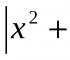Audio recording of the table of division by 2 and 3. Division
Lesson 15. TABLES OF DIVISION BY 2 AND 3. FINDING VALUES OF NUMERICAL EXPRESSIONS. SOLUTION OF PROBLEMS
Target: repeat the techniques of drawing up the division table; develop the ability to solve problems containing the action of division, find the values of numerical expressions; develop logical thinking; improve computing skills; develop an interest in mathematics.
During the classes
I. ORGANIZATIONAL MOMENT
II. UPDATING REFERENCE KNOWLEDGE
1. Checking homework
What are some examples with the answer 18; 21 and 27.
2. Game "Help Owl solve circular examples"
3. Frontal poll
What are the names of numbers in multiplication?
How to find an unknown factor?
What are the division numbers called?
From each expression and its meaning, compose and write down the equality with division by 2 (p. 22, task 132).
III. LESSON TOPIC MESSAGE
Today in the lesson we will review the division table by 2 and 3; finding the values of numerical expressions; we will solve division problems and learn to work independently.
IV. WORKING ON THE TOPIC OF THE LESSON
1. Repetition of material related to fission (p. 22, task 133)
Drawing up a table of division by 2; 3.
2. Calculation of examples with commentary (p. 22, task 134)
3. Work on the problem (p. 22, task 135)
12: 3 = 4 (UAH) - each daughter received
Make the inverse problem.
Mom gave three daughters 4 UAH each. How much money did mom have? (4 ∙ 3 = 12 (UAH))
Physical education
V. DEVELOPMENT OF MATHEMATICAL KNOWLEDGE
1. Work on the problem (p. 22, task 136)
Analysis of the problem on the teacher's questions.
1) 26 - 8 = 18 (og.) - left
2) 18: 3 = 6 (og.)
Answer: 6 cucumbers were placed in each jar.
2. "Blitzkontrol of knowledge"
Option 1
1) In which expression is the number 34 missing?
a) + 25 = 59;
b) 68 - = 31;
c) 26 + = 50.
a) 2 + 2 + 2 + 2- 4 = 2 ∙ 4;
b) 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 2 ∙ 4;
c) 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 2 ∙ 4.
3) The difference between the numbers 75 and 23 is increased by 14. Mark the correct answer.
4) Note the equation where the term is 25.
a) 16 + x = 40;
b) x + 7 = 32;
c) x + 9 = 17.
5) If a = 18, then 92 - a =.
6) Eight pies were divided equally among the four students. How many pies did each student receive?
7) 3 bags poured 15 kg of potatoes, after which 12 kg of potatoes remained in the bag. To find out how many kilograms of potatoes were in the bag first, you need:
a) 15 + 12 + 15;
8) What is the perimeter of a square if one side of it is 3 cm?
9) 12 boys and 15 girls took part in the competition. All students were divided into 3 teams. How many members were on each team?
b) (12 + 15): 3;
2 option
1) In which expression is the number 26 missing?
a) 25 + = 58;
b) 73 - = 30;
c) + 34 = 60.
2) Mark the correct equality:
a) 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 6 = 3 ∙ 6;
would) 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 = 3 ∙ 5;
c) 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 - 2 = 3 ∙ 5.
3) The sum of numbers 47 and 18 is reduced by 15. Mark the correct answer.
4) Find the equation where the term is 35.
a) 7 + x = 42;
b) 17 + x = 48;
c) x + 9 = 54.
5) If a = 13, then 61 - a =.
6) Place 3 plums on each plate. How many plums are there on 7 plates?
7) The book has 45 pages. The girl read several pages, and she had 17 pages left to read. To find out how many pages a girl has read, you need to:
a) 45 - 17 - 17;
8) What is the perimeter of a triangle if it is 6 cm long and 2 cm wide?
9) There were 12 desks in the classroom. Then 6 more desks were brought. All desks were placed in three rows, equally in each. How many desks were placed in each row?
b) (12 + 6): 3;
Vi. LESSON OUTCOME
What seemed difficult for the freaks?
What task did you like?
What else did you want to work on?
Vii. HOMEWORK
P. 22, task 137; 138.
Division is one of the four basic mathematical operations ( addition , subtraction , multiplication). Division, like other operations, is important not only in mathematics, but also in Everyday life... For example, you will hand over money to the whole class (25 people) and buy a gift for the teacher, but you will not spend everything, there will be change. So you will need to divide the change among all. The division operation comes in to help you solve this problem.
Division is an interesting operation, as we will see with you in this article!
Division of numbers
So a little theory and then practice! What is division? Division is splitting something into equal parts. That is, it can be a bag of chocolates that needs to be split into equal parts. For example, there are 9 sweets in a bag, and the person who wants to get them - three. Then you need to divide these 9 chocolates among three people.
It is written like this: 9: 3, the answer will be the number 3. That is, dividing the number 9 by the number 3 shows the number of three numbers contained in the number 9. The reverse action, checking, will be multiplication... 3 * 3 = 9. Right? Absolutely.
So let's look at example 12: 6. First, let's name each component in the example. 12 - dividend, that is. a number that can be divided into parts. 6 is the divisor, this is the number of parts by which the dividend is divided. And the result will be a number called "quotient".
Divide 12 by 6, the answer will be the number 2. You can check the solution by multiplying: 2 * 6 = 12. It turns out that the number 6 is contained 2 times in the number 12.

Division with remainder
What is division with remainder? This is the same division, only the result is not an even number, as shown above.
For example, divide 17 by 5. Since the largest number divisible by 5 to 17 is 15, the answer is 3 and the remainder is 2, and it is written like this: 17: 5 = 3 (2).
For example, 22: 7. In the same way, we determine the maximum number divisible by 7 to 22. This number is 21. The answer then will be: 3 and remainder 1. And it is written: 22: 7 = 3 (1).
Division by 3 and 9
A special case of division will be the division by the number 3 and the number 9. If you want to know whether a number can be divided by 3 or 9 without a remainder, then you need:
Find the sum of the digits of the dividend.
Divide by 3 or 9 (whichever you want).
If the answer is obtained without a remainder, then the number will be divided without a remainder.
For example, the number 18. The sum of the digits is 1 + 8 = 9. The sum of the digits is divisible by both 3 and 9. The number 18: 9 = 2, 18: 3 = 6. Divided without remainder.
For example, the number 63. The sum of the digits 6 + 3 = 9. Divisible by both 9 and 3. 63: 9 = 7, and 63: 3 = 21. Such operations are performed with any number to find out whether it is divisible with the remainder 3 or 9 or not.
Multiplication and division
Multiplication and division are opposite operations. Multiplication can be used as a test for division, and division as a test for multiplication. You can learn more about multiplication and master the operation in our article about multiplication... Which describes in detail the multiplication and how to do it correctly. There you will also find the multiplication table and examples for training.
Let's give an example of checking division and multiplication. Let's say the example is 6 * 4. Answer: 24. Then check the answer by division: 24: 4 = 6, 24: 6 = 4. Resolved correctly. In this case, the check is performed by dividing the answer by one of the factors.
Or an example is given for division 56: 8. Answer: 7. Then the check will be 8 * 7 = 56. Right? Yes. IN this case verification is done by multiplying the answer by the divisor.

Division 3 class
In the third grade, division is just beginning. Therefore, third-graders solve the simplest problems:
Problem 1... A factory worker was given the task of arranging 56 cakes in 8 packs. How many cakes do you need to put in each package to get the same quantity in each?
Task 2... On New Year's Eve at school, children were given 75 sweets for a class of 15 students. How many sweets should each child get?
Problem 3... Roma, Sasha and Misha collected 27 apples from the apple tree. How many apples will each get if they are to be divided equally?
Problem 4... Four friends bought 58 cookies. But then they realized that they could not divide them equally. How many guys need to buy cookies so that everyone gets 15 pieces?
Division 4 class
The division in the fourth grade is more serious than in the third. All calculations are carried out by the method of division into a column, and the numbers that participate in the division are not small. What is long division? You can find the answer below:
Long division
What is long division? This is a method that allows you to find the answer to the division of large numbers. If prime numbers like 16 and 4 can be divided, and the answer is clear - 4. Then 512: 8 in the mind is not easy for a child. And to tell about the technique for solving such examples is our task.
Consider an example, 512: 8.

Step 1... Let's write the dividend and divisor as follows:

The quotient will be written as a result under the divisor, and the calculations under the dividend.
Step 2... We start division from left to right. First, we take the number 5: 
Step 3... The number 5 is less than the number 8, which means that it cannot be divided. Therefore, we take one more digit of the dividend:
Now 51 is more than 8. This is an incomplete quotient.
Step 4... We put a dot under the divider.

Step 5... After 51 there is another number 2, which means that the answer will contain one more number, that is. the quotient is a two-digit number. We put the second point:

Step 6... We start the division operation. The largest number that can be divided without a remainder by 8 to 51 is 48. Dividing 48 by 8, we get 6. Write the number 6 instead of the first dot under the divisor:

Step 7... Then we write the number exactly under the number 51 and put the “-” sign:

Step 8... Then subtract 48 from 51 and get the answer 3.

* 9 step*. We demolish the number 2 and write next to the number 3:

Step 10 Divide the resulting number 32 by 8 and get the second digit of the answer - 4.

So the answer is 64, no remainder. If we were dividing the number 513, then the remainder would be one.
Division of three-digit
Division of three-digit numbers is performed by long division, which was explained in the example above. An example of just the same three-digit number.
Division of fractions
Division of fractions is not as difficult as it seems at first glance. For example, (2/3) :( 1/4). The method for this division is quite simple. 2/3 is the dividend, 1/4 is the divisor. You can replace the division sign (:) with multiplication ( ), but for this you need to swap the numerator and denominator of the divisor. That is, we get: (2/3)(4/1), (2/3) * 4, this equals - 8/3 or 2 integers and 2/3 Let's give another example, with an illustration for better understanding. Consider fractions (4/7) :( 2/5):
As in the previous example, flip the divisor 2/5 and get 5/2, replacing division with multiplication. We get then (4/7) * (5/2). We make a reduction and the answer: 10/7, then we take out the whole part: 1 whole and 3/7.
Dividing a number into classes
Let's imagine the number 148951784296 and divide it by three digits: 148 951 784 296. So, from right to left: 296 - class of units, 784 - class of thousands, 951 - class of millions, 148 - class of billions. In turn, in each class, 3 digits have their own category. From right to left: the first digit is ones, the second digit is tens, the third is hundreds. For example, class of units is 296, 6 is units, 9 is tens, 2 is hundreds.

Division of natural numbers
Division of natural numbers is the simplest division described in this article. It can be with or without a remainder. The divisor and divisible can be any non-fractional, whole numbers. 
Take the course "Speeding Up Verbal Counting, NOT Mental Arithmetic" to learn how to quickly and correctly add, subtract, multiply, divide, square, and even root. In 30 days, you will learn how to use light tricks to simplify arithmetic operations. Each lesson has new techniques, clear examples, and helpful assignments.
Division presentation
Presentation is another way to visually show the topic of division. Below we will find a link to a great presentation that explains well how to divide, what division is, what is the dividend, divisor and quotient. Don't waste your time, but consolidate your knowledge!
Division examples
Easy level
Average level
Difficult level
Games for the development of oral counting
Special educational games developed with the participation of Russian scientists from Skolkovo will help improve the skills of oral counting in an interesting way.
Guess the operation game
The game "Guess the operation" develops thinking and memory. Main essence the game needs to choose a mathematical sign for the equality to be true. There are examples on the screen, look carefully and put the desired "+" or "-" sign so that the equality is correct. The sign "+" and "-" are located at the bottom of the picture, select the desired sign and click on the desired button. If you answered correctly, you collect points and keep playing.

Simplification game
Simplify develops thinking and memory. The main point of the game is to quickly perform a mathematical operation. A student is drawn on the screen at the blackboard, and a mathematical action is given, the student needs to calculate this example and write an answer. Below there are three answers, count and click the number you need with the mouse. If you answered correctly, you collect points and keep playing.

Fast addition game
The Fast Addition game develops thinking and memory. The main point of the game is to choose numbers, the sum of which is equal to a given number. This game is given a matrix from one to sixteen. A given number is written above the matrix, you need to select the numbers in the matrix so that the sum of these digits is equal to the given digit. If you answered correctly, you collect points and keep playing.

Visual Geometry Game
The game " Visual geometry»Develops thinking and memory. The main point of the game is to quickly count the number of painted objects and select it from the list of answers. In this game, blue squares are shown on the screen for a few seconds, they must be quickly counted, then they are closed. Below the table there are four numbers written, you need to select one correct number and click on it with the mouse. If you answered correctly, you collect points and keep playing.

The game "Piggy bank"
The game "Piggy bank" develops thinking and memory. The main point of the game is to choose which piggy bank has more money. In this game you are given four piggy banks, you need to count which piggy bank has more money and show this piggy bank with the mouse. If you answered correctly, then you collect points and continue to play further.

Fast Add Reload Game
The Rapid Addition Reloading game develops thinking, memory and attention. The main point of the game is to choose the correct terms, the sum of which will be equal to a given number. In this game, three numbers are given on the screen and a task is given, add the number, the screen indicates which number needs to be added. You select the desired numbers from three digits and press them. If you answered correctly, then you collect points and continue to play further.

Developing phenomenal oral counting
We've just covered the tip of the iceberg, to understand math better - sign up for our course: Speeding up verbal counting - NOT mental arithmetic.
From the course, you will not only learn dozens of techniques for simplified and quick multiplication, addition, multiplication, division, percent calculation, but also work them out in special tasks and educational games! Verbal counting also requires a lot of attention and concentration, which are actively trained when solving interesting problems.

Speed reading in 30 days
Increase your reading speed 2-3x in 30 days. From 150-200 to 300-600 words per minute or from 400 to 800-1200 words per minute. The course uses traditional exercises for the development of speed reading, techniques that speed up the work of the brain, the method of progressively increasing the speed of reading, the psychology of speed reading and the questions of the course participants are discussed. Suitable for children and adults reading up to 5000 words per minute.
Development of memory and attention in a child 5-10 years old
Purpose of the course: to develop memory and attention in a child so that it would be easier for him to study at school, so that he could better memorize.
After completing the course, the child will be able to:
- 2-5 times better to memorize texts, faces, numbers, words
The brain, like the body, needs fitness. Exercise strengthens the body, mental exercises develop the brain. 30 days of useful exercises and educational games for the development of memory, concentration, intelligence and speed of reading will strengthen the brain, turning it into a tough nut to crack.

Money and the mindset of a millionaire
Why are there problems with money? In this course, we will answer this question in detail, look deeper into the problem, consider our relationship with money from a psychological, economic and emotional point of view. From the course you will learn what you need to do to solve all your financial problems, start accumulating money and invest it in the future.
Knowledge of the psychology of money and how to work with it makes a person a millionaire. 80% of people with an increase in income take more loans, becoming even poorer. On the other hand, self-made millionaires will make millions again in 3-5 years if they start from scratch. This course teaches competent distribution of income and cost reduction, motivates to study and achieve goals, teaches to invest and recognize a scam.

Our teaching division table simulator in cartoons is designed for students of grade 2, grade 3, grade 4 of the school, developed on the basis of a unique method of studying the division of two-digit numbers into single-digit numbers, created to help children master division techniques using colorful pictures and melodies from famous cartoons.
Through the game Division tables in cartoons you can quickly learn the child the table of division by 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 and other numbers, while the math lesson will be interesting, funny and exciting, the student will firmly consolidate his knowledge of dividing numbers and have a great time considering the characters of your favorite cartoons. The division of numbers in the simulator is accompanied by watching cartoon characters and listening to music.
Game division table in cartoons
This training simulator for the division table is designed for students who have difficulty with mathematics and would like to improve their knowledge of multiplication and division in a more playful way, would like to consolidate their knowledge, while playing, looking through pictures and listening to funny music from domestic and foreign cartoons. films.The present division table game will help students better deal with such examples after 5 minutes of using the simulator, while fixing both the division table and the multiplication table in the game. Excellent students in mathematics will not be hurt by additional training in mathematics knowledge before independent or test work on this subject in a comprehensive school.
In the simulator program, the student can choose the interface language: Russian, Ukrainian or English. The game was created in the Borland Delphi programming environment.
On this page it is possible to download division table program.
At every stage Division tables 9 examples and 9 answer options are offered, with each completed example the hidden picture from the cartoon is partially opened, and if there are no division errors in the game, it will open completely and a fragment of the melody from the corresponding cartoon will be played. If there are division errors in the simulator, the transition to the repeated passage of the tour occurs, and a new picture of the animated film is generated in this case.
Trainer division table in cartoons
The last final round of the multiplication and division table simulator in cartoons consists of 25 examples per division and the corresponding number of answers, while pictures with melodies and examples are randomly displayed in a scatter, thus complicating division and multiplication in the game simulator. The simulator game can be downloaded for free below on this page.Correct answers in the Table of divisions in cartoons are marked in green, their number is displayed on the equalizer on the right (vertical bar), incorrect answers are marked in red and their number is displayed on the equalizer on the left - a vertical bar of the game simulator for division of numbers.
The educational game simulator according to the division table is suitable for grade 3 students, contains many examples of division and multiplication of numbers, stores 27 hidden frames of cartoons and the same number of melodies from the best cartoons of Russia, Ukraine and abroad. The goal of a training session with the simulator is to go through all the stages of the game, open images, listen to music from your favorite cartoons and come to victory without making mistakes in the division examples.
Operating system: Windows 98 / ME / 2000 / XP / 2003 / Vista / 7/8
Interface language: Russian, Ukrainian, English
school director, teacher of computer science and mathematics Andreychuk Nikolai Vasilievich.
Date of creation: 14.12.2012.
Our cartoon division table educational game and simulator is free to download. When placing a division table simulator or its description on other sites, the presence of a direct link to this author's page is a prerequisite for the developer!
Banner code for the Obuchonok website:
![]()
Despite the fact that mathematics seems difficult to most people, this is far from the case. Many mathematical operations are fairly easy to understand, especially if you know the rules and formulas. So, knowing the multiplication table, you can quickly multiply in your mind. The main thing is to constantly train and not forget the rules of multiplication. The same can be said about division.
Let's take a look at the division of integers, fractional and negative. Let's remember the basic rules, techniques and methods.
Division operation
Let's start, perhaps, with the very definition and name of the numbers that are involved in this operation. This will greatly facilitate further presentation and perception of information.
Division is one of four basic mathematical operations. Its study begins in primary school... It is then that the children are shown the first example of dividing a number by a number, the rules are explained.

The operation involves two numbers: the dividend and the divisor. The first is the number to be divided, the second is the number to be divided by. The division is the quotient.
There are several designations for recording this operation: ":", "/" and a horizontal bar - write in the form of a fraction, when the dividend is at the top, and the divisor is below, below the line.
Rules
When studying a particular mathematical operation, the teacher is obliged to acquaint students with the basic rules that should be known. True, they are not always remembered as well as we would like. This is why we decided to brush up on four fundamental rules a bit.
Basic rules for dividing numbers that you should always remember:
1. You cannot divide by zero. This rule should be remembered first.
2. You can divide zero by any number, but in the end there will always be zero.
3. If the number is divided by one, we get the same number.
4. If the number is divided by itself, we get one.
As you can see, the rules are pretty simple and easy to remember. Although some may forget such a simple rule as the impossibility or confuse it with dividing zero by a number.
by the number
One of the most useful rules is the attribute by which the possibility of division is determined. natural number to another without a remainder. So, there are signs of divisibility into 2, 3, 5, 6, 9, 10. Let's consider them in more detail. They make it much easier to perform operations on numbers. We also give an example of dividing a number by a number for each rule.

These rules-signs are widely used by mathematicians.
Divisibility by 2
The easiest sign to remember. A number that ends in even digit(2, 4, 6, 8) or 0, always divisible by two. Pretty easy to remember and use. So, the number 236 ends in an even digit, which means that it is evenly divisible by two.
Let's check: 236: 2 = 118. Indeed, 236 is divisible by 2 without a remainder.
This rule is best known not only to adults, but also to children.
Divisibility by 3
How to properly divide numbers by 3? Remember the following rule.
A number is evenly divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is a multiple of three. For example, let's take the number 381. The sum of all the digits will be 12. This is three, which means it is divisible by 3 without a remainder.
Also check given example... 381: 3 = 127, so everything is correct.

Divisibility of numbers by 5
Everything is also simple here. You can divide by 5 without a remainder only those numbers that end in 5 or 0. For example, take numbers such as 705 or 800. The first ends with 5, the second - by zero, therefore they are both divisible by 5. This is one of the simplest rules, which allows you to quickly divide by a single number 5.
Let's check this feature on the following examples: 405: 5 = 81; 600: 5 = 120. As you can see, the sign is valid.
Divisibility by 6
If you want to know if a number is divisible by 6, then you first need to find out if it is divisible by 2, and then by 3. If so, then the number can be divided without a remainder by 6. For example, the number 216 is divisible by 2 , since it ends with an even digit, and with 3, since the sum of the digits is 9.
Let's check: 216: 6 = 36. The example shows that this feature is valid.
Divisibility by 9
Let's also talk about how to divide numbers by 9. This number divides the sum of digits which is a multiple of 9. Similar to the rule of division by 3. For example, the number 918. We add all the numbers and get 18 - a multiple of 9. So it is divisible by 9 without remainder.
Let's solve this example for verification: 918: 9 = 102.
Divisibility by 10

The last sign worth knowing. Only those numbers that end in 0 are divisible by 10. This pattern is quite simple and easy to remember. So, 500: 10 = 50.
These are all the main signs. By remembering them, you can make your life easier. Of course, there are other numbers for which there are divisibility criteria, but we have identified only the main ones.
Division table
In mathematics, there is not only a multiplication table, but also a division table. Having learned it, you can easily perform operations. In essence, the division table is the reverse multiplication table. It is not difficult to compose it yourself. To do this, rewrite each row from the multiplication table in this way:
1. We put the product of the number in the first place.
2. Put the division sign and write down the second factor from the table.
3. After the equal sign, write down the first factor.
For example, take the following line from the multiplication table: 2 * 3 = 6. Now rewrite it according to the algorithm and get: 6 ÷ 3 = 2.
Quite often, children are asked to compile a table on their own, thus developing their memory and attention.
If you do not have time to write it, then you can use the one presented in the article.

Division types
Let's talk a little about the types of division.
To begin with, you can highlight the division of integers and fractional numbers. Moreover, in the first case, we can talk about operations with integers and decimal fractions, and in the second - only about fractional numbers. In this case, the fraction can be either a dividend or a divisor, or both at the same time. due to the fact that operations on fractions differ from operations on integers.
Based on the numbers that are involved in the operation, two types of division can be distinguished: into single-digit numbers and into multi-digit ones. The simplest division is considered to be a single-digit number. Here you will not need to carry out cumbersome calculations. In addition, a division table can help a lot. Divide into others - two-, three-digit numbers - is harder.
Consider examples for these types of division:
14: 7 = 2 (division by a single number).
240: 12 = 20 (division by a two-digit number).
45387: 123 = 369 (division by a three-digit number).
The latter can be distinguished by division, in which positive and negative numbers participate. When working with the latter, you should know the rules by which the assignment to the result of a positive or negative value occurs.
When dividing numbers with different signs(the dividend is a positive number, the divisor is negative, or vice versa) we get a negative number. When dividing numbers with one sign (both the dividend and the divisor are positive or vice versa) - we get a positive number.
For clarity, consider the following examples:
Division of fractions
So, we have sorted out the basic rules, gave an example of dividing a number by a number, now let's talk about how to correctly perform the same operations with fractions.

Even though dividing fractions may seem like a daunting task at first, it's actually not that hard to work with. Dividing a fraction is done in much the same way as multiplying, with one difference.
In order to divide a fraction, you must first multiply the numerator of the dividend by the denominator of the divisor and fix the result as the numerator of the quotient. Then multiply the denominator of the dividend by the numerator of the divisor and write the result as the denominator of the quotient.
You can make it easier. Rewrite the divisor's fraction by swapping the numerator with the denominator, and then multiply the resulting numbers.
For example, let's split two fractions: 4/5: 3/9. To begin with, flip the divisor, we get 9/3. Now we multiply the fractions: 4/5 * 9/3 = 36/15.
As you can see, everything is pretty easy and no more complicated than dividing by a single digit. Examples are not easy to solve, if you do not forget this rule.
conclusions
Division is one of the mathematical operations that every child learns in elementary school. There are certain rules that you should know, techniques that facilitate the implementation of this operation. Division can be with a remainder and without, there is a division of negative and fractional numbers.
It is quite easy to remember the peculiarities of this mathematical operation. We have sorted out the most important points, considered more than one example of dividing a number by a number, even talked about how to work with fractional numbers.
If you want to improve your knowledge of mathematics, we advise you to remember these simple rules. In addition, we can advise you to develop your memory and mental arithmetic skills by completing math dictations or simply trying to calculate the quotient of two random numbers orally. Believe me, these skills will never be redundant.