A dash in the non-union complex suggestion of the typed structure. Punctuation directory - Rosenthal DE drifted here Rye began to yellow
A dash between parts of the non-union complex proposal is set if the content of the first part indicates the time, the condition, the reason for what is said in the second part, and also if the content of the first part is sharply opposed to the content of the second part.
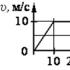
1. Driving here - Rye began to turn yellow. (M. Privine.)
The first part indicates the time of what is said in the second part (before the first part you can insert the union when).
2. Will you work up to sweat - eat in hunt. (Proverb.)
The first part indicates the condition that it is said in the second part (you can insert the union before the first part. if a).
![]()
3. Suddenly, the peasants with the axes appeared - the forest slaughtered, groaned, shook. (N. Nekrasov.)
The first part indicates the reason why it is said in the second part (you can insert the union before the first part as), and the second part indicates a consequence of what is said in the first part (between parts of a complex sentence can be inserted so).
4. Summer suppresses - winter eats. (Proverb.) The first part of the content is sharply opposed to the content of the second (between parts of a complex sentence you can insert the union but or but).
5. Birch in the forest without a vertex - the hostess without a husband in the house. (N. Nekrasov)
The second part contains a comparison, compared with what is said in the first part (the unions can be inserted between parts of a complex sentence as if as if).
199. Read offers with comparable or explanatory intonation. Explain the formulation of a dash in non-union complex suggestions, using samples of reasoning data in the rule.
Note that in some cases the value of the first part can be determined in different ways: and as temporary, and as conditional. For example: I saw the ridge - I will meet the spring. (Proverb.) ( When I saw the risk, I will meet the spring or: If I saw the risk, I will meet the spring).
Write out four non-union proposals that are appropriate in the rules of schemes. Make an intonation scheme written offices.
1. Samples .. I didn't run - the legs from fear did not move. (L. Tolstoy.) 2. And he will beat me - you go out for the Holy Trouble and Mother. (M. Lermontov.) 3. Slices of hairs of Lisa do not please ... left the tail of it. (I. Krylov.) 4. The sun looked out - she had fun. (V. Korolenko.) 5. You are lining .. they are a wet bush - you will be thrown by the accumulated night smell. (I. Turgenev.) 6. Begging (c) Single - Life does not turn over. 7. Wrivery - Bread will be guessing. 8. In a lot of water, the water will be water. 9. Bogatyr will die - his name remains (T, th). (Proverbs.)
200. By setting the missed punctuation marks, write down the simple sentences first, then complex. Emphasize the grammatical foundations of the proposals.
In what non-union complex suggestions, the value can be understood and as conditional, and how is temporary?
1. In the summer at home, sit in winter bread not habits. 2. Cowardly every w...rous trouble. 3. In .. Yuga da M..tels under February flew. 4. SUGDOW Yes, in .. I have two friends. 5. July summer macushka. Winter hat. 6. The Sun of PR. It will take everything. 7. In the spring of a walk .. We have a week (not) probably. 8. The wind will be the traces of the deputy..t. 9. Measure wind (not) Escape Verder. 10. Many snow is a lot of bread. 11. Many water is a lot of grass. 12. Winter without snow summer without bread. 13. In autumn (no), nastye seven weather in the courtyard of the CE .. it is cool .. it's cool .. it turns (c) the top l .. it (c) the bottom M..t. 14. More snow on the fields more bread in the covers. 15. In winter, the snow is deep in summer. High bread. 16. Snow Nadu..t Bread PR .. Bathing Water Rolling .. Sena Nab..rot. 17. Do not want a cold to love the forest (c) to the MOLOD. 18. Summer at-wear Winter Podper.
(Proverbs.)
201. The non-union complex offers are widely used in oral speech, as well as in the works of fiction, especially in the dialogues and monologues of the heroes, when the writers seek to reflect the features of oral speech syntax. Find in the 3rd Action of the Comedy D. Phonvizin "Nepali" non-union complex suggestions. Write them out and explain the formulation of punctuation marks.
202. The writing. Painting N. M. Romadina "The village of Khmelevka" (from the series "Volga - Russian River") was written in 1944 at the end of the Great Patriotic War. The artist depicts the village, what a lot, and wants to show his nonsense. calm beauty. In the picture, we see the village as a whole, its panorama: it is rapidly spread over the gentle slopes of a large ravine, overgrown with grass, shrub, trees.
What do you think, from what point of review, the artist wrote his picture so that this panorama opens our eyes? What time of year I portrayed an artist? Why does glue gold paints prevail in his picture? What is depicted in the foreground? What shines on the horizon? What details attracted your attention? You felt like this village, these broad, unbarrible gave your name. attract to yourself?
Select a possible situation and write down your story or review.
A dash in a non-union complex proposal, decaying two parts, is set:
1) if the second part contains unexpected accession, indication of the fast change of events(Between both parts you can insert the union and ), eg: Ivan Ivanovich approached the gate, thundered the thaw– From the inside rose a dog bark (Gogol); Suddenly the Kamorka door quickly opened– all the cheese immediately, the Kubarem rolled down from the stairs (Turgenev); Ignat descended the troc– The gun gave drying (Chekhov); Sun ray falls on grass– (Bitter); Metelitsa was already completely close to the fire– Suddenly, horse rzhanier ran out in darkness (Fadeev); Still shot– Kucher dropped the entrance and quietly slipped under the wheels (Shukshin);
2) if in the second part is expressed contrast in relation to the content of the first part (between parts you can insert the union but or but ), eg: Week passed, month– He did not return home to his home (Pushkin); Up to ten o'clocks, we shrugged in reeds and in the woods– No beast(Lermontov); He painfully spent his eyes across the ceiling, wanted to go off the place, run– The legs did not obey (Goncharov); At that time, you already meet the class of people in France, which with the general loss acquires: the nobility is deprived of rights– They exacerbate their own; People dies with hunger– they are fed, the people are equipped and goes into the enemies– They are profitable supply Sukna, Provit (Herzen); On the courtyard paled summer heat– the house was cool and mixed with the cool world smell of naphthalene (Bunin); In the fairy tales, Andersen acquire a gift of speech not only flowers, winds, trees– They come to life and homemade world of things and toys (Paustic); Not a bag of bears stolen– The last hope is kidnapped (Neurors); Bold win– cowardly dying (proverb);
3) if the second part encompass consequence, output From what is said in the first part (between parts you can insert words therefore, then ), eg: I'm dying– I have nothing to lie (Turgenev); There was no possibility to leave unnoticed– He came out openly, as if walking on the courtyard, and sleeved into the garden (Fadeev); Taking out the matches from the pocket at the same time, and the lighter, the cords lit cord– They broke out (Popov).
Note. In the works of classic writers, occasionally and in modern fiction, instead of a dash, a colon is found in the case under consideration, for example: There was nothing to do: Marya Ivanovna sat in a carriage and went to the palace ... (Pushkin); We drove rear: Nobody saw (Lermontov); Small rain sow in the morning: Impossible impossible (Turgenev); Volodine Horse Chrome: Dad ordered to settle a hunting for him (L. Tolstoy); Care, chagrins, failures of the poor father to extreme: He became an incredulous, yellow ... (Dostoevsky).
4) if the first part indicates time The action referred to in the second part (at the beginning of the first part you can add the Union when ), eg: Dan here– Rye began to yellow. Now I'm leaving back– this rye people eat (Provine); The weathered face is burning, and you cry your eyes– all the land so sailing under his feet (Bunin); Ahead made his way to the senior, filed a team with a careful hand movement: raise his hand over his head– everyone immediately stopped and silence; pull out the hand to the slope to the ground– Everyone at the same second quickly and silently lay down; Walk hand forward– all moved forward; Shows back– All slowly fivefold back (Kataata); Nice boy. Sampling him now a beard, put on the costume– teacher (Shukshin); Pashut arable land– Do not make hands (proverb);
5) if the first part indicates conditionsthe action referred to in the second part (at the beginning of the first part you can add the union if when in meaning "if a", eg: There will be a rain– there will be fungi; There will be fungi– There will be a body (Pushkin); What will need– tell Pavlu or Tatiana (Turgenev); Loads you at all– you will not cry for you (Chekhov); Sun ray falls on grass– Cream grass emerald and pearls(Bitter); Swear will– Do not be afraid (Smooth); Like to draw – draw on health, no one forbids (V. Panova). Cf. Proverbs: Called Gruzd– Frames in the body; Love to ride– Love and sanocho carry; We miss fire– do not extinguish; He took up– Do not say that not a duzh; Wolves fear– In the forest, do not walk; Forest cabin– pinch fly; Positive Lychka– Give the strap; Death afraid– in the light not live and etc.;
6) if the second part contains comparison With what is said in the first part (you can add alliances before the second part as if, as if ), eg: Palloon word– nightingale sings (Lermontov);
7) if the second part (often incomplete offer) is of an extreme value (you can insert the union before it what ), and in the first part does not contain an intonation warning on the subsequent presentation of any fact, for example: Someone screames, it seemed to me– mouse; You call in the apartment, grandmother will ask– Who are called;
8) if the second part is attachment offer and in front of him can insert the word this is, which may be in the proposal itself, for example: On the wall not a single image– bad sign (Lermontov); Inga was excited, Levshin watched her too much– this is rushed to the eyebreaker (Fedin); There is a big water– this is In most interesting (Gorbatov).
The second part can begin with plain words so, this, such eg: The order is order– So His Front brought up(Sparrow); Curves Streets, Little Wooden Houses– such There was Moscow at the beginning of the century.
Note. To delimitate cases of colon and dash in non-union complex suggestions, it is possible to proceed from the following general situation: if the main part of the statement (corresponding to the main proposal in complex proposals) is concluded in the first part, and in the second (appropriate attachment in complex proposals) is explained, disclosure The content of the first part, the presentation of any fact, indication of the cause, then between the parts is put by the colon; If, on the contrary, the main part of the statement is enclosed in the second part, and the first has a subordinate value (indicates time, condition, etc.), then there is a dash between parts. Wed: Impossible impossible: on the street pouring rain (The main statement is contained in the first part, the second indicates the reason). - On the street pouring rain– Impossible impossible(The reason is indicated in the first part, in the second consequence, the conclusion that is the basis of the statement). Cf. Also while maintaining the same order of parts of the non-union complex proposal: Youth gone: on the evening it became boring (Gone, because it became boring). Youth gone– on the evening it became boring (Gone, therefore it became boring).
Tasks for independent work
1. Explain why the colon is delivered to the BSP.
but) In the pale light, the dawn stood a little birch in the tub, and I suddenly noticed: Almost all she for this night will yellow(K. Pouustovsky).
b) Looked at the clock: they showed the beginning of the eighth (FAD.)
in) To go swimming now the trouble: my chel is not strong, the messenger breaks (Vzhukovsky).
d) The old man made an exception in his lifestyle in honor of the Son's arrival: he ordered him to let him in his half during dressing before dinner (A. Tolstoy).
e) I don't understand alone: \u200b\u200bhow could she bite you? (Chekhov)
e) Like all Moscow, your father is such: I would wish the son-in-law with stars and ranks (Gr.).
2. Explain the formulation of the dash in the BSP
but) Suddenly, the door of the Kamorka quickly swung open - the whole of the cheese of the Kubarem rolled down from the stairs (Turgenev); Ignat lowered the trigger - Ruzho gave a mischief (Chekhov).
b) Week passed, month - he did not return home to his home (Pushkin); Up to ten o'clocks, we shrugged on the reeds and in the woods - no beast (Lermontov)
in) Snow fell - automotive traffic jams began in the city center. I'm dying - I have to lie to me. There was no opportunity to go unnoticed - he came out openly, as if he was going to the courtyard, and chemged into the garden.
d) I was driving here - rye began to yellow. Now I'm leaving back - this rye people eat (Provine); Win - Build a stone house (A. N. Tolstoy)
e) There will be a rain - there will be fungi. Swear will be - do not be afraid. Like to draw - draw on health, no one forbids(Panova)
e) She was in a stunning dress - I saw such only in the photo in glossy magazines.
g) Will look - the ruble ends(Necr.)
h) I bought my PSU a wig - a thief with infarction in intensive care was taken.
3. Make a syntactic analysis
A minute later, screeching and laughter again: I had to go under a huge housing stone (Chekhov).
In the non-union complex sentence, the dash between parts is usually raised in cases where the main part of the statement (sometimes the main part of the complex proposal) is contained in the second part of the complex proposal, and the first part (corresponding to the apparent part) has a subordinate value in meaning, indicating the time or condition The action involving in question in the second part, sometimes the cause, assignment, etc. [Conditions of forming a colon in the non-union complex proposal, see § 44,]
Wed: It is impossible to exit: on the street pouring rain- the main content is concluded in the first part, the second indicates the reason; On the street pouring rain - it is impossible to get out- the reason is indicated in the first part, the second is a consequence, conclusion, which is the basis of the statement;
Youth left: on the evening it became boring- 'left, because: what became boring'; Youth left - on the evening it became boring- 'left, so it became boring'.
With equal semantic relations between parts of the sentence, they have the value of comparison, opposition, etc.
1. In the non-union complex sentence, disintegrated into two parts, before the second part is rated, if it contains unexpected accession, an indication of a quick change of events: Week passed, the other - suddenly drives me to the yard stroller(P.); Cheese fell - with him there was a cheating(Cr.); Ivan Ivanovich approached the gate, threatened the cheek - from the inside the dog lady rose(); Give him only a knife yes let him down on a big way - will dance, I will dance for a penny(); You pass by the tree - it will not flush, it is not enough (T.); Suddenly, men with axes appeared - the forest rang, groaned, shook(N.); Ignat lowered the trigger - Ruzho gave a mischief(C.); Falling the ray of the sun on the grass - the grass flames emerald and pearls(M. G.); Blowed the wind - everything flounded, it came to life and laughed(M. G.); Metelitsa was already completely close to the fire - suddenly Konsky Rzhana rang out in darkness(F.); At noon go through the dead street - a person will not meet(W); Did not have time to warm the land - all the sky(Bub.) [Cf. With the Union Proposition: I did not have time to pay with the old my yammer, as Dunya returned with a samovar(P.)].
2. Before the second part of the non-union complex proposal is rated, if it is expressed in it contrast in relation to the content of the first part (between parts you can insert the unionbut or a) : Would be happy to serve - Serve sick(Gr.); Chin followed him - he service suddenly left (Gr.); Sew will sew - does not know how to take a needle; It is fermented - she is silent(P.); Week passed, month - he did not return home to his home(P.); I walk over the belt - there is no pistol(L.); I began to call the owner - silent; Knook - silent(L.); Up to ten o'clocks, we shrugged on the reeds and in the woods - no beast (L.); Oak holds - To the ground, the Costinka soldered(Cr.); He painfully spent his eyes on the ceiling, wanted to get off the place, to run - the legs did not obey(Rock.); At that time, you already meet the class of people in France, which, with a general loss, acquires: the nobility is deprived of rights - they exacerbate their; The people dies with the hunger - they are full; The people are equipped and goes to loud enemies - it is profitable supplies Sukna, Provit(Hertz.); Sixteen years serve - there was no such thing with me(L. T.); Mowed a mile - twitched pen(M. G.); Falcon takes off, it's up to Earth(M. G.); The peak was taken for Shtivo - the threads were confused and rushed; sat down in checkers play - losing (F.); In the fairy tales, Andersen acquire a gift of speech not only flowers, winds, trees - the home world of things and toys come to life in them(Paust.); Not a bag of bears stolen - the last hope was kidnapped(Ne.); This is not a tired, sick soldier walked from the front - this was the builder(Hump.); He is a guest - I am a master(Bagr.); The battle is not our will begun - our glory finish him(AU.); Not wounds, not sick light tormented him - annoying the consciousness of unnecessaryness(Paul.); I'm per candle - candle in the stove(Chuk.); Bold won - cowardly dying(Last); Summer suppresses - Winter eats(Last); Was not - I will go; Knocks are not knocking - not dismiss; Crying do not cry - you do not turn the lost; I will die - I will not say.
3. Before the second part of the non-union complex proposal, a dash is set if it contains a consequence, the result or withdrawal of what is said in the first part (therefore, it is possible to insert the words therefore, then, then, p.): I'm dying - I have nothing to lie(T.); You will push the wet bush - you will be thrown away with the accumulated warm smell of the night(T.); There was no opportunity to leave imperceptibly - he came out openly, as if he was going to the courtyard, and cheaming into the garden(F.); I would go to the pilots - let me teach me(M.); Taking out the matches from the pocket at the same time, and the lighter, the cords burned down - they broke out(Dad.); Our accommodation - we are preserved; They put samovar in the sensee - the smell of smoke is spread around; During the night, everyone rested - you can again be taken for the interrupted work; The key is lost - break the door.
Notes: 1. If the value of the investigation is not emphasized, then the comma is installed between parts of the non-union complex supply: ... I i will ask him carefully, he will not notice(C.); Man is not a needle, we will find(C.).
2. In the works of classics writers, instead of a dash in the case, colon meets: There was nothing to do: Marya Ivanovna sat in a carriage and went to the palace(P.); We drove from behind: no one saw(L.); Small rain sow in the morning: it is impossible to exit(T.); Care, grieving, failures of the poor father to extremes: he became incredulous, yellow(Cost.).
4. Before the second part of the non-union complex proposal, a dash is raised if the first part indicates the time of the action referred to in the second part (at the beginning of the first part you can add the unionwhen) : WIN - Build a stone house(A. T); I was driving here - rye began to yellow. Now I'm leaving back - this rye people eat(Arrived.); Ahead made his way to the senior, she filed a team with careful movement: raise his hand over his head - everyone immediately stopped and froze; pull out the hand to the side with the slope to the ground - everything at the same second quickly and silently lay down; waving a hand forward - everyone moved forward; Shows back - everything slowly fivefold back(Cat.); Passage plow - do not make hands(Ambassador).
5. Before the second part of the non-union complex proposal, it is rated if the first part refers to the condition of the action referred to in the second part (at the beginning of the first part you can add the unionif a ): There will be a rain - there will be fungi; There will be fungi - there will be a body(P.); Well done will pass - the girl will go, will pass - it will hurt, and the Houchrs will be held - sing the song(L.) - the values \u200b\u200bof the conditions and time are combined; What will be needed - tell Pavlu or Tatiana (T.); Invented - done(T.); Loads you really - we will not cry about you (C.); ... sin will happen - do not ask for mercy(C.); You will believe your eye - melt crooked(M. G.); Will not give - Drop!(M. G.); …The less you know the better you sleep(M. G.); Swear will be - do not be afraid(Ch.); Like to draw - draw on health, no one forbids(Pan.); Ordered - you're lucky(A. T). Cf. In proverbs: Gruzdev called himself get in the body; Do you like to ride - love and sosochos to carry; You will miss the fire - do not extinguish; He took himself - do not say that not a duzh; Wolves fear - not to walk into the forest; You will regret the skirt - give the strap; Plow deeper - more bread see; Death fear - in the light not liveand etc.
Note. If the second part of the non-union complex proposal of this type begins the particle, then after the first part with the meaning of the condition instead of the dash, the comma is installed: Every given to vodka,so himself will soon have to starve(P.); Watch, T. get out of the patience!(Cr.); All to take everythingso in a car soon fall(Acr.).
6. Before the second part of the non-union complex proposal is raised if it contains a comparison with what is said in the first part (you can add the union before the second partas if or as if) : ... look - the ruble will give(N.).
7. Before the second part of the non-union complex proposal is rated, if it (often - incomplete offer) is of an extreme value (you can insert the union before itwhat), and in the first part does not contain an intonation warning on the subsequent presentation of any fact: Sheep says - she slept all night(Cr.); Sometimes I think - you need to escape(M. G.); ... hears - Behind the bushes of elderly girl laughs(M. G.); The silence was so complete and sullen, and the sky is so stuffy that the boy seemed to be somewhat alone only a sharp sound, and something terrible would happen in nature(Cat.); Yesterday, on the neighboring winter, they told - a man's bear shaved(Arb.); I hear - step again(Paust.); The movement is suspended, let's hope for a short time; Someone scraws, it seemed to me - the mouse; But I see - she does not listen to me; They write that we must come - will meet; They knew - there will be a storm; Leave, you do not see - I'm busy.[Cf. § 44, p. 3.]
8. Dash is placed before the locomotive words so, this, suchbeginning connecting proposal, which is part of the non-union complex proposal:The order is order- So his Front brought up(Thief.); Curves Streets, Little Wooden Houses -such there was a significant part of Moscow at the beginning of the 20th century. Go ahead- Taks there was a choice of a partisan detachment;
In these sentences, judgments are pronounced, the subject of which is named in the first part, and the predicate forms the second part. If the logical relationship between both parts is another character, then the comma and dash are put between them: Environmental pollution threatens life on earth, it cannot continue to continue(Gas.). [Cm. § 46, p. 2.]
9. If the second part of the non-union complex proposal is attachment A proposal, it is rated (it is possible to insert the word this, which sometimes exists in the proposal itself): On the wall not a single image - a bad sign(L.); You have no souls, you have a pride instead of the soul - that's what I tell you(Already.); Inga was excited, Levshin watched her too intently - it was chalked into the eyes(Fed.); There is a big water - it's only more interesting(Hump.); He always loved to chat - it was me perfectly known(Kav.); They will break up, they already parted - this thought stoley(Gran.).
Note. Often, if there is a word between parts of the non-union complex sentence, the comma and dash are set to the word. Russian intelligentsia grew and developed in conditions of absolutely brutally, -it is indisputable (M. G.). [Cm. § 46, p. 1.]
The comma and dash can also be placed before the connecting proposal containing additional note: The village of Pervomaysky was the oldest mining village in the area, - from him, actually, and the city began(F.).
See: Ivanchikova E. A: On the development of the syntax of the Russian language in the Soviet era // Development of the syntax of the modern Russian language. M., 1966 (from there and some examples are borrowed).
Topic: non-union complex proposal.
Educational:
Systematize the material on the syntax of the non-union complex proposal;
improve students' knowledge about the nature of the semantic relationship between parts of the BSP;
Developing:
Develop the skills of forming punctuation marks between parts in the BSP;
Develop the ability to create BSP schemes;
Develop intelligent skills: analyze, classify and systematize material on the syntax of a complex offer.
Educational:
Raise the desire for self-control and reflection;
Rail interest in the study of the subject.
Expected result: students can define non-union complex proposals, determine the semantic relationships in the BSP, are able to arrange punctuation marks.
Visuality: Interactive board, cards with tasks, video tracks, envelopes with tasks, markers, glue.
Type of lesson: a lesson of generalization, systematization and testing of knowledge.
During the classes:
Organizational moment (2 min)
a) Teacher's introductory word.
- Hello guys! I'm glad to see you. Today we have an unusual lesson. Guests are present at the lesson. Your task: show everything you can and know about the BSP and not only. I hope that the lesson will be interesting for you and useful.
b) division into groups on cards with the schemes of non-union proposals.
A) with a dash - b) with a colon:
II. Theme and objectives of the lesson (2nd)
What is drawn on cards?
What do they differ from each other?
What do you think, what will be the topic of our lesson?
Yes, right. Write down in the notebooks today and theme lesson.
Our goal is to repeat and summarize knowledge on the topic "BSP".
You will evaluate your participation in the lesson yourself. To do this, you will specify an estimate in the corresponding column on the cards, and at the end of the lesson, fold all the numbers and divide the number of all tasks, and thus it will be an assessment for the lesson.
III. Repetition of the studied BSP
1. "Repeat is a mother of teaching." Drawing up a conceptual card (BSP) - 3min
2. Taxonomy Bloom - 5 minutes
Why is the proposal of Naz-Xia Nessoy?
Why is the comma in BSP?
Why is the point with a comma?
Why is the colon?
Why is the dash?
Test video transmission - 8 minutes
3. "Create a passport" (work in groups) -5 minutes.
(For example: 1. BSP 2. Consists of 2-sentences 3. put the colon, because ...
4. Offer scheme
Workout. 2-min (skeletons)
4. "Mail". Tasks for groups in 2 envelopes - 5 minutes
Clouded clouds, it rained.
It would be happy to serve - to serve sick.
For everything to take - not to do anything.
I understood: only chance can help out us.
Behind me: With my friend is not.
5. "I want to ask" -5 min What is put?
IV. Reflection. "Telegram". 2 minutes
Red - excellent, yellow - good, green - bad.
semicolon | colon | ||
|
|
|
|
V. Evaluation (count points)
Vi. Homework
1) - If parts of the proposal are closely related in meaning and denote events that occur in consistently after each other.
2) - if parts are less related in meaning and more common (inside them there are additional punctuation marks).
3) If the second offer explains the first. And you can mentally substitute the union namely.
4) If the second proposal complements the first, it contains additional information ..
5) If the second sentence calls the cause of the first. From the first sentence you can put a question why?
6) If the first sentence contains a condition, an union can be substituted if.
7) If the second proposal contains a consequence of events referred to in the first part and the second proposal may be added by the Union due to something or so.
8) If a union may be substituted in the first sentence when
9) If the Union A can be substituted into the second sentence.
10) If parts of the proposal are closely connected in meaning and denote events that occur simultaneously.
"Repeat is a mother of teaching." | "Taxonomy Blooma" | "Create a passport" | "I want to ask" |
| ||
"Repeat is a mother of teaching." | Taxonomy Blooma | "Create a passport" | "I want to ask" |
| ||
"Repeat is a mother of teaching." | Taxonomy Blooma | "Create a passport" | "I want to ask" |
| ||
"Repeat is a mother of teaching." | Taxonomy Blooma | "Create a passport" | "I want to ask" |
| ||
"Repeat is a mother of teaching." | Taxonomy Blooma | "Create a passport" | "I want to ask" |
| ||
"Repeat is a mother of teaching." | Taxonomy Blooma | "Create a passport" | "I want to ask" |
| ||
"Repeat is a mother of teaching." | Taxonomy Blooma | "Create a passport" | "I want to ask" |
| ||
"Repeat is a mother of teaching." | Taxonomy Blooma | "Create a passport" | "I want to ask" |
| ||
"Repeat is a mother of teaching." | Taxonomy Blooma | "Create a passport" | "I want to ask" |
| ||
"Repeat is a mother of teaching." | Taxonomy Blooma | "Create a passport" | "I want to ask" |
| ||
|
1. I looked at the clock and understood: the train was already gone. 2. Snowped the snow - automotive traffic jams began in the city center. 3. In my eyes I darkened, my head was spinning. 4. The waves flew - the summer will be good. 5. Schin followed him - he served suddenly left |
|
1. I looked at the clock and understood: the train was already gone. 2. Snowped the snow - automotive traffic jams began in the city center. 3. In my eyes I darkened, my head was spinning. 4. The waves flew - the summer will be good. 5. Schin followed him - he served suddenly left |
|
1. I looked at the clock and understood: the train was already gone. 2. Snowped the snow - automotive traffic jams began in the city center. 3. In my eyes I darkened, my head was spinning. 4. The waves flew - the summer will be good. 5. Schin followed him - he served suddenly left |
|
1. I looked at the clock and understood: the train was already gone. 2. Snowped the snow - automotive traffic jams began in the city center. 3. In my eyes I darkened, my head was spinning. 4. The waves flew - the summer will be good. 5. Schin followed him - he served suddenly left |
|
1. I looked at the clock and understood: the train was already gone. 2. Snowped the snow - automotive traffic jams began in the city center. 3. In my eyes I darkened, my head was spinning. 4. The waves flew - the summer will be good. |
|
1. These things can be left: they will not be useful to us. 2. The evening came, it rained, from the north the wind blew. 3. How many times looked around - there was no one. 4. Crew and Obomlel: He seemed to him. 5. Titled Gruzd - Fly in the body. |
|
1. These things can be left: they will not be useful to us. 2. The evening came, it rained, from the north the wind blew. 3. How many times looked around - there was no one. 4. Crew and Obomlel: He seemed to him. 5. Titled Gruzd - Fly in the body. |
|
1. These things can be left: they will not be useful to us. 2. The evening came, it rained, from the north the wind blew. 3. How many times looked around - there was no one. 4. Crew and Obomlel: He seemed to him. 5. Titled Gruzd - Fly in the body. |
|
1. These things can be left: they will not be useful to us. 2. The evening came, it rained, from the north the wind blew. 3. How many times looked around - there was no one. 4. Crew and Obomlel: He seemed to him. 5. Titled Gruzd - Fly in the body. |
|
1. These things can be left: they will not be useful to us. 2. The evening came, it rained, from the north the wind blew. 3. How many times looked around - there was no one. 4. Crew and Obomlel: He seemed to him. 5. Titled Gruzd - Fly in the body. |
All the way from the station to the farm was silent: the shaking ride was prevented.
In my eyes I darkened, my head was spinning.
I drove here - rye just started shrust.
Behind me: There is no friend with me.
All day I stood on the spot, because we dried the property and rested.
Q. I repeated the invitation, but he answered nothing.
C. If geese is highly flying, then there will be a lot of water.
Group "Good luck". Rearrange complex union proposals in Nessu-Union. Write them down, arranging punctuation signs.
A. It was decided to go early, and we got up a little light.
V. I approached the window and saw that at night the snow was torn off the whole garden.
C. When the morning will come, move the way.
Group "Joy". Rearrange complex union proposals in Nessu-Union. Write them down, arranging punctuation marks
A. I tried to run, but the legs from fear did not move.
V. Quietly plow is not suitable, because instead of bread, grass is erupted.
S. I immediately understood that the rooster was somewhere here.