What is ammonia? Ammonia formula and properties
Ammonia - a compound, which is the most important source of nitrogen for living organisms, as well as found applications in various industries. What is ammonia, what are its properties? Let's figure it out.
What is ammonia: main characteristics
Ammonia (hydrodium nitride) is a nitrogen compound with hydrogen having a chemical formula NH 3. The molecule form resembles the trigonal pyramid, at the top of which is a nitrogen atom.
Ammonia is a gas that does not have color, but having a sharp specific smell. Ammonia density is almost two times less than air density. At a temperature of 15 o C, it is 0.73 kg / m 3. The density of ammonia liquid under normal conditions is 686 kg / m 3. Molecular weight of the substance - 17.2 g / mol. A distinctive feature of ammonia is its high solubility in water. Thus, at a temperature of 0 ° C, it reaches about 1,200 volumes in the volume of water, at 20 ° C - 700 volumes. The "ammonia - water" solution (ammonia water) is characterized by a weakly alkaline reaction and a rather unique property compared to other alkalis: with an increase in concentration, the density decreases.
How is Ammonia formed?
What is ammonia in the human body? This is a finite product of nitrogen exchange. Its large part of the liver is converted into urea (carbamide) less toxic substance.
Ammonia in natural conditions is formed as a result of the decomposition of organic compounds containing nitrogen. For industrial use, this substance is obtained by artificially.
Getting ammonia in industrial and laboratory conditions
In industrial conditions, ammonia is obtained by catalytic synthesis from nitrogen and hydrogen:
N 2 + 3H 2 → 2NH3 + Q.
The process of obtaining a substance is carried out at a temperature of 500 ° C and a pressure of 350 atm. As a catalyst, the resulting ammonia is removed by cooling. Nitrogen and hydrogen, which have not reacted, returned to synthesis.
In laboratory conditions, ammonia is obtained mainly by weak heating of the mixture consisting of ammonium chloride and haired lime:
2NH 4 Cl + Ca (OH) 2 → CaCl 2 + 2NH 3 + 2H 2 O.
To drain, the finished connection is passed through a mixture of lime and caustic soda. Quite dry ammonia can be obtained by dissolving metal sodium and subsequent distillation.
Where is ammonia?
Hydrogen nitride is widely used in various industries. Huge amounts are used for and various fertilizers (urea, ammonium nitrate, etc.), polymers, sinyl acid, soda, ammonium salts and other types of chemical production products.

In the light industry, ammonia properties are used when cleaning and staining such fabrics, like silk, wool and cotton. In steel production, it is used to increase steel hardness by saturating its surface layers with nitrogen. In the petrochemical industry with the help of hydrogen nitride neutralize acidic waste.
Due to its thermodynamic properties, liquid ammonia is used as refrigerant in refrigeration equipment.
NH 3 + HNO 3 → NH 4 NO 3.
When interacting with HCl, ammonium chloride is formed:
NH 3 + HCl → NH 4 Cl.

Ammonium salts are solid crystalline substances that decompose in water and possessing properties inherent metal salts. Solutions of compounds formed as a result of the interaction of ammonia and strong acids have a weakly acidic reaction.
Due to the nitrogen atoms, hydrogen nitride is an active reducing agent. Recovery properties are manifested when heated. When burning in an oxygen atmosphere, it forms nitrogen and water. In the presence of catalysts, the interaction with oxygen gives hydrogen nitride has the ability to restore metals from oxides.
Halogens as a result of a reaction with ammonia form nitrogen halides - dangerous explosives. When interacting with carboxylic acids and their derivatives, the hydrogen nitride forms amides. In coal reactions (at 1000 ° C) and methane it gives
With the ions of Metals, ammonia form amino acids, or ammonia (complex compounds), having a characteristic feature: a nitrogen atom is always associated with three hydrogen atoms. As a result of complexation, the painting of the substance changes. So, for example, a blue solution with the addition of hydrogen nitride acquires intensive blue-purple color. Many of the amino acids are sufficiently resistant. Due to this, they can be obtained in solid form.

In liquid ammonia, both ionic and non-polar inorganic and organic compounds are well dissolved.
Sanitary and hygienic characteristics
Ammonia is referred to the fourth maximum allowable maximum-time concentration (MPC) in the air of settlements is 0.2 mg / m 3, average daily - 0.04. In the air of the working area, the ammonia content should not be higher than 20 mg / m³. At such concentrations, the smell of substance is not felt. Fixed with human smell it begins at 37 mg / m³. That is, if the smell of ammonia is felt, this means that the allowable standards of finding a substance in the air are significantly exceeded.
Impact on the human body
What is ammonia from the point of view of the impact on a person? This is toxicant. It is referred to substances capable of reinforcing and neurotropic effect, inhalation poisoning that can lead to edema and affecting the nervous system.
Ammonia couples are annoyingly affect the skin, mucous membranes of the eyes and respiratory organs. The concentration of the substance at which the irritation of the oce is manifested is 280 mg per cubic meter. Meter, eye - 490 mg per cube. meter. Depending on the amount of hydrogen nitride in the air, there may be an arrangement in the throat, difficulty of breathing, cough attacks, eye pain, abundant tearing, chemical burns of cornea, vision loss. When the content of ammonia is 1.5 g per cubic meter. The meter for an hour is developing toxic pulmonary edema. When contacting liquid ammonia and its solutions (in high concentrations), redness is possible, itching, burning, dermatitis. Since the liquefied nitride of the water water supply during evaporation absorbs heat, frostbite is frostbite.
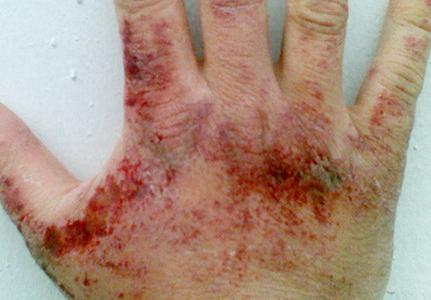
Symptoms of poisoning ammonia
The poisoning of this toxicant can cause a decrease in the auditory threshold, nausea, dizziness, headache, etc. There may be changes in behavior, in particular strong arousal, nonsense. The manifestation of symptoms in some cases is intermittent. They may stop over for a while, and then renew with a new force.
Given all the possible consequences of the impact of ammonia, it is very important to comply with precautions when working with this substance and prevent exceeding its concentration in the air.