary to do a special massage. With a gradual revival of motor functions, active movements are added to the complex, aimed at strengthening muscles, normalizing tone and leveling gait. Great success in treatment can be achieved by adding water activities to this complex. They can be done in the bathroom, or you can sign up for the pool. Water helps reduce stress on the joints, so the healing process is faster and less painful.
The medication course of drugs is selected individually by the neuropathologist. Usually, Dibazol, Proserin, Melliktin and intramuscular injections of vitamin B1 are prescribed. With a dangerous form of paralysis, corticosteroid drugs and salicylates are added to this complex. In extreme cases, electrotherapy is used. For vascular disorders, there are special preparations for improving the metabolic processes of the brain and saturating it with oxygen.
It is treated with datrolene in combination with imidazoline and benzodiazepine gabaleptin. There are cases in which Botox is used, which can help damaged muscles relax and return to their former shape. It is not excluded in the case of a spastic type of paralysis and surgical intervention. But to address this at least, it must take at least 6 months. If no shifts in a positive direction are observed during this period, the surgeon takes over.

It must be remembered that the main thing for the patient is movement. If the patient cannot do this on his own, you need to help him, because the more a person is in motion, the faster he will recover.
With prolonged stay in bed, blood circulation is disturbed, which leads to frequent dizziness and fainting, the respiratory system, cardiovascular, joints suffer, skin condition deteriorates and much more.
It is imperative to involve the lungs in active work and perform simple breathing exercises, knead the body with massage all the time and strengthen it with physical education.
Prevention of paralysis
- Get regular medical check-ups once a year.
- Complete elimination of alcohol and drugs.
- Maintaining a healthy sports lifestyle (moderate physical activity, daily morning exercises, walks in the fresh air, a healthy 8-hour sleep).
- Following the rules of proper nutrition (excluding fried and smoked foods, eating fruits and vegetables that are rich in vitamins, moderate consumption of sweets).
- Blood pressure control.