What is a ravine? Features and Description
What is a ravine? This is a form of relief that resembles a canyon or a valley with steep parties, but in a slightly reduced form. The ravine may have an active stream of water all year round or expand during the rainy season, and some remain dry due to climate change from the moment of its formation.
How are ravines formed?
The ravines are formed under the action of the flow that destroys the land. What is a ravine? This is a portion of the river in mountainous areas and at lower altitudes that have hills and changing land relief. As a rule, its width is about 30 meters.

The ravine is a reduced version of the valley with steep parties. This form of relief is a river slope with relatively steep transverse parties, with a bias from twenty to seventy percent. The ravines (photo in the article) may have or not to have active streams flowing along the downlink channel, which originally formed them. In addition, often they are characterized by intermittent streams, since their geographic scale may not be enough to support long-term watercourse.
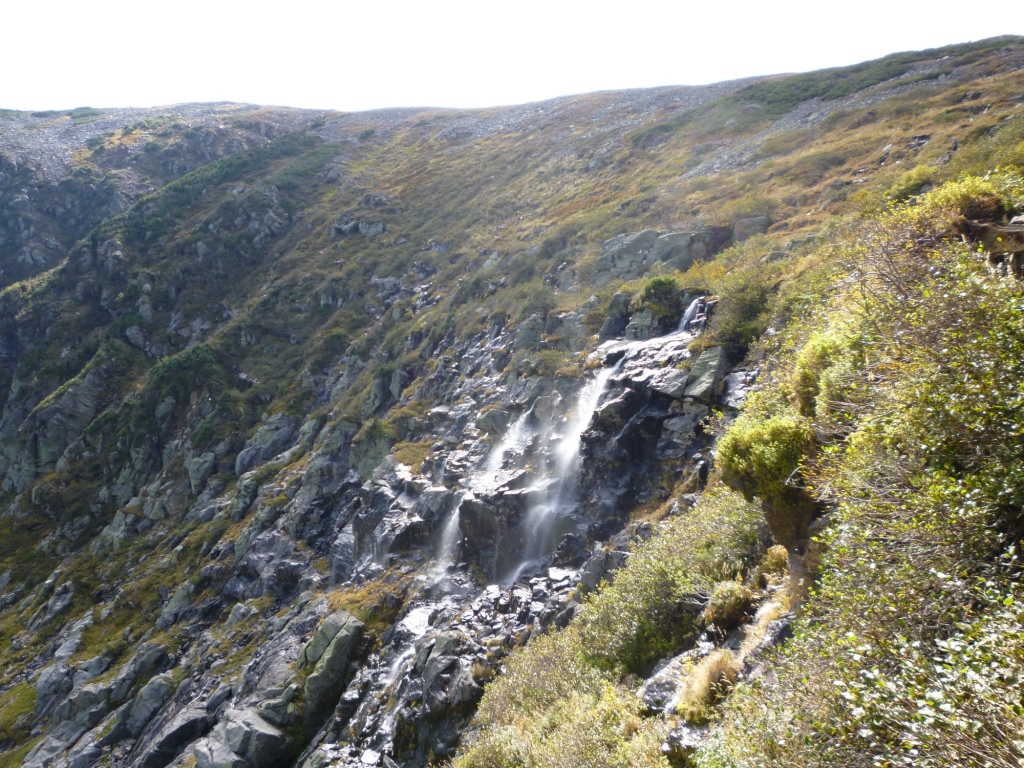

What is a ravine?
This is a deep valley formed as a result of linear (dendritic) erosion of loose and naked soil. What is a ravine? This is an erosion sign that exists on the continuum of the scale. The ravine is defined as a small, narrow and deep flowing. They can often be identified using a combination of relief attributes, including slope, profile curvature and accumulation of flow.

This form of soil erosion, as a rule, is formed when many thresholds are connected together and further expand with a depth of more than 30 cm. The formation of the ravine depends on the characteristics of the drain, producing the drain, drainage area, the characteristics of the soil, alignment and slope of the bed. Based on the size, the ravine can be classified as a small ravine with a depth of 5 m.
Extreme soil erosion form
These sites cannot be eliminated by treating soil or plowing due to their depth and slope. Strong erosion occurs due to water action. This is the formation of wide and deep channels, usually V-shaped or U-shaped, on loose lands. These large ditches or small valleys have a depth and width of the pair to tens of meters.

Little Valley
The formation of ravines occurs more intensively in places where the continental climate is dominated. Mix three stages of formation.
- Small fish appears, which is gradually doing deeper water flows. This is a very fast stage. As the depot is reepened. Under the influence of snow and rain, water flows from it like a waterfall, soaring the base of the ledge. Over time, it collapses, and the ravine slows slowly. When growth stops, the ambigues begin to overgrow.
- Beam. Over time, the overwhelming ravine takes the appearance of the beam used often under the haystock, gardens and even settlements. However, ravines can bring more harm than good. They cause fairly significant damage, putting out large arrays of agricultural land and destroy the soil cover.
- Actually ravines formed and located on the hills and high river shores. The formed ravine has a vertex, often steep and ribbed slopes, mouth and bottom, which is the lowest point of the ravine.
 $(document).ready(function() {
$('.highslide-container').on('click', function() {
$(this).find('.highslide').click();
});
$('.highslide').magnificPopup({
type: 'image',
gallery: {
enabled: true,
preload: [1, 1],
navigateByImgClick: true,
tClose: 'Закрыть (Esc)',
tPrev: 'Предыдущее фото (стрелка влево)', // title for left button
tNext: 'Следующее фото (стрелка вправо)', // title for right button
tCounter: 'Фотография %curr% из %total%' // markup of counter
},
});
});
$(document).ready(function() {
$('.highslide-container').on('click', function() {
$(this).find('.highslide').click();
});
$('.highslide').magnificPopup({
type: 'image',
gallery: {
enabled: true,
preload: [1, 1],
navigateByImgClick: true,
tClose: 'Закрыть (Esc)',
tPrev: 'Предыдущее фото (стрелка влево)', // title for left button
tNext: 'Следующее фото (стрелка вправо)', // title for right button
tCounter: 'Фотография %curr% из %total%' // markup of counter
},
});
});