Recultivation of the Earth - Definition, Essence and Features. Reclamation of agricultural land
Certain types of industrial, mining and construction activities may cause serious damage to the soil. The violation of environmental and agrotechnical properties does not allow the use of land in agricultural purposes. In particular, such consequences can be given the gasket of communication systems, the construction of linear facilities, the development of careers for mining, etc. Reassemble the situation can only recult the agricultural land, which is a set of recovery events.
What is Recultivation?
As a rule, reclamation involves restoring the initial properties and characteristics of the soil layer for its subsequent use in agricultural needs. However, such events can also be applied for other purposes. For example, to restore the recreational and forestry parameters of the processed area. In other words, land reclamation is a combination of activities aimed at ensuring the necessary environmental and agrotechnical properties of the soil.
In this case, this process does not mean that the cover should be recovered to increase lost fertility. For example, forest reserves are made in working with forestry lands at the expense of new plantations. But mainly reclamation is subject to agricultural land. True, in this area there are different directions. For example, the recultivation of the Earth may also provide for the organization of perennial pastures, and the creation of areas for future passengers, as well as the preparation of soil for gardens and hayneokos.
What land is subject to reclamation?

The most common category of exposed areas belongs to the lands on which pipelines were laying, and construction work was performed. From the point of view of the difficulty of recovery, it is worth noting the squares that were used as polygons for the disposal and storage of hazardous waste. In such cases, a special recultivation of contaminated land is carried out, the timing of which may be calculated for years - depending on the nature of the waste and the severity of their environmental impact. The development of deposits in a complex with exploration and exploration activities has a negative impact on the soil layer. One way or another, for each case a special reclamation project is being developed.
What is taken into account in the Recultivation Project?
First of all, experts take into account primary data on natural location conditions. Climatic, vegetative and hydrological factors are taken into account. Next, the actual state of land at the time of recultivation is analyzed. At this stage, the area, ingrowth intensity, the form of the relief, the nature of the use of land, the degree of pollution, as well as the condition of the soil cover is determined. In addition to these data, the land reclamation project also contains information on the chemical and particle size composition of the soil, its agricultural and agrochemical parameters. Estimated in the documentation and the possible deadlines for the operation of the Earth after reclamation. At the same time, the risk of re-violation of the optimal state of soil cover is taken into account.

Technical recultivation of land
At this stage, layouts, create slopes, as well as removal and updating the soil layer. Depending on the project requirements, hydrotechnical and landoral devices can be organized. In general, this is the main part of events aimed at the preparation of the Earth to further target use. Work is carried out in several directions, among which heat engineering, hydraulic and chemical operations. Heat engineering land reclamation is soil heating due to mulching, which is covered with a fertile layer. The use of hydraulic technologies aims to get rid of the area from excess moisture, as well as a change in the frequency of flooding of lands. Chemicals allow you to restore the initial properties and characteristics of the soil due to the introduction of such components, like lime, clay, gypsum, sorbents, etc.
Biological land reclamation

At the stage of performing biological reclamation, agrotechnical and phytomeliorative procedures are involved, which should improve biochemical, agrochemical, agrophysical and other characteristics of the Earth. Unlike technical measures, in this case it is supposed to work with the most severe violations. In particular, the recultivation of the land of this kind helps to resume the territories that were damaged under the influence of dangerous industrial waste. We can talk about the complete destruction of natural natural components of flora and fauna. Modern means of biological recovery show the efficiency of recultivation, but in time and financial costs they can also significantly exceed the traditional technical means of soil updates.
The result of the recultivation
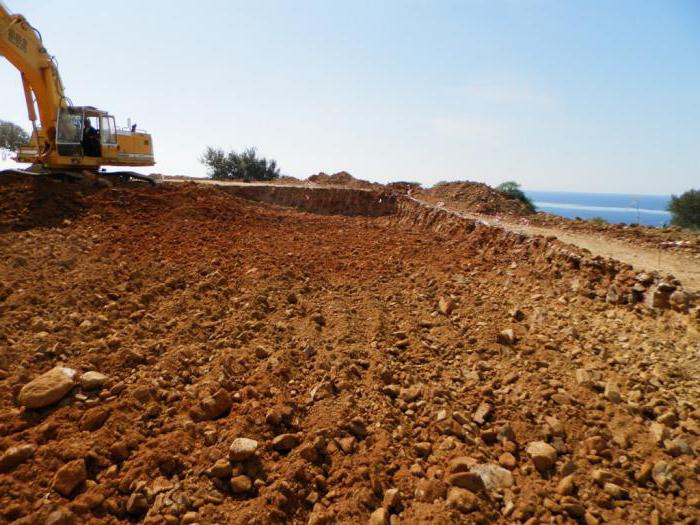

The quality of the recultivation can be judged by several parameters. First of all, it is the absence of unnecessary objects, among which can be fragments of rocks, construction trash and manufacturing structures. Also, the site should have a solid structure of the landscape without the presence of obvious duties, pita, drainage channels, shaft failures and embankments. In addition, the land reclamation must necessarily contribute to the full or partial renewal of the soil formation process. Modern technologies make it possible to significantly increase the ability of the soil to self-cleaning. Against the background of such processes, the biological state of lands occurs.
Conclusion

Even if you do not take into account the feasibility of using land in agricultural needs, the restoration of fertility ability has a beneficial effect on the natural components associated with the territory. For this reason, the recultivation should be carried out in obligatory, regardless of its further use. Of course, if the stakeholder has a plan for specific operation of the territory, then the project of reclamation should initially correct under the objective objectives. In such cases, recovery measures not only help eliminate the consequences of harmful effects on the soil, but also, if possible, enrich it with the necessary components, meaningful from the point of view of future use.