Watch what is "skin" in other dictionaries:
Leather I.
Leather (Cutis)
The skin is involved in the processes of immunity. There is a non-specific, independent infections or vaccinations, which is impact on the exposure to UV radiation, and a specific, developing when penetrating in K. agents, to which it is especially sensitive, for example, the pathogen of Siberian ulcers. The skin has low electrical conductivity, and its electrical resistant, especially the horn layer, is great. Electrology resistance decreases on wet areas K., especially with an increased sweating, as well as in individuals with the predominance of the tone of the parasympathetic nervous system. The electrical resistance depends on the physical properties of K., the functional state of the sebaceous and sweat glands, blood vessels K., nervous and endocrine systems. Through the skin (excluding K. Head) per day allocates 7-9 g.carbon dioxide and absorbs with t ° 30 ° 3-4 g.oxygen, which is about 2% of the total gas exchange in the body. The skin is enhanced by increasing the ambient temperature, during physical work, an increase in barometric pressure, with digestion, acute inflammatory processes in the skin, and others. Skin breathing is closely related to redox processes, sweat glands rich in blood vessels and nerve fibers. The absorption function is complex and not sufficiently studied. Through K. water and dissolved salts in mammals, it practically does not occur due to the presence of brilliant and horn layers impregnated with lipids performing. The fat-soluble substances are absorbed directly through the epidermis, and water-soluble - through, hair follicles and the withdrawal ducts of sweat glands during the braking of sweating. Gaseous (for example, carbon dioxide) and some substances dissolving and soluble in them (chloroform, ether, etc.) are easily absorbed. Most toxic gases, in addition to the skin-disruptive type of iprite, lisitis, through K. does not penetrate. Morphine, monoethyl ether ethylene glycol, dimethyl sulfoxide and other substances, in minor quantities are easily absorbed. The excretory function K. is carried out by sweather and silent glands. The number of substances allocated through K. depends on the floor, age, topographic features of the skin (see sweat glands ,
Sebaceous glands) .
In case of insufficiency of the kidney or liver function through K. such substances that are usually derived with urine (, bile pigments, etc.), increases. It occurs synchronously at different parts of K. under the control of the Ts.N.S. The PAT includes organic substances (0.6%), chloride (0.5%), urea impurities, choline, volatile fatty acids. On average per day highlighted from 700 to 1300 mlsweat. Pot depends on the ambient temperature, the state of K., the intensity of the main exchange, etc. The sweating increases with increasing ambient temperature, air dryness, hyperemia to.; During sleep or anesthesia, it decreases sharply and even stops. The sebaceous glands consists of 2/3 of the water, and 1/3 of the encodes of casein, cholesterol and some salts. Free fat and unlimited acids, the products of the exchange of sex hormones and others are highlighted, the maximum sebaceous glands from the period of puberty and up to 20-25 years. The skin plays the role of a filter that prevents excessive water to the surface. Pigment-forming function K. is to develop melanin. This melanocytes produced, which contain specific cytoplasmic organelles - melanosomes, on the protein matrix of which melanin is synthesized from tyrosine under the action of tyrosinase. It is postponed in the form of a melanoprotein complex. Melanogenesis is regulated by a melanocystimulating pituitary hormone. Skin is due to the main deposition of melanin. However, K. person contains other pigments - melanoid, oxymemoglobin and restored. The impaired pigment formation leads to hyperpigmentation (for example, with Addison disease) or depigmentation (et al.). Among the nerve fibers innervating blood vessels K., isolated adrenergic and cholinergic. The blood vessels are constantly regulating neurohumoral factors. , norepinephlation and rear lobe of the pituitary gland cause narrowing of vessels, a, acetylcholine, and androgens expand them. Normally, most of the blood vessels K. is in a semi-crushed state, the rate of blood flow in capillaries is insignificant; It changes greatly depending on local and general reasons. Extended blood vessels of dermis can accommodate up to 1 l.blood (depositing the role of the skin); Their rapid expansion can lead to a significant circulatory impairment. In the thermoregulation of the body, K. plays a very important role. The production of thermal energy in the body due to thermoregulation is supported at a certain level. Despite the fluctuations in the ambient temperature (see thermoregulation) .
80% occurs through K. by radiating, heat-level and due to the evaporation of sweat. Fat lubricant surface K. and poor thermal conductivity of subcutaneous fiber prevent both over-in flow of heat or cold from outside and excessive heat loss. Heat regulation is a complex reflex act, in which brain is involved (thermoregulation centers) and sympathetic; It also affects vascular and respiratory centers, sweating, adrenal glands, pituitary glands, thyroid and sex glands. Temperature K. Depends on the time of day, meals, the intensity of the flow and salo waste, muscle work and the age of a person. During the day, a person stands out about 2,600 calories of heat, children are somewhat more. The temperature K. in its different sections is not the same (from 31.1 to 36.2 °), the highest temperature in the skin folds - up to 37 ° normal. The skin plays a big role in metabolic processes. In addition to the gas exchange carried out under the skin breathing, in K. there is an intermediate carbohydrate, protein, fatty, salt and vitamin. According to the intensity of water, mineral and carbonate exchange K. slightly inferior to the liver and muscles. K. Faster and easier than other organs, accumulates and gives a large amount of water. Through K. Water stands out twice as much as through the lungs. The processes of metabolism and acid-alkaline equilibrium depends on many factors, including from human nutrition (for example, in the abuse of sour food in K. Sodium content decreases). K., especially subcutaneous fiber, is a powerful depot of nutrient materials, which are spent by the body during the starvation. The skin is a huge receptor field by which the body's connection with the environment is carried out. It participates in various reflex reactions - to cold, high temperature, etc., as well as in plantar, sawmother and other reflexes. Exteroceptors K. perceive various external irritations, which in the form of a nervous impulse are transmitted to the Ts.S. There are various types of skin sensitivity. Holy occurs when exposed to mechanical, thermal stimuli and electric current, temperature - cold and thermal stimuli. Tactile sensitivity (see Touch) is most pronounced on the pads of the fingers, in K. external genital organs, in the area of \u200b\u200bthe nipples, where there is the largest number of highly differentiated nerve endings. Its option, obviously, is the wicked sensitivity of K., which occurs when tapping to hair and depending on irritation of a complex basket of nervous plexus of the hair follicle. The complexity of sensitivity includes a sense of space (localization), stereogeneic, two-dimensional and sense of separateness (discriminatory sensitivity). Different areas K. are not equally perceived by the same thing. Believe that on 1 cM 2.skin is 100-200 pain points, 12-15 cold, 1-2 thermal and about 25 pressure points. Most skin receptors are polyvalent in their function. Under the influence of various environmental factors, the number of functioning sensitive receptors may vary, develops, especially to tactile and temperature irritation. To painful irritation is the weakest. Unconditional and conditional skin plays an important role in the vital activity of the body. Newborn has congenital unconditional skin reflexes - sucking and grasping. Skin-skin reflexes are distinguished (irritation and response occurs on K.), muscular-hair, vascular unconditional - reflex dermographism ,
Vasodent reactions in response to intradermal administration of adrenaline, histamine, etc. The skin-muscular belongs to the abdominal, cremaster reflex, plantar. There are also a skin-galvanic reflex, reflex. Pulses coming from skin receptors support normal muscles. Skin-muscular reflexes are of great importance in human labor activities, especially in the automation of movements, the accuracy of which is produced as a result of the differentiation of skin and visual sensations, combined with proprioceptive, coming from muscles and tendons. Pain irritation K. is accompanied by a change in the secretion of pituitary gland, increased altitude of adrenaline, braking the digestion process, changes in brain biotlines. There are also skin and respiratory, skin-vascular and other skin-visceral reflexes. The reflexive, arising not only at the form of blood-sucking insects, but even at one mention of them, conditional reflex (the so-called erythema shame, anger), "goose skin". The same conditioned reflector mechanism underlies hemorrhages, blisters and even bubbles caused by suggestion. The skin revealed structural proteins:, reticulin, and keratin. Focused mainly in the dermis, it is about 70% of deprived water and skin fat (see collagen) .
Reticulin and elastin are contained in K. in significantly smaller quantities, they form the basis of the reticulin and elastic fibers of the dermis, connective tissue shells of the sebaceous and sweat glands, are part of the membrane of hair follicles. Keratin is the basis of the horn layer K. in its cells ends (the process of formation of a horny matter in the epidermis), which begins in basal epidermocytes. The skin also contains spree products of protein:, uric acid, and creatinine, ammonia, etc. in their skin three times more (up to 150 mg.%) than in blood; Especially much accumulates in pathologically changed areas K. with the predominance of decay processes. The process of the rown formation is regulated by genetic mechanisms, as well as endocrine and immune systems. Violations of the energization () are observed in skin tumors, Darya disease, etc. The significant part of the K. cells as other cells of the body (especially their nuclei) make up nucleoproteins and (and RNA). From carbohydrates in K. contain, glycogen and glycosaminglikans. In the depolymerization of glycosaminglikans (for example, with the increase in the activity of hyaluronidase) decreases by the gels formed by them and so Raised K. for microorganisms and various toxic products, in K. is formed and accumulated in fat cells; It plays a big role in the regulation of microcirculatory processes. In the skin and on its surface contains a variety of lipids. Neutral constitute the bulk of subcutaneous fiber. They prevail the highest solid triglyceride - triolein (up to 70%), and therefore human has the lowest melting point (15 °). On the surface of K. Lipids mixed and form. The water content in K. ranges from 62 to 71%. The skin is rich in enzymes, the most important of which are phosphorylase ,. The mineral components of K. accounts for from 0.7 to 1% of its dry weight, and in subcutaneous tissue - about 0.5%. The skin is an important depot of sodium, potassium, calcium and other trace elements. Zinc, arsenic, and some others who are part of enzymes, vitamins or playing the role of activators of biological processes are the most important importance to the normal state. The skin participates in the exchange of substances of the body; It deposits blood, lymph, fabric exchange products, macro and trace elements; Due to the fact that protein is temporarily delayed in K. temporarily delayed, their toxic effect on other organs weakened. K. frees the body from excess water, toxic metabolites, which improves thermoregulation processes, increases barrier, bactericidal and other functions. Separate stages of the chemical conversion of a number of substances involved in metabolic processes occur in other organs and tissues of the body occur in the skin. It forms skin fat and. Violation of protein exchange leads to the development of gout (gout) ,
Amyloidosis ,
Porphyry ,
muzinosis of the skin (deposit in K. Muzin) and other diseases with pronounced changes to K. Violation of lipid metabolism is the cause of lipidosis (lipidosis) .
Changes in carbohydrate exchange, accompanied by accumulation in the blood and K., lead to the necrobiasis of lipoid (necrobiosis lipoid) ,
contribute to the occurrence of furunculez (see the furuncle ,
chronic Piedlemiths and other diseases K. Deviations and activity of enzymes are marked with dermatoses, such as eczema (eczema) ,
Neurodimer ,
Psoriase .
Nervous and hormonal factors affect the exchange of substances in K.. In the occurrence of skin diseases, violations of the biochemical processes on cellular and intracellular levels play a major role. In particular, the important pathogenetic mechanism of psoriasis is the violation of the cell regulatory system of adenyl cyclase - cyclic. The lack of vitamin A plays a certain role in the development of ichthyosis ,
sebori (Seborrhea) ,
DEVERGES OF DISEASES (DEVERGES DIFFERENCE) ,
nail dystrophy (see Nails) et al. Lack of vitamin RR causes the development of Pellagra (Pellagra) with a pronounced skin lesion, and vitamin C -
qingi (qing) .
The pathogenesis of neurodermites is associated with a lack of vitamins of group V. Especially in 6. In the pathogenesis of some skin diseases, impaired water and mineral exchange. Acid-alkaline equilibrium shifts affect bactericidal skin functions, in adult pH of the skin surface 3.8-5.6: in women, this indicator is somewhat higher than that of the Chin's husband. In the armpits, the inhabited femoral folds of the sweat has a weakly alkaline or weakly acidic reaction (pH 6.1-7.2). The pronounced pH shifts in the direction of the alkaline reaction contribute to the occurrence, mycoses (mycoses) .
In addition to common biochemical processes for the body, in K., the transformation inherent only to it: the formation of keratin, melanin, sebum and sweat.
With slowly developing acidosis, intercellular edema () occurs, manifested by multi-chamber bubbles (see rash) .
In disruption of intercellular bonds, single-chamber intapidermal bubbles are formed. Coagulative and conquering cell death (see Necrosis) leads to erosion that is healing without a scar, or ulcer (ulcer) ,
penetrating into the connecting part of K. and heating with the formation of the scar. Often inflammation K. is accompanied by the development of purulent exudate and the formation of Pustul (see rash) .
With productive inflammation, cellular with a dermal papule or tubercock (with specific inflammation) is formed. , resolved without necrosis, ends with scar atrophy, and disintegrating - by the scar. A special group of inflammatory processes make up chronic granulomas. Inflammatory infiltration in the dermis, breaking, determines the emergence of various secondary changes in the epidermis (swelling, atrophy, etc.). The inflammation of the subcutaneous fiber is manifested by edema, the formation of a node or diffuse infiltrate. Inflammation of K. may occur as a result of increased sensitivity to a strictly defined antigen (see Allergy) ,
In other cases, it is not specific and caused by any strong stimulus. CO state is associated with the state of the whole organism. Nephropathy is often accompanied by the so-called skin uremia due to azotemia, oxelemia, urea delay. Foci of chronic infection (in almonds, teeth, etc.) may be the cause of a number of dermatosis. Often the background for the emergence and development of eczema, urticaria (urticaria) ,
Neurodermit, circular hair loss serve neurovegetative disorders. After mental injuries, red flat, psoriasis and other skin responds to violation of the endocrine system. Thus, the disorder of the function of the thyroid gland contributes to the development of the skin of the skin, high sweating, itching, urticaria, eczema, etc.; Violation of the ovarian function - chloazma (see skin dyschromy) ;
The disease of the adrenal glands - girsutism (see virile syndrome) ,
strengthening pigmentation; Pancreatic diseases are accompanied by a stubborn furunculosis, etc. Any adverse effect on K. can have some (for example,), atmospheric factors (long, wind, cold, etc.), mechanical, physical, chemical impact. Constant phenomena in the circulatory system contribute to the emergence of varicose yaseries, etc. A variety of actors acting on K., the complexity of its morphological structure and a wide range of functions performed determine a large number of skin diseases (about 2 thousand different forms), the classification of which is finally not developed (see dermatosis) .
The large group is the defeat of K., associated with hereditary factors (see Generatormatoz) or who are congenital fines of the development of the fetus as a result of adverse effects in the processes of embryogenesis (intrauterine intoxication of infection, circulatory disorders, etc.) K., due to genetic factors, differ in a large variety ; Often they wear a family. Congenital deformities and abnormalities of the development of the body, not related to genetic factors, more rare. Part of the defects of the development of K. are an abortive manifestations of more complex congenital defects: swimming membranes - an abortive form of Syndactilia (see Brush) ,
Hyperitrichosis of the sacrum - the manifestation of hidden, congenital sines and cysts on the neck and face - the result of incomplete infecting of congenital gaps, added breast nipples - incomplete gynecomastia, etc. With other congenital anomalies K. The main violations of the development of the fetus are concentrated in K. So, the congenital absence is known - K., accompanied by the underdevelopment of the appendages of K. and the teeth (congenital ectodermal). Congenital aplasia of the skin (defect of the epidermis and dermis) is characterized by the child at the birth of ulcers to 10 cm In the rare, occipital or rear auricular area of \u200b\u200bthe head. Congenital defect K. is formed by the fetus in the form of a bullous lesion (bubble), by the time the child's birth at the site of the bubble is formed. Gradually, it closes, leaving behind scar atrophy. Congenital Aplasia K. can be combined with the defect of the bones of the skull. With other types of Aplasia K. Plots, devoid of skin, can be located on the body, limbs. They are covered with a thin membrane through which the subjects and tissues are well distinguishable. Such congenital anomalies, as the rubber hyperoelastic K., imperfect desmogenesis, Pahidermia, are associated with changes in the connective tissue. Robbin spots, angioma, lymphangiomas are among the defects of development include diverse clinical forms. The large group consists of disease caused by damage to K. - mechanical (for example, loss, coylase ,
Intertrigo) ,
radiation, incl. ionizing radiation (see dermatitis ,
Photodermatosis) ,
exposure to electric current, high and low temperatures (see burns ,
Frostbite) ,
as well as various chemical and biological factors.
Allergic reactions of the organism, the changes of the nervous and endocrine systems (see toxidermy (see Toxidermia can be lessed by K. inflammatory nature ,
Hives ,
Eczema ,
Neurodermit ,
Scratch and others). The skin is often amazed at diffuse diseases of the connective tissue (diffuse diseases of the connective tissue) ,
Sarcoidosa ,
vasculitis Skin (Skin Vasculitis) ,
Violations of metabolic processes in the body (see Lipidoz ,
Amyloidosis ,
Calcine ,
Xantomatosis, etc.). Pathological processes in K., connected mainly with individual morphological structures of the skin, - see hair ,
Nails ,
Sweet glands ,
Sebaceous glands .
Tumors of leather. According to the histological classification of WHO (1980) among tumors, K. distinguish the skin, benign, predictable (precancerous) skin diseases, tumors with cesspool growth and malignant tumors. By origin, epithelial, pigment and connective tumors of the skin are distinguished. Vices of skin development. These include papillomatous, comedone neust, epidermal cyst, hair cyst, dermoid cyst (see Dermoid) ,
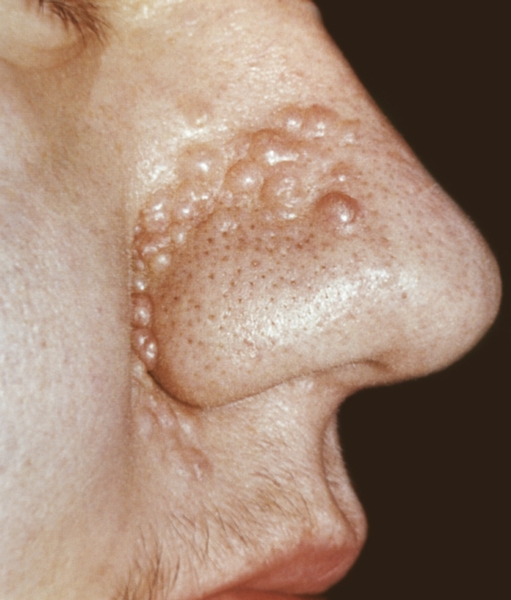
White acne, atheroma, etc. The papillomatous malformation is characterized by the appearance of from the moment of birth or early childhood at any site of K. warts papillomatous expansions (hyperkeratetic neust). The limited shape is isolated as a dense grayish-brown focus and a multiple shape, in which lesion foci may tend to orderly localization (in Zakharin zones - Ging). It is often combined with other damage to the development of the skin (Pigment Nevus, Nevous Song glands). Comedon Neva is localized mainly on the limbs and torso. It is, within which follicular papules are closely grouped. The central part of the papural is permeated with dark gray or black horn masses (after their removal is saved). Seborrheic keratosis, or seborrheic, is more common in elderly people (after 40 years); Localizes in closed areas of the skin, such as a torso ( fig. 3.
). It is characterized by the appearance of sharply hyperpigmented (from brown to black) plaques more often than multiple diameters 0.5-4 cm and more coated with easily removable silent crusts. Benign epithelial tumors can come from sweat glands, hair follicles and sebaceous glands. Benign tumors of sweat glands are papillary, Eccreen trigger, Popples, Eccreen Spiradenoma, etc. Papillary hydradenoma is a single moving tumor of the apocryan gland. It is found mainly in women, localized in K. outer genital organs, as well as in the crotch area. It has a soft consistency and large dimensions (4-6 cm). Growing usually slowly. Eccline trigger is a tumor of the intradermal part of the flow of the Eccreen sweat gland. Localizes mainly on the plantar surface of the stop, on the palms, the inner surface of the fingers of the brushes. It is a single flattened tumor formation in the form of a plaque with a diameter of 10-20 mM. With a smooth or hyperkelotical surface of pink or dark brown. Eccreen cause is painless during palpation; can ulcerate. Poofing siringocystatenoma () - output of sweating gland. It is usually uncomfortable education. It is rare, usually in children and people of youth. It is located more often on the scalp, neck, in inguinal and axillary folds. It has the form of single or multiple tumor-like formations of dense consistency, grayish or grayish yellow with papillomatous sprouts on the surface. Eccreen spiradenoma is a tumor that develops from the glomerular part of the sweat glands. It is rare, more often is observed in young men. Localizes, as a rule, on K. Persons, the front of the body. It is a dark yellow or bluish-red, dense consistency, sometimes painful when palpation. The benign epithelial tumors of the hair follicle include a cylinder, trico epithels, etc. Localizes on the face and scalp (the so-called turban tumor). Represents a large tumor with a smooth surface ( fig. four
), is characterized by progressive growth, a tendency to relapse after surgical excision. Trichoeepitheloma is multiple and solitary. Multiple shape occurs more often in childhood - hereditary. Numerous small nodules are located mainly on the face ( fig. five
), sometimes the scalp, neck, the front surface of the body. A single form arises mainly in adults - actually trico-epitheloma. Localizes on any part of the body, usually on the face. A benign tumor is the true adenoma of the sebaceous glands. It is very rare, mainly in old age. It has the appearance of single, dense, round, sometimes sitting on the leg of nodules or nodes. Fibre may appear on any plot K. distinguish hard and soft fibromus. The solid fibrom has a wide base, a dense consistency, a smooth surface, a color of normal skin or a slurose. This is a limited moving tumor, towering over the surface K. Soft fibroma is multiple and solitary. It is localized mainly on the neck, the front surface of the chest, in the inguinal folds and axillary depressures. It has the form of a bag-shaped hanging tumor of various sizes with a wrinkled surface of a pinkish or brown. Dermatofibrome can be solitary ( fig. 6.
) and multiple. It is usually found in women, on K. Upper and lower extremities. Dense consistency, dark brown, rounded shape is deeply located in K. More often does not protrude above its surface. Sphewing dermatofibrosarcoma is a local invasive tumor. It occurs more often in men in the area of \u200b\u200bthe shoulder belt, on the head. Itself single and multiple. He performs above the surface K., has a smooth bug stem that can ulcerate. The slow and tendency to develop recurrences after excision is characteristic. Hemangioma develops from blood vessels. Highlight capillary ( fig. 7.
), arterial, arteriovenous and cavernous ( fig. eight
) Forms (see Blood vessels ,
tumors). The special form of hemangioma is pyrogen granuloma ( fig. nine
). Arises due to, localized on the face, more often in the field of lips, on the upper limbs. It is a dark red tumor on a leg or wide base with erosive surface. Lymphangioma is a tumor arising from lymphatic vessels. Received often from birth. Localled on any skin area. Combined with hemangioma. Distinguish capillary, cystic and cavernous forms. Against the background of cystic and cavernous lymphangi, parts of papillomatosis and hyperkeratose can develop. Secondary lymphangioma can be a manifestation of lymphostasis, sometimes appears after the suffered infectious disease (for example, faces). Leiomiomioma is a tumor arising from muscles lifting hair. 3 clinical varieties are isolated: multiple leuomioma, solitar leomyoma on genitals and nipples and angioleomy, developing from small blood vessels K. Multiple Leiomioma is characterized by the appearance on the body and limbs of small tumors (3-5 mM. In diameter) rounded shape, with a smooth surface, painful when palpation, having a tendency to group. Solitary Leiomioma is size up to 20 mM. in diameter; Around the lesion is observed Erythema. - solitarian tumor of saturated red color, dense elastic consistency. Localizes often in the field of large joints. Lipoma -
tumor of adipose tissue in the form of single or multiple foci. Localize on any plot K., towering over its surface. It's usually large sizes (up to 10 cm In diameter), test consistency, color of normal skin. The lipoma variant is a symmetric multiple (Derkoma), which is characterized by the appearance mainly on the upper limbs of foci of lesion, painful during palpation. Unionable pigment tumors K. include various forms of pigment nevus and. Pigment units are characterized by the appearance on K. spots or neoplasms consisting of non-non-non-non-cell cells. They arise after birth or in the first years of life; Sometimes appear in youthful and middle age under the influence of sunlight or during pregnancy. Pigment nurses - spots or flat nodules of dark gray, brown or black, elongated either rounded shape, diameter 1 cm and more ( fig. 10
). The surface of the pigment nevus is more often smooth, but sometimes there are papillary warthogs. In some cases, the neust of large sizes occupies a significant part of K. torso, faces, neck or limbs and is a cosmetic defect (giant pigment nevus). On its surface, hair is often growing. Sometimes neust has a blue color - blue neust. It is more common in women on the skin of the face and the forearm. A variety of blue nevus is Mongolian. It arises predominantly among the persons of Asian origin 1-2 days after birth, as a rule, in the lumbar-sacral region. It has a bluish or brownish color, diameter up to 10 cm and more. After 4-5 years, the spot will gradually pale and disappears. Nesus Othus is more often observed in women - representatives of Asian peoples. It happens congenital or appears in the first years of life. It has the type of pigment stain, located on the face along the I and II branches of the trigeminal nerve (, the scoop area, the wings of the nose, as well as the sclera and eyes). Neston Neston (Satton disease) is also isolated - a pigment spot of small sizes with a rim of depigmented leather, localized on a torso or limbs. Blue Necess, Nestus Othe, Pigment Neva with papillary warthasty growths during trauma can be transformed into melanoma. Reasonable skin diseases. These include pigment kronoderm (pigment kservation) ,
Radia skin damage (see Radio Damage) ,
Solar keratosis and others. A number of authors include in this group of also Bowen's disease, Caera's disease and PEDGET disease (during localization outside the nipple and the organ of the breast), which are rare. Solar keratosis occurs as a result of excess insolation. At the same time, on the background of caigious classmia (combination of foci of hyperpigmentation with atrophy areas) multiple foci of hyperkeratose appear in the form of extended or oval plaques up to 0.5-1 cm In the diameter covered with dense gray scales. In the affected areas, the disease of Bowen or flat-stitching cancer can develop. Bowen's disease Most researchers are considered as intapidermal cancer. It is observed predominantly among people of middle and old age, it is often localized by K. Persons, torso. It is usually a single grayish brown plaque is weakly infiltrated, with incorrect, clear boundaries covered with scales or crusts. The focus of the lesion slowly grows along the periphery, its surface is often ulcerated, there are sections of atrophy, which, together with scales and cortical layers, gives the tumor a motley look. Internal organs of the internal organs are often revealed in persons suffering from Bowen's disease. Pedge's disease during localization outside the nipple and breast ranges is characterized by limited foci of maceration and mocking, located mainly in the area of \u200b\u200bthe crotch and navel. Tumors with locastroneal growth. The epithelial tumor with local growth is (basal cell cancer). Develops from the basal layer of epidermis or appendages K. (sebaceous and sweat glands). This is the most common epithelial tumor K. is observed mainly in old age. Characterized by invasive growth; Extremely rarely metastasis. Clinical manifestations are diverse. Select the surface (most favorable form), cystic, ulcerative, scleroderm-like and pigment form of basaloma. Surface basaloma - a limited spot, on the periphery of which there is a roller consisting of individual nodules ("Pearls"). Localizes more often in open areas of body, exposed to insolation, long mechanical irritation. Persons with light skin can arise multiple foci, which merge into large plaques covered with scales ( fig. 12
). Often in the center of the plaques, spontaneous, and in the periphery - the growth of the tumor (self-containing basaloma). In the cystic basalome, the lesion focus is more likely to be solitary, drawnly excreted from the surrounding fabric, bright pink color, test consistency; There are often teleangectas on the surface. Localizes mostly on the skin of the face (around the eyes, nose). Ulceal basaloma ( fig. 13. 14.
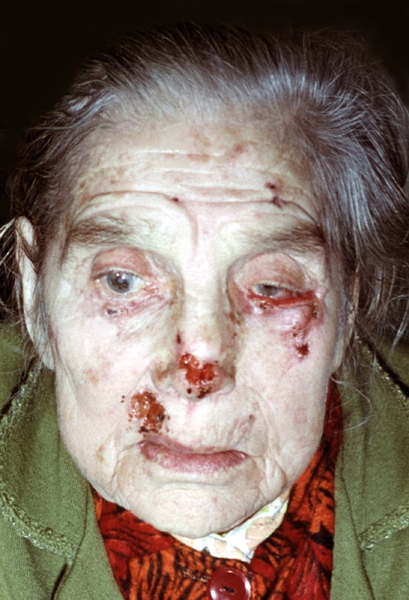
) It may develop from superficial or cystic. It occurs more often on the chin, at the base of the nose or inner corner of the eye. It is manifested by the formation of nodules prone to ulceration. It is characterized by tumor infiltration of the fabrics with the development of defect up to the destruction of bone and cartilage tissue. The most severe forms of ulcerative basalomas are a corrosive ulcer ( fig. fifteen
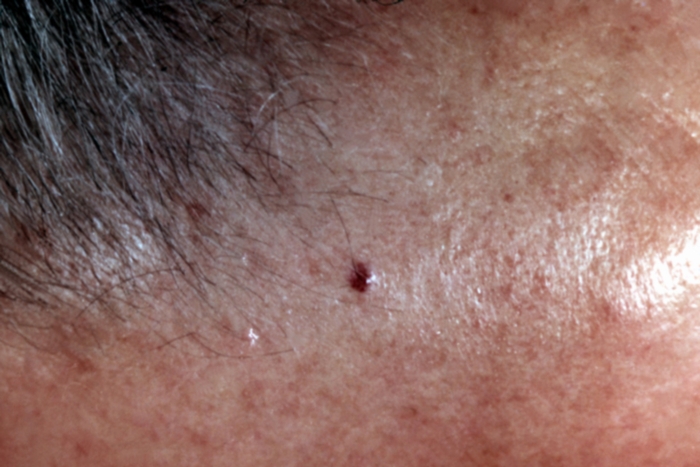
) and ULCUS TEREBRANS (penetrating ulcer). With ULCUS TEREBRANS, the process is distributed over the periphery. In some cases, papillomatous expansions appear on the ulcene surface (the verrucrosite-ulcer basaloma). With a scleroderm-like basalome on the face, the upper part of the body is formed plaques of dense consistency with clear boundaries. They resemble the foci of sclerodermia, at which there is a erythematous whisk along the periphery of the hearth. In contrast to sclerodermia with a scleroderm-like basalome on the periphery of the lesion, the rolic-shaped edge and single nodules are detected - "pearls", Pigment basalome is darker (from yellowish brown or bluish-brown to dark brown or black), which is associated with the presence of melanin in the cytoplasm of tumor cells. Depending on the histological picture, multicenter, solid and adenoid forms of basaloma are distinguished. The natural relationship between the histological picture and the clinical form of basalomas is usually not observed. In cases where histologically detect structures resembling, talk about trichcomed. It is localized on K. LBA, the scalp in the form of a single, less often multiple nodules rounded shapes from 2 to 5 mM. In diameter, dense consistency, dark gray or brownish color. In rare cases, the nodules are larger, they have an uneven surface, sometimes with pronounced telegangectasis. To malignant skin tumors include flat-belling cancer, pigment tumors - pre-dust and melanoma (melanoma) .
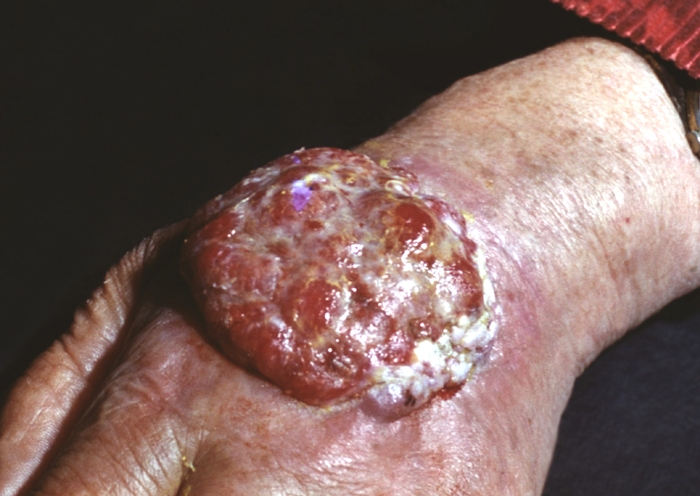
PlateLock Cancer K. is an epithelial malignant tumor. It occurs more often in the places of constant irritation, mechanical, on the background of long-lasting trophic ulcers, fistula, radiation damage to K., and can also develop from foci of lesion characteristic of Bowen's disease, pigment kservois, solar keratosis. The clinical picture distinguishes endophyte (ulcerative) and an exofite (tumor or papillary) form of flat-belling cancer. With ulcerative form, a crater ulcer with a dense bottom and rolling edges is formed. Slowly, but steadily grows, bleeding. In papillary form, single solid nodules are similar to the wart or keratoacant, merge among themselves into large foci of lesions resembling cauliflower ( fig. sixteen
). A flat-belling oroging cancer is characterized by infiltrative growth in the subjectable tissues, gives metastases into lymph nodes and lymphatic vessels, and in the running cases - into blood vessels. The prejudition melanosis dybie is a slowly growing tumor, usually arising after 30 years, more often in women. Localizes, as a rule, in open areas K. has the type of single plaques of large size (40-60 mM. In diameter) with uneven outlines and uneven pigmentation (from light brown to dark brown and black). Trend towards growth, a change in tumor color (darkest), the development of papillomatous growths on the surface or the appearance of atrophy sites indicate its transformation into melanoma. Treatment. Most tumors K. is not accompanied by noticeable subjective sensations. With the appearance of neoplasms, K. The patient should be sent to a consultation to an oncologist or a dermatologist (oncologist), which establishes on the basis of the data of the anamnesis, clinical signs and the results of histological and cytological research and conducts. With benign tumors K. Surgical treatment (tumor removal) are carried out in the case of localization of the tumor in places being injured, as well as at the request of the patient (for example, with a cosmetic defect). Relocular diseases are subject to compulsory treatment. For this purpose, surgical, incl. Electrosurgical, cryodestruction, radiation therapy (radiation therapy) ,
Laser (see Lasers) .
According to the testimony, various cytostatic drugs (5-fluorouracil, fluorofour, recidine, etc.) are also deployed. Prevention It is an early detection of initial signs of the tumor K., carrying out preventive inspections and identification of risk groups (persons suffering from non-healing ulcers, with scarsing skin changes, etc.), in the active treatment of precancerous dermatoses. Excess insolation and contact with oncogenic substances should be avoided. Bibliography: Apatenko A.K. Epithelial tumors and malformations of skin development, M., 1973; Berenbein B.A. Pseudorak skin, M., 1980; Differential skin diseases, ed. B.A. Berenbein and A.A. Studynign, p. 366, M., 1989; Kalantaevskaya K.A. And human skin physiology. Kiev, 1972; Kozhevnikov P.V. General, L., 1970; Guide to the pathologist diagnosis of human tumors, ed. ON THE. Kraevsky and A.V. Smolyannikova, p. 403, m, 1976, bibliogr.; Trapeznikov N.N. and others. Pigment nurses and neutractions of the skin, M., 1976, bibliogr. Fig. 1. Man's finger structure: 1-5 - epidermis (1 - basal layer, 2 - hipped layer, 3 - grain layer, 4 - brilliant layer, 5 - horny layer); 6 - output duct of the sweat gland; 7-8 - Derma (7 - puffing layer, 8 - mesh layer); 9 - terminal sweat gland; 10 - hypoderma. The node in the field of the bottom of the ear shell "\u003e the patient can contribute to the fact that the course of developing defeat K. Weaves or even be suspended. By adopting a number of precautions, you can prevent the distribution of a number of infectious skin diseases before applying to the doctor. In childhood children, there is an exudative-catarrhal, manifested in the hereditary tendency of the child's body to inflammatory processes, allergic reactions. The first signs of such diathesis can be the nature of the dairy stamp, the thrust delicates of the skin, the so-called geographical language. Milk Screw It is manifested in the form of scaly-crusts of yellowish color, rather tightly sitting on the skin of the child's head, especially in the parietal area. In these cases, a nursing mother must be carefully analyzing its diet and exclude products from it with an allergizing effect (see below). On crusts should be applied for several hours. Warm boiled vegetable oil (sunflower, olive, peach), then cautiously combat the scallop softened peels and then wash her head; If necessary, the procedure is repeated. With an overly tight of the child's swaddling, overheating it, not sufficiently thorough skin care (especially in the area of \u200b\u200bthe axillary, inhabitteless femoral, inter-fodded folds), as a result of irritating the effects of skin secretion (salla, sweat), as well as urine, feces, the skin is blushing Maceris - there is a dealer. To prevent the further development of this process, it is necessary to make adjustments to the care system for the child, ensure that it does not overheat, often change the underwear, boil, stroke it. An important role is to carefully observe the toilet of the genital organs and the crotch: after each urination and the act of defecation, it is necessary to wash the skin with a slurozoic solution of potassium mangartage or decoction of chamomile, the bark of oak, a hunter or a series divorced in boiled water to weakly mounted color. Skin folds should be treated with sterile oil (olive, peach, sunflower, chipovnikov, sea buckthorn), fish oil, calcium liniment or children's cream. You can also use the powder from the talc. The affected parts of the body are desirable to leave more often open. Persistently persistent diatles can be a sign of exudative diathesis, and therefore should be revised by a nursing mother (see below). If there are erosions and abrasion in the field of diaper, it is easy to join, a child in this case should be shown a doctor. In the conditions of incorrect care of the child (excessive, insufficient injection of the liquid) in children, weakened, suffering from rickets, fevering, as a result of the imperfection of the thermoregulation system and reinforced sweating often on the skin of the back, the back surface of the neck, buttocks appear small (point) pink nodules and bubbles - prickly heat. In this case, daily hygienic with the addition of chamomile decoction are appropriate. After washing, the skin is carefully blocked by soft carefully swallowed diapers or a towel. The child's skin must be wiped daily with warm alcoholic solution (vodka in half with boiled water). You should also take a rude child, take care of more comfortable clothes, stop excessive wrapping, apply air baths, avoid use during long-term sleep glue or plastic film in the form of linings under sheet, which will help to avoid overheating and sweating. Since children's skin is characterized by tenderness, its slightest injuries and pollution can lead to appearance. gnetic- small red nodules with a purulent head on top or bubbles with yellowish purulent content. When such skin changes appear, it is necessary to refrain from bathing a child, processed if they are single, a solution of a diamond green (green), fuccinic or a gential venture, and rub around them with a warm alcohol solution (vodka in half with boiled water). Very important in this case of a frequent change of linen, which is necessarily boiling and thoroughly stroke. If there are a lot of rashes or they continue to appear, you should contact a dermatologist or pediatrician. Manifestations of allergies on the skin. With a violation of a diet with a nursing mother (use of oranges, chocolate, honey, condensed milk, etc.), with the introduction of feeding or transition to artificial feeding in infants, there may be manifestations of exudative diatela in the form of redness of the skin, bright red small nodules, bubbles, with The autopsy of which are formed by mocking areas of the skin. After a while they are covered with yellowish scales, crust. More specifically, such skin changes occur on the face (especially on the cheeks), buttocks, the back of the brushes, the forearm, stop, legs, hips and are accompanied by itching. These skin changes can go to children's ecase and other difficult to treat allergic skin diseases. Combing the affected skin, the child will be able to make the foci of the defeat of the infection of infection, as a result of which the process will be aggravated by the process. The development of exudative diathesis contributes to the age immaturity of the digestive apparatus, insufficient secretory activity, and sometimes insufficient enzymes, as a result of which a number of food products can cause an allergic reaction in such children's lesion. It should be borne in mind that the leading food allergens for children most often can be cow milk, especially its protein lactoglobulin (boiling milk causes the destruction of a lactoglobulin, and the milk becomes less allergic); Chicken eggs, especially protein (thermal processing reduces their allergic properties, but does not destroy completely); Fish, caviar, crayfish, crabs, shrimps and products of them (Heat treatment does not affect the degree of allergic reaction to these products); grain products (more often wheat, rye,); Fruits and (most often oranges, tangerines, lemons, strawberries, strawberries, tomatoes, carrots); and nuts; Honey, chocolate, coffee, cocoa. The spread of artificial feeding, early introduction of mixtures cooked from cow's milk, often leads to a rapid increase in sensitivity to food allergens. It can be combined with medicinal, household (home, fluff, animal wool), pollen (pollen of herbs, flowering trees). If the child is pronounced to Molok, then you can try to use in its nutrition (kefir, matsoni, bioolk, etc.). Acidophilic products prepared by the fermentation of dairy products are also appropriate, including dry, special acididophilic lactobacteriums with proteolytic (destructive protein) and antibacterial properties. You can enter in earlier dates, fruit, vegetable puree and beef meat, and porridge cooking on fruit and vegetable chambers. Products are more often prepared for a pair to reduce the content of extractive substances. G h potatoes, white cabbage, salad, peeled cucumbers, green onions, puree from green apples, plums, dried fruits, from the berries of rosehip, beef meat, cottage cheese. It is impossible to give such children meat, chicken, fish broths, tomatoes, citrus, cauliflower, green peas, spinach. More older children should be very careful with the introduction of chicken, eggs into the diet. With good tolerance, it is possible to give boiled chicken meat once a week (without leather and chicken broth), chicken egg welded by screwing. Proper nutrition will allow in many cases to prevent the development of chronic allergic diseases. At the same time, in power mode, it is necessary to provide for admission to the body of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, trace elements, vitamins, since this is a condition for the normal functioning of the body and, in particular, its immune system, which plays an important role in the development of allergic reactions. An indispensable components of food are protein products, whose insufficiency in a child can lead to height delay, violation of metabolic processes, adverse changes in the liver function, pancreas, etc.. Very important is the participation of proteins in the formation of protective mechanisms of the body (immunity). And vitamins contribute to the synthesis of hormones, enzymes. At the same time, it is easily absorbed, fats that come in large quantities in the body slow down the synthesis of protective antibodies, increase the tender tende to inflammatory reactions, strengthen sensitization processes. Among products that should be avoided both children and adults when an allergic rash appears on the skin, - eggs, canned food, citrus, mushrooms, smoked and fatty sausages, crabs, strawberries, chocolate and honey. Adults should adhere to a predominantly milky-vegetable diet with a reduced content of the cooking salt, the exception of sharp, smoked, salt products, alcohol. In the diet there may be boiled meat, fish, mostly river (low-fat), cottage cheese, kefir and other lactic acid products, buckwheat, rice and oatmeal, vegetarian soups, vegetables, fruits.