What is geology and that she studies
The study of land is engaged in geology and science are interrelated with each other. Geophysics studies mantle, bark, external liquid and inner solid core. As part of the discipline, oceans, surface and underground water are investigated. Also, this science studies the physics of the atmosphere. In particular, aeronomy, climatology, meteorology. What is geology? Within the framework of this discipline, several other studies are carried out. Next, find out what studies geology.
General
General Geology is discipline, within the framework of which the structure and patterns of land development, as well as other planets belonging to the solar system are investigated. In addition, it applies to their natural satellites. General Geology is a complex of sciences. The study is carried out using physical methods.
Main directions
There are three of all three: historical, dynamic and descriptive geology. Each direction is distinguished by its basic principles, as well as research methods. Next, consider them more.
Descriptive direction
It studies the placement and composition of the corresponding bodies. In particular, this refers to their forms, size, relationship and sequence of climbing. In addition, this direction is engaged in a description of rocks and various minerals.
Study of the evolution of processes
This is the dynamic direction. In particular, the processes of the destruction of rocks, their movement by wind, underground or terrestrial waves, glaciers are investigated. Also, this science considers the internal eruptions of volcanoes, earthquakes, and precipitation. 
Chronological order
Speaking that he studies geology, it should be said that research applies not only to phenomena with a place on Earth. One of the directions of the discipline analyzes and describes the chronological order of processes on Earth. These studies are carried out within historical geology. Chronological order is organized in a special table. She is more famous as she, in turn, is divided into four intervals. This was done in accordance with stratigraphic analysis. The first interval covers the following period: the formation of the Earth is the present time. Subsequent scales reflect the last segments of the previous ones. They are noted using stars on an enlarged scale.
Features of absolute and relative age
The study of the geology of the Earth is essential for humanity. Thanks to the research, it became known for example. Geological events are assigned an accurate date relating to a specific time point. In this case, we are talking about absolute age. Events can also be attributed to certain scale intervals. This is a relative age. Speaking about what geology is, it should be said that, first of all, this is a whole complex of scientific research. Within the framework of the discipline, various ways of determining periods to which concrete events are attached to.
Radioisotope dating method
It was opened at the beginning of the 20th century. This method provides an opportunity to determine absolute age. Before his discovery, geologists were very limited. In particular, only relative dating methods were used to determine the age of relevant events. Such a system is able to establish only the sequential order of the latest changes, and not the date of their commission. However, this method still remains very effective. This applies to the case when materials devoid of radioactive isotopes are available. 
Comprehensive research
Comparison of a certain stratigraphic unit on the other occurs at the expense of the formation. They consist of sedimentary and rocks, fossils and surface deposits. In most cases, the relative age is determined using the paleontological method. At the same time, the absolute is basically based on the chemical and physical properties of rocks. As a rule, this age is determined by radioisotope dating. This refers to the accumulation of decay products of the corresponding elements, which are part of the material. Based on the data obtained, an exemplary date of each event is set. They are placed at certain points of the general geological scale. To build an accurate sequence, this factor is very important.
Main sections
Briefly answer the question of what geology is quite difficult. It should be noted here that science includes not only the above directions, but also various groups of disciplines. At the same time, geology is continuing today: new branches of the scientific system appear. The previously emerging new disciplines are associated with all three directions of science. Thus, there are no accurate boundaries between them. What studies geology is in one degree or another is investigated by other sciences. As a result, the system is contacted with other areas of knowledge. There is a classification of the following groups of sciences:
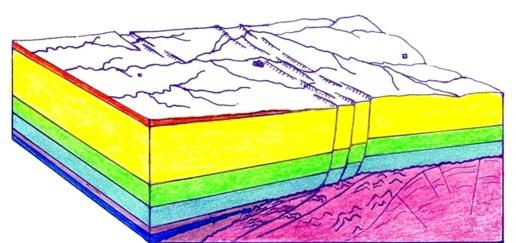
Mineralogy
What does geology studies within this section? Studies relate to minerals, their genesis, as well as classification. Lithology is engaged in the study of rocks that were formed in the processes associated with the hydrosphere, the biosphere and the atmosphere of the Earth. It is worth noting that they are still inaccurately called sediment. Geocryology is engaged in the study of a number of characteristic features and properties that are acquired by multi-metered rock rocks. Crystallography was originally one of the directions of mineralogy. Currently, it can be directly attributed to physical discipline.
Petrography
This section of geology is studied by metamorphic and magmatic rocks mainly from the descriptive side. In this case, we are talking about their genesis, composition, textural features and classifications.
The earliest section of geotectonics
There is a direction that is engaged in the study of the impairment of the earth's crust and the forms of the concerned bodies. His name is structural geology. It must be said that as the science of geotectonic appeared at the beginning of the XIX century. Structural geology investigated medium and small-scale tectonic dislocations. Size - dozens of hundreds of kilometers. This science was finally formed only by the end of the century. Thus, there was a transition to the allocation of tectonic units of a global and continental scale. In the future, the teaching gradually turned into geotectonic.
Tectonics
This section of geology studies the movement of the earth's crust. It also includes the following directions:
- Experimental tectonics.
- Strong.
- Geotectonics.
Narrow sections
- Volcanology. Pretty narrow geology section. He is engaged in the study of volcanism.
- Seismology. This section of geology is engaged in the study of geological processes that arise during earthquakes. This also includes seismic conjunction.
- Geocryology. This section of geology is concentrated on the study of multi-nesting rocks.
- Petrology. This section of geology is studying genesis, as well as the conditions for the origin of metamorphic and magmatic rocks.

Sequence processes
All that geology is studying, contributes to a better understanding of those or other processes on Earth. For example, the chronology of events is the most important subject. After all, each geological science is historical in one degree or another. They consider existing formations from this point of view. First of all, these sciences find out the sequence of formation of modern structures.
Classification of periods
All the history of the Earth is divided into the two largest stages called by the Eon. The classification occurs in accordance with the advent of organisms with solid parts, which leave traces in sedimentary rocks. According to Paleontology, they allow to determine the relative geological age.
Research objects
Puerozoa began with the advent of fossils on the planet. Thus, an open life has developed. This period was preceded by Damkiberia and Cryptose. At that time there was a hidden life. Geology of Precambrian is considered a special discipline. The fact is that it studies specific, mostly repeatedly and highly metamorphous complexes. In addition, it is characterized by special research methods. Paleontology is concentrated on the study of ancient forms of life. It conducts a description of the fossil residues and traces of the life of organisms. Stratigraphy determines the relative geological age of sedimentary rocks and the dismemberment of their thickness. It also is engaged in the correlation of various formations. Paleontological definitions are a data source for stratigraphy.
What is applied geology
Some directions of science in one way or another interact with others. However, there are disciplines that are on the border with other branches. For example, the geology of minerals. This discipline is engaged in the methods of searching and intelligence breeds. It is divided into the following types: geology geology, gas, oil. There is also a metal. Hydrogeology is concentrated on the study of groundwater. Disciplines are quite a lot. All of them are practical. For example, what is a section involved in the study of the interaction of structures and the environment. The geology of soils closely comes closely, since it depends on the soil composition, for example, the choice of material for the construction of buildings. 
Other subtypes
- Geochemistry. This section of geology is concentrated on the study of the physical properties of the Earth. This includes a complex of exploration methods, among them the electrical exploration of various modifications, magneto, seismic and gravity.
- Geobarothermometry. This science is engaged in the study of the complex for determining the temperature and pressure of rock formation and minerals.
- Microstructural geology. This section is engaged in studying the deformation of rocks on the micro level. Measures the scale of aggregates and grains of minerals.
- Geodynamics. This science is concentrated on the study of processes in the planetary scale, which occur as a result of the evolution of the planet. The connection of the mechanisms in the earth's crust, mantle and core is studied.
- Geochronology. This section is engaged in determining the age of minerals and breeds.
- Lithology. It is also called petrography sedimentary rocks. It is engaged in the study of the relevant materials.
- History of geology. This section is focused on the combination of information received and ore.
- Agrogeology. This section is responsible for finding, extraction and use of agricultural purposes. In addition, it studies the mineralogical composition of soils.
The following geological sections are focused on studying the solar system:
- Cosmology
- Planetology.
- Space geology.
- Cosmochemistry.
Mountain geology
It is differentiated by type of mineral raw materials. There is a division on the geology of non-metallic and ore useful breeds. This section is studying the pattern of placement of relevant deposits. Also establish their connection with the following processes: metamorphism, magmatism, tectonics, sedimentation. Thus, an independent branch of knowledge appeared, which is called metal-generation. The geology of non-metallic minerals is also divided into science on combustible substances and caustobiolites. This includes shale, coal, gas, oil. Geology of non-combustible breeds includes building materials, salts and much more. Also in this section included hydrogeology. It is devoted to underground waters.
Economic Direction
It is a rather specific discipline. She appeared at the junction of the economy and geology of minerals. This discipline is concentrated on the value estimates of the sections of the subsoil and deposits. The term "mineral resources", given this, you can rather attribute to the economic sphere than to the geological one. 
Features of intelligence
The geology of the field is an extensive scientific complex, within the framework of which measures are being carried out to determine the industrial importance of the areas of rocks that have received a positive assessment on the results of search and evaluation actions. During exploration, the installation of geological and industrial parameters. They, in turn, are necessary for the appropriate assessment of the plots. It also refers to the processing of recoverable minerals, ensuring operational measures, designing the construction of mining enterprises. Thus, the morphology of bodies of the corresponding materials is determined. This is very important to select a system for subsequent processing of minerals. The installation of the contours of their bodies occurs. At the same time, geological boundaries are taken into account. In particular, this refers to the surface of the faults and contacts of lithologically different rocks. It also takes accounting the nature of the distribution of minerals, the presence of harmful impurities, the content of passing and main components.
Top horizons of the crust
Engineering geology is engaged in studying. The information that is obtained during the study of soils provide the ability to determine the suitability of the relevant materials for the construction of specific objects. The upper horizons of the earth's crust are often referred to as a geological environment. The subject to study this section is information about its regional features, dynamics and morphology. Interaction with engineering structures is studied. The latter are often referred to as elements of the technosphere. This takes into account the planned, current or implemented human economic activity. Engineering and geological assessment of the territory involves the allocation of a special element, which is characterized by homogeneous properties.
Several basic principles
The above information makes it possible to clearly understand what geology is. At the same time it must be said that science is considered historical. It has many important tasks. First of all, it concerns the determination of the sequence of geological events. For the qualitative implementation of these tasks, a number of intuitively regular and simple signs relating to the temporary ratio of rocks have long been developed. The intrusive relationships are the contacts of the respective rocks and their thickness. All conclusions are made based on the found signs. Relative age allows you to determine the sequential relationships. For example, if it breaks rocks, it allows us to conclude that the result was formed later. The principle of ensuring continuity lies in the fact that the building material from which layers are formed can be stretched over the surface of the planet if it does not limit some other mass.
Historical information
The first observations are accepted to relate to dynamic geology. In this case, it is meant in mind the information about the movement of coastlines, the erosion of the mountains, the eruption of volcanoes and earthquakes. Attempts to classify geological bodies and describe Minerals were Avicenna and Al-Burini. Currently, some scientists suggest that modern geology originated in the medieval Islamic world. Dzhirolamo Fracastoro and Leonardo da Vinci were engaged in similar studies in the revival era. They were the first to put forward the assumption that fossil shells are remnants of extinct organisms. They also believed that the history of the land itself is much longer than the biblical ideas about it. At the end of the XVII century, a general theory of the planet emerged, which began to be called diluvianism. Scientists of that time believed that fossils and sedimentary rocks themselves were formed due to the worldwide flood.
Mineral needs have already increased very quickly towards the end of the 18th century. Thus, the subsoil began to be studied. Mainly accumulated actual materials, descriptions of properties and features of rocks, as well as studies of the conditions for their occurrence. In addition, observation techniques were developed. Virtually the entire XIX century Geology has fully engaged in the exact age of land. The estimated estimates varied quite highly: from one hundred thousand years to billions. However, the age of the planet was originally defined at the beginning of the 20th century. In many ways, radiometric dating contributed. The resulting estimate is about 2 billion years. Currently, the true age of the Earth is set. It is approximately 4.5 billion years.