In what cases is the analysis of hemostasis and for what
Hemostasis translated from Greek Indicates Haima - this is blood, and Stasis is standing. You can interpret this term as a blood retention system in the required state.
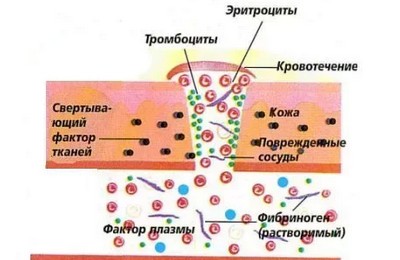
First of all, blood should be liquid and in the required consistency. It should not leave the circulatory bed, that is, the blood system is closed. In the event of damage to the vessels, blood due to coagulation should not leave the closed system and allow blood loss.
In the event of various disorders, unnecessary thrombus can be formed, which must be dissolved. The regulatory function in these issues belongs to the blood hemostasis system. This is a very complex complex of simultaneously performed tasks.
Hemostasis of blood consists of four main components:
- endothelial layer of the vessel;
- shaped blood elements (platelet, erythrocyte, leukocyte cells);
- plasma components (coagulation systems, antoslude and fibrinolytic systems);
- regulatory factors.
According to the mechanism of action, the hemostasis system must be divided into primary and secondary.
What is hemostasis in vascular timboxic type
The primary hemostaste of blood includes platelet factors of cessation of blood loss, which consist in the active formation of temporary microtrombov in vessels.
With a small injury to the vessels of small caliber (capillary bleeding) it can be enough to stop the blood loss. However, when lescriminate the larger caliber, a secondary, coagulation coagulation mechanism is required.
Secondary hemostasis. What is it
Secondary, coagulative hemostasis is the path of cessation of blood loss activated by platelet hemostasis and providing a long-lasting stopping of blood loss.
Coagulative hemostasis of blood provides the density of the thrombocyte clock formed, due to the formation of the fibrin network in it. It also contributes to a more dense fixation of platelet blood cloth to the damaged vascular endothelium.
Hemostasis scheme:
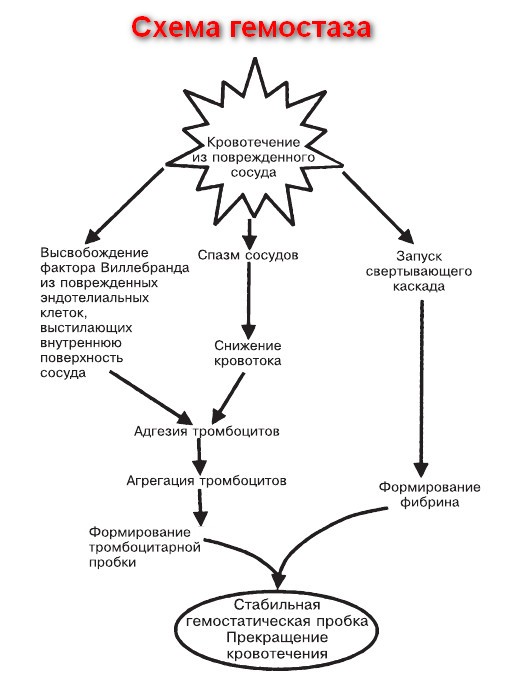
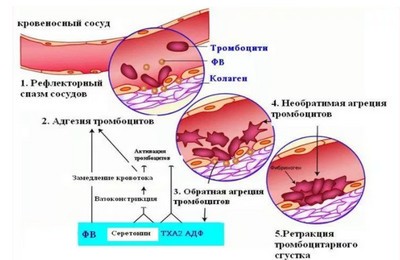
Primary blood hemostasis mechanism
Reference. When violating the integrity of the vascular bed, spasmodation of vessels, contributing to a decrease in blood flow in the damaged area and facilitating the further sticking of platelets (aggregation) and their connection to vascular intima (adhesion).
In parallel with the spasming of the affected vessels begins the active separation of damaged endothelium by cells. This factor increases the adhesive properties of platelet cells and facilitates the formation of primary thrombus.
After the stage of trobocyte agglutination (dense bonding), the reaction of the release of special active components that contribute to maintaining the vascular spasm and primary coagulation processes is occurring.
Reference. The primary hemostasis of blood also contributes to the launch of the coagulation cascade and the beginning of the secondary stop of the blood loss.
Mechanisms of secondary hemostasis
 The secondary cessation of bleeding is long and is able to stop the blood loss during the damage to the vessels, larger caliber. The task of the coagulation cascade is that it leads to the formation of fibrin, stabilizing and tightly fixing the usual thrombochar-liter thrombus on a damaged vessel section.
The secondary cessation of bleeding is long and is able to stop the blood loss during the damage to the vessels, larger caliber. The task of the coagulation cascade is that it leads to the formation of fibrin, stabilizing and tightly fixing the usual thrombochar-liter thrombus on a damaged vessel section.
In fact, the coagulation cascade cascade is a series of consecutive, chain reactions. Each reaction is activated using a special coagulation factor (specific proteins that are responsible for normal coagulation).
Important! Due to the fact that all reactions are chain (completion of one reaction leads to the activation of the following), then with a violation of one link, all subsequent reactions are disturbed.
External and internal hemostasis
- external, launched by the work of tissue coagulation factors;
- the internal, activating as a result of the work of coagulation factors in the blood, plasma (also in this mechanism is the activity of enzymes and platelet cells).
It should be noted that the mechanism of internal and external hemostasis differs only until the activation of Prothrombin. Next, their work is no different.
For the primary activation of the external mechanism of hemostasis, the destruction of endothelium cells is necessary. In the presence of damage, the tomblalastin factor (third coagulation factor) occurs from the membranes of endothelial cells. The third factor begins to interact with the prisoner (seventh factor) of SA (fourth factor).
Important. The presence of calcium ions in sufficient quantities is mandatory for a full blood hemostasis.
To activate the indoor path, it is necessary to have a "contact phase", that is, to start the coagulation cascade, it is necessary to contact blood with a damaged vascular intimate and a foreign damaging surface (needle, knife, glass, etc.). As a result, the activation of the twelfth Factor Hageman is activated.
The implementation of the internal cascade is provided by alternately activation:
- the twelfth factor of the eleventh (plasma precursor of thromboplastin);
- eleventh - ninth (Christmas factor);
- ninth - eighth (antihemophilic).
After that, activation of the stewart factor is activated. Further reactions are similar to the external hemostasis mechanism.
For all the internal mechanism reactions, calcium ions are also needed.
The diagram of the internal and external hemostasis of blood:
(Activated complexes are marked with a)

Second, third and fourth blood hemostasis phases
 After education, the first phase of coagulation is completed, further coagulation and in the external, and the inner mechanism are equally.
After education, the first phase of coagulation is completed, further coagulation and in the external, and the inner mechanism are equally.
In the second phase, thrombin (active thrombin formation) begins to form. This phase lasts from two to five seconds. Protromine with the help of the protegride and the tenth factor turns into active thrombin.
In the first and second phase of coagulation, blood is in a liquid state.
In the 3rd phase, the blood in the area of \u200b\u200bdamage passes into the gel-like shape and the formation of fibrin, which constitutes the stable base of thrombus.
Under the influence of active thrombin, in the 3rd phase there is a transformation into fibrin and formation in the place of damage to the dense fibrin network.
The fibrin network stabilizes the continuing thrombocharger thrombus and improves its fixation on the endothelium. The red color of the thrombus is explained by the fact that the network contains a large number.
The third phase takes from three to five seconds.
The blood hemostasis in the fourth phase is to compress and seal the formed thrombus and further dissolution of the clutch.
Attention! All processing cascade processes in all phases occur in the presence of calcium ions. Also, for the normal formation of fibrin, vitamin K and adequate liver work (almost all coagulation factors are synthesized by the liver).
The finite coagulation product is fibrin resulting from fibrinogen.
The whole process of hemostasis occurs on the thromboplasty matrix. It provides high speed and coagulation efficiency, as well as the walness of hemostasis. That is, the blood formation process occurs on a limited portion of the vascular wall.
Important. Similarly, an antoslude system that prevents excessive growth of thrombus, the development of the engine, as well as microtromotic formation in vessels is activated, activates an antoslude rolling system of hemostasis.
The functions of the hemostasis system
Hemostasis system provides: 
- constant blood maintenance in liquid state;
- termination of blood loss in damage to the vascular bed;
- blood purification from non-bacterial phagocytosis products;
- regeneration of damaged vascular endothelium and helps to restore the integrity of vessels and tissues.
For the full functioning of the hemostasis system requires:
- the presence of vesselsistance dealers of vascular endothelium (anti-aggregative, anticoagulant and fibrinolytic properties of vessels supported by prostacyclines, nitrogen oxide, endothelins, antithrombin, etc.);
- the ability of plasma hemostasis factors to move into an inactive state;
- blood circulation continuity in vessels;
- the active work of the fibrinolytic system and the presence in the blood of anticoagulants.
Violation of hemostasis
Disruption of coagulation
 In this case, the patient will suffer from high bleeding. At the same time, complaints are characterized by long-term bleeding during cuts, frequent nose, gum bleeding, easily formed and long-term convergent bruises. Women complain of long-term, abundant menstruation, frequent intercicular bleeding.
In this case, the patient will suffer from high bleeding. At the same time, complaints are characterized by long-term bleeding during cuts, frequent nose, gum bleeding, easily formed and long-term convergent bruises. Women complain of long-term, abundant menstruation, frequent intercicular bleeding.
In hereditary coagulopathies, which are characterized by the mutations of hemostasis genes, profuse nasal, gastrointestinal, uterine bleeding, hemorrhage in joints and muscles may occur.
Hemorrhagic rash may also be celebrated.
Reference. The hemostasis disorders that appear enlarged bleeding are included in the group of hemorrhagic diathesis.
According to the mechanism for the development of coagulation disorders, shared on the associated with:
- thrombocyte defects (here include thrombocytopenic purpura and thrombocytopathy);
- coagulation disorders (hemophilia A, B, from type, Willebrand disease, the disease of Stewart Puera, etc.);
- damage to the vascular wall (hemorrhagic vasculitis, teleangioectasis, hemangioma, etc.).
Disorders of an antoslude system
These violations manifest themselves a tendency to elevated thrombosis. The formation of blood clots in the vessels leads to:
- circulatory disorders
- insufficient blood supply and tissue ischemia,
- thromboembolic violations
- thrombosis (most often lower limbs),
- diseases of the cardiovascular system (IBS, heart attack), strokes, etc.
Indications for testing for blood hemostasis
- the presence of autoimmune pathologies;
- kidney diseases;
- violation of the proteintetic liver function;
- malignant neoplasms;
- bone marrow damage;
- endocrine pathologies;
- hypocalcemia;
- ascorbic acid deficits and vitamin P;
- severe intoxication;
- some infections (measles, rubella, influenza, rapid tit, hemorrhagic fever, meningitis, leptospirosis, etc.);
- immunocomplex vasopathy (Shenlayan-genecia disease);
- hereditary coagulopathy (hemophilia, disease Osler-Randy, etc.).

Hemostasis system studies are carried out at:
- the appearance of symptoms of reduced or increased blood coagulation (bleeding or thrombosis),
- diseases of the SCC and the monitoring of their treatment;
- the need for surgical interventions;
- states after operations;
- diseases accompanied by a blood hemostasis violation;
- pregnancy.
Hemostasis during pregnancy
Blood test for hemostasis during pregnancy is included in the list of mandatory studies, since even minor deviations from  norms in this period, are fraught with serious consequences for the health of the mother and the kid.
norms in this period, are fraught with serious consequences for the health of the mother and the kid.
Increased blood clotting can lead to:
- impaired placental blood circulation
- fetal hypoxia
- failure to pregnancy
- spontaneous abortion,
- the usual unbearabity of pregnancy.
Very important. Reducing blood coagulation during pregnancy can lead to severe bleeding in childbirth.
The most formidable complication is the DVS syndrome, which can develop against the background of eclampsia (late gestosis of pregnancy).
In the disseminated intravascular blood coagulation, four phases are isolated:
- hypercoagulatory, accompanied by enhanced thrombosis;
- hypocoagulating, without depletion of coagulation factors;
- hypocoagulating, with the full exhaustion of all coagulation factors;
- restoration (with timely provision of specialized medical care) or complete non-brooding of blood, with the development of profuse bleeding and fatal outcome.
Normally, blood test on hemostasis during pregnancy should be carried out at least three times.
Hemostasis during pregnancy for emergency testimony is carried out at:
- hyperthonus of the uterus;
- the threat of the placenta detachment;
- the threat of spontaneous abortion or the spontaneous abortion started (the appearance of pain in the abdomen and moderate bleeding);
- the development of preeclampsia and eclampsia (the emergence of edema, resistant rise of blood pressure, the development of hypertensive crisis, strong headaches, convulsions).
Important. Analysis on hemostasis allows you to identify and diagnose the cause of violations and preserve pregnancy.
Ideally, tests for blood hemostasis should surrender at the stage of pregnancy planning. When disrupted violations, a gemostasiologist's doctor is treated at first (a hemostasist is a specialist dealing with blood clotting problems).
Blood on hemostasis is mandatory with:
- burdened with family history (thrombosis, varicose veins, infarction, strokes in relatives);
- infertility;
- habitual non-banking pregnancy;
- failure to pregnancy in history;
- heavy gestoses, pale placenta or bleeding with past pregnancies.
Attention. According to recent studies, about 50 percent of cases of female infertility or without pregnancy is associated with violations in the hemostasis system.
Treatment of hemostasis disorders
The complexity of the system entails difficulties with treatment. With problems of blood clotting disorders should be addressed to the doctor  hemostasiologist, who recommends to make a coagulogram and will appreciate its results. All therapy is carried out strictly under the control of the tests.
hemostasiologist, who recommends to make a coagulogram and will appreciate its results. All therapy is carried out strictly under the control of the tests.
As a rule, therapy with hemostasis violations is aimed at:
- elimination of any possible harmful effects, including the reassignment of used drugs that may disrupt blood clotting and platelet functions,
- elimination of all accompanying diseases that can aggravate the existing hemostasis disorders,
- promoting the strengthening of the vascular wall due to vitamin therapy ascorbic acid, routine, herbal fees,
- the use of substitution therapy with the preparations of coagulation factors,
- use of aminocaproic acid, ditinona, adroxon,
- the use of hormonal regulation of the menstrual cycle.
Attention! Treatment schemes and therapy duration depend on the cause of blood coagulation disorders. With hereditary coagulopathy treatment for life. If necessary, surgical intervention patients must undergo special preoperative preparation.
Hemostasis. Video
Very interesting short lecture on hemostasis system. Doctor of science tells, Professor (despite the youth) M.Pantuelyev: