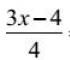Pyramid. Formulas and properties of the pyramid
apothem apothem
(from the Greek apotíthēmi - I postpone), 1) a segment (as well as its length) of a perpendicular a, dropped from the center of a regular polygon to any of its sides. 2) In the correct pyramid, the apothem is the height a side edge.
APOTHEMAPOPHEMA (Greek apothema - something postponed),
1) a segment (as well as its length) of the perpendicular a, dropped from the center of a regular polygon to any of its sides.
2) In a regular pyramid, apothem is the height of the side face.
encyclopedic Dictionary. 2009 .
Synonyms:See what "apothem" is in other dictionaries:
See APOTEM. Dictionary of foreign words included in the Russian language. Chudinov A.N., 1910. APOTHEMA, see APOTHEMA. Dictionary of foreign words included in the Russian language. Pavlenkov F., 1907 ... Dictionary of foreign words of the Russian language
- (from Greek apotithemi I postpone) ..1) a segment (as well as its length) of the perpendicular a, lowered from the center of a regular polygon to any of its sides2)] In a regular pyramid, apothem is the height of the side face ... Big Encyclopedic Dictionary
Exist., number of synonyms: 3 apotema (2) length (10) perpendicular (4) Dictionary ... Synonym dictionary
APOTHEM- (1) the length of the perpendicular dropped from the center of a circle circumscribed around a regular polygon to any of its sides; (2) the height of the side face of a regular pyramid; (3) the height of the trapezoid, which is the side face of a regular truncated ... ... Great Polytechnic Encyclopedia
- (from the Greek apotithçmi I put aside) 1) the length of the perpendicular dropped from the center of a regular polygon to any of its sides (Fig. 1); 2) in a regular pyramid A. the height a of its lateral face (Fig. 2). Rice. 1 to… … Great Soviet Encyclopedia
- (from the Greek apotfthemi I postpone) 1) a segment (as well as its length) of the perpendicular a, lowered from the center of a regular polygon to any of its sides. 2) In a regular pyramid A., the height a of the side face (see figure). To Art. Apothem... Big encyclopedic polytechnic dictionary
The length of a perpendicular dropped from the center of a regular polygon to one of its sides; the apothem is equal to the radius of the circle inscribed in the given polygon. A. was also called the inclined side of the cone ... Encyclopedic Dictionary F.A. Brockhaus and I.A. Efron
- (from the Greek apotithemi I postpone), 1) a segment (as well as its length) of the perpendicular a, lowered from the center of a regular polygon to any of its sides. 2) In a regular pyramid A. the height a of the side face ... Natural science. encyclopedic Dictionary
Apothem, apothem, apothem, apothem, apothem, apothem, apothem, apothem, apothem, apothem, apothem, apothem, apothem (
- apothem- the height of the side face of a regular pyramid, which is drawn from its top (in addition, the apothem is the length of the perpendicular, which is lowered from the middle of a regular polygon to 1 of its sides);
- side faces (ASB, BSC, CSD, DSA) - triangles that converge at the top;
- side ribs ( AS , BS , CS , D.S. ) - common sides of the side faces;
- top of the pyramid (v. S) - a point that connects the side edges and which does not lie in the plane of the base;
- height ( SO ) - a segment of the perpendicular, which is drawn through the top of the pyramid to the plane of its base (the ends of such a segment will be the top of the pyramid and the base of the perpendicular);
- diagonal section of a pyramid- section of the pyramid, which passes through the top and the diagonal of the base;
- base (ABCD) is a polygon to which the top of the pyramid does not belong.
pyramid properties.
1. When all side edges are the same size, then:
- near the base of the pyramid it is easy to describe a circle, while the top of the pyramid will be projected into the center of this circle;
- side ribs form equal angles with the base plane;
- in addition, the converse is also true, i.e. when the side edges form equal angles with the base plane, or when a circle can be described near the base of the pyramid and the top of the pyramid will be projected into the center of this circle, then all the side edges of the pyramid have the same size.
2. When the side faces have an angle of inclination to the plane of the base of the same value, then:
- near the base of the pyramid, it is easy to describe a circle, while the top of the pyramid will be projected into the center of this circle;
- the heights of the side faces are of equal length;
- the area of the side surface is ½ the product of the perimeter of the base and the height of the side face.
3. A sphere can be described near the pyramid if the base of the pyramid is a polygon around which a circle can be described (a necessary and sufficient condition). The center of the sphere will be the point of intersection of the planes that pass through the midpoints of the edges of the pyramid perpendicular to them. From this theorem we conclude that a sphere can be described both around any triangular and around any regular pyramid.
4. A sphere can be inscribed in a pyramid if the bisector planes of the internal dihedral angles of the pyramid intersect at the 1st point (a necessary and sufficient condition). This point will become the center of the sphere.
The simplest pyramid.
According to the number of corners of the base of the pyramid, they are divided into triangular, quadrangular, and so on.
The pyramid will triangular, quadrangular, and so on, when the base of the pyramid is a triangle, a quadrilateral, and so on. A triangular pyramid is a tetrahedron - a tetrahedron. Quadrangular - pentahedron and so on.
To successfully solve problems in geometry, it is necessary to clearly understand the terms that this science uses. For example, these are "straight line", "plane", "polyhedron", "pyramid" and many others. In this article, we will answer the question, what is an apothem.
Double use of the term "apothem"
In geometry, the meaning of the word "apothem" or "apoteme", as it is also called, depends on what object it is applied to. There are two fundamentally different classes of figures in which it is one of their characteristics.
First of all, these are flat polygons. What is the apothem for a polygon? This is the height drawn from the geometric center of the figure to any of its sides.
To make it clearer what is at stake, consider a specific example. Let's assume that there is a regular hexagon shown in the figure below.
The symbol l denotes the length of its side, the letter a denotes the apothem. For the marked triangle, it is not only the height, but also the bisector and the median. It is easy to show that in terms of the side l it can be calculated as follows:
Similarly, the apothem is defined for any n-gon.
The second is the pyramids. What is an apothem for such a figure? This issue requires more detailed consideration.
On this topic: How to make your eyelashes long and thick in just one month?
Pyramids and their apothem
First, let's define a pyramid in terms of geometry. This figure is a three-dimensional body formed by one n-gon (base) and n triangles (sides). The latter are connected at one point, which is called the top. The distance from it to the base is the height of the figure. If it falls on the geometric center of the n-gon, then the pyramid is called straight. If, in addition, the n-gon has equal angles and sides, then the figure is called regular. Below is an example of a pyramid.

What is an apothem for such a figure? This is the perpendicular that connects the sides of the n-gon to the top of the figure. Obviously, it represents the height of the triangle, which is the side of the pyramid.
The apothem is convenient to use when solving geometric problems with regular pyramids. The fact is that for them all the side faces are equal to each other isosceles triangles. The last fact means that all n apothems are equal, so for a regular pyramid we can talk about a single such straight line.
Apothem of a quadrangular pyramid correct
Perhaps the most obvious example of this figure will be the famous first wonder of the world - the pyramid of Cheops. She is in Egypt.

For any such figure with a regular n-gonal base, formulas can be given that allow one to determine its apothem in terms of the length a of the side of the polygon, in terms of the side edge b and the height h. Here we write the corresponding formulas for a straight pyramid with a square base. The apothem h b for it will be equal to:
On this topic: Flag of Bashkiria - description, symbolism and history
h b \u003d √ (b 2 - a 2 / 4);
h b \u003d √ (h 2 + a 2 / 4)
The first of these expressions is valid for any regular pyramid, the second - only for a quadrangular one.
Let us show how these formulas can be used to solve the problem.
geometric problem
Let a straight pyramid with a square base be given. It is necessary to calculate its base area. The apothem of the pyramid is 16 cm, and its height is 2 times the side of the base.
Every student knows: to find the area of the square, which is the base of the pyramid under consideration, you should know its side a. To find it, we use the following formula for the apothem:
h b \u003d √ (h 2 + a 2 / 4)
The meaning of the apothem is known from the condition of the problem. Since the height h is twice the length of the side a, this expression can be converted as follows:
h b = √((2*a) 2 + a 2 /4) = a/2*√17 =>
a = 2*h b /√17
The area of a square is equal to the product of its sides. Substituting the resulting expression for a, we have:
S \u003d a 2 \u003d 4/17 * h b 2
It remains to substitute the value of the apothem from the condition of the problem into the formula and write down the answer: S ≈ 60.2 cm 2.
Read also:
Note. This is part of the lesson with problems in geometry (section solid geometry, problems about the pyramid). If you need to solve a problem in geometry, which is not here - write about it in the forum. In tasks, instead of the "square root" symbol, the sqrt () function is used, in which sqrt is the square root symbol, and the radical expression is indicated in brackets.For simple radical expressions, the sign "√" can be used.Theoretical materials and formulas, see the chapter " Correct pyramid ".
A task
The apothem of a regular triangular pyramid is 4 cm, and the dihedral angle at the base is 60 degrees. Find the volume of the pyramid.Solution.
Since the pyramid is correct, consider the following:
- The height of the pyramid is projected onto the center of the base
- The center of the base of a regular pyramid according to the condition of the problem is an equilateral triangle
- The center of an equilateral triangle is both the center of the inscribed circle and the circumscribed circle.
- The height of the pyramid forms a right angle with the plane of the base
V = 1/3 Sh
Since the apothem of a regular pyramid forms a right triangle together with the height of the pyramid, we use the sine theorem to find the height. In addition, let's take into account:
- The first leg of the considered right-angled triangle is the height, the second leg is the radius of the inscribed circle (in a regular triangle, the center is both the center of the inscribed and circumscribed circles), the hypotenuse is the apothem of the pyramid
- The third angle of a right triangle is 30 degrees (the sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 degrees, the angle of 60 degrees is given by the condition, the second angle is a right angle according to the properties of the pyramid, the third is 180-90-60 = 30)
- sine 30 degrees equals 1/2
- the sine of 60 degrees is equal to the square root of three
- the sine of 90 degrees is 1
4 / sin(90) = h / sin(60) = r / sin(30)
4 = h / (√3 / 2) = 2r
where
r=2
h = 2√3
At the base of the pyramid lies a regular triangle, the area of \u200b\u200bwhich can be found by the formula:
S of an equilateral triangle = 3√3 r 2 .
S = 3√3 2 2 .
S = 12√3.
Now find the volume of the pyramid:
V = 1/3 Sh
V = 1/3 * 12√3 * 2√3
V \u003d 24 cm 3.
Answer: 24 cm3.
A task
The height and side of the base of a regular quadrangular pyramid are 24 and 14, respectively. Find the apothem of the pyramid.Solution .
Since the pyramid is regular, then at its base lies a regular quadrilateral - a square. In addition, the height of the pyramid is projected into the center of the square. Thus, the leg of a right triangle, which is formed by the apothem of the pyramid, the height and the segment connecting them is equal to half the length of the base of a regular quadrangular pyramid.
From where, according to the Pythagorean theorem, the length of the apothem will be found from the equation:
72 + 242 = x2
x2 = 625
x=25
Answer: 25 cm