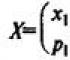Presentation for a history lesson "the first ruler of a unified China." Presentation for a history lesson "the first ruler of a united China" Presentation on the topic of the first ruler of a united China
Sections: History and social studies
- To lead students to understand the significance of the formation of a unified China and the inventions of the Chinese.
- Continue developing the skills to build a story based on text and video materials; skills of relating historical facts over time.
- To cultivate respect for the work and culture of ancient people.
Equipment:
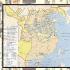
- Map "Growth of the territory of states in antiquity."
- Video cassette “Great Wonders of the World. Great creations of people." Reader's Digest. Video fragment “The Great Wall of China”.
- Presentation “The First Ruler of a United China.”
- Handout:
a) cards for describing the film;
b) fragments of workbooks;
c) contour maps “India and China in ancient times.” - Tokens are “dragons”.
During the classes
I. Organizational moment.
We continue our study of Ancient China. Today in the lesson we will learn what the ruler Qin Shihuang became famous for. Write down the topic of the lesson. 1st slide.
II. Repetition.
They say that in ancient times, the Chinese queen drank tea on the open terrace of her palace. Suddenly, from a branch of a mulberry tree that bent over the terrace, a butterfly cocoon fell into the tea. The queen tried to remove it from the bowl with her long painted nail, but a thin thread caught on the nail. The queen pulled the thread, and the cocoon, steamed in hot tea, began to unwind. Five thousand years have passed since then.
Let's remember the history of other ancient peoples. 2nd slide.
Now let's see if we were wrong. 3rd slide.
Tell us and show on the map where China is?
Why was the Yellow River called "China's grief"?
How and what was written in during the time of Confucius?
How should polite Chinese behave, according to the sage Confucius?
(Students' answers and teacher's comments).
To move on to studying a new topic, let's remember the dates. What happened?
| 1500 BC | Conquests of Pharaoh Thutmose |
| 612 BC | Destruction of Nineveh - the capital of Assyria |
| 3rd century BC | Uniting India into a single state |
| More than 2 million years ago | The emergence of man |
| 40 thousand years ago | The emergence of "Homo sapiens" |
| 525 BC | Capture of Egypt by the Persians |
| 10 thousand years ago | The emergence of agriculture and cattle breeding |
| 1792-1750 BC. | Hammurabi's reign in Babylonia |
| 538 BC | Capture of Babylon by the Persians |
| 3000 BC | Formation of a single state in Egypt |
| Around 2600 BC | Construction of the Cheops pyramid in Egypt |
| 221 BC | The unification of China into a single state. |
For every correct answer - a token!
III. New topic.
Write in your notebook: 221 BC. - unification of China into a single state. Draw a timeline:
What came first: the unification of India by Ashoka or the unification of China?
How much earlier? (For 79 years). (Work at the board).
1. Politics of Qin Shihuang.
The ruler of one of the Chinese states called Qin united all of China under his rule. He began to call himself Qin Shihuang, i.e. "The First Lord of Qin." In his decree, he announced that his son would be called the “Second Lord of Qin,” then a third would rule—and so on, tens of thousands of his heirs. Qin Shihuang declared that peace would now last forever. The capital of China became the city of Xianyang. See map on page 101. However, after stopping the wars within China, Qin Shi Huang began to launch campaigns against neighboring countries.
China "gradually ate up foreign territory like a silkworm eats leaves." In the north, China's opponents were the nomadic tribes of the Huns.
Which tribes are called nomadic? (Working with a dictionary).
In order to retain the lands conquered from the Huns and protect trade routes from raids, the construction of the Great Wall of China began. Pay attention to the map.
Watch the film carefully and try to answer the questions as the film progresses. If you don’t have time to write something down, don’t distract your comrades. After watching, you can help each other.
2. The Great Wall of China. Watching a video clip – 7 minutes.
Work on card No. 1.
Physical education minute:
- Close your eyes as tightly as possible, and now make them look as surprised as possible. (2-3 times).
- And now, guys, stand up,
They quickly raised their hands up.
Turned right, left,
Sit down quietly and get back to business!
Conversation on table questions. Additions and clarifications. Pay attention to page 106 of the textbook, read and write down dictionary word in the margin. Loophole- a shooting hole in the wall of the fortress.
3. Indignation of the people.
In order to maintain a huge army, a lot of money was required. Taxes became higher and higher. To prevent people from grumbling, they were kept in constant fear. For the slightest offense, a person was beaten on the heels with a bamboo stick, his nose was cut off, and he could be boiled in a cauldron. For the misdeed of one person, all his relatives were punished. Qin Shihuang became more and more arrogant and cruel, and came up with new terrible executions. But even the mighty emperor himself was powerless against time. The skin on his face wrinkled like a baked apple, and the slits of his eyes became even narrower. “Everything that is born between heaven and earth is mortal,” said one ancient sage. But Shi Huang considered himself the one and only, hoping that fate would make an exception for him. He forbade talking about death, gathered scientists and magicians, ordering them to find a means that would grant immortality. Scientists went through all the forests, but only one of them brought an unusual mushroom - red with white dots - at the appointed time. The scientist was ordered to taste the mushroom, and he died in terrible agony.
What kind of mushroom was this? (Amanita).
Someone told the emperor about the elders who had not done a single evil deed in their entire lives, who were known for this as righteous people, and who lived 200 and 300 years. The elder was brought to the ruler, but when the elder opened his mouth, everyone saw that he had no tongue. His tongue was cut out 30 years ago because he condemned the ruler for cruelty. The emperor and his adviser Li Si ordered to burn all the books and execute 460 scientists, bury alive in the ground those who thought that life had previously been better than under him. In the same year, Li Si was torn apart by the chariots, as his actions caused condemnation.
The emperor became completely decrepit. His nose sunken and his voice became hoarse, like a jackal’s. That's when a scientist named Lu Shen came to the palace. He said: “Let not a single official know which of the 37 palaces you live in, not a single servant enters the chamber where you sleep, and let no one see you eat - this is the secret of immortality.” The terrible years of the reign of the invisible man began. Horror gripped the inhabitants of the Celestial Empire. Never before have the emperor's laws been carried out so thoroughly.
One day, a suffocating smell appeared in the Shaqiu Palace. When the stench became unbearable, it was decided to open the door. There was the corpse of the ruler of the Celestial Empire. Qin Shihuang was buried in a huge underground tomb, all his wives who did not bear him children were killed and buried with the deceased. In the tomb, 6 thousand warriors the size of a man in full armor were placed in a row - to guard the peace of their ruler. See page 109 of the textbook. The afterlife army, armed with swords, spears, and bows, was supposed to guard the entrance to the huge tomb on the surface of the earth.
Qin Shihuang's son began his reign by executing his brothers. The patience of the people was exhausted, armed with sticks and hoes, people gathered in detachments, warriors went over to the side of the rebels. The heirs of Qin Shihuang failed to rule “tens of thousands of generations”; the people overthrew the hated oppressors; the new rulers had to make concessions to the people and alleviate their situation.
IV. Primary control.
Show on the map China and its main rivers, the Great Wall and the Great Silk Road.
What good and what bad did Qin Shi Huang's rule bring to China?
The Great Wall of China was built to protect against which tribes?
Talk about the Great Wall using the text on the card.
V. Consolidation.
Work on card No. 2. Sample – 16th slide.
The dragon in China is a symbol of goodness, peace and prosperity!
Applications.
Card number 1. The Great Wall of China.
Card No. 2.
Which sentences talk about India and which ones talk about China? Write the sentence numbers in the appropriate columns.
- In this country, the entire population was divided into closed hereditary groups - castes.
In this country, many things were invented and discovered that are successfully used to this day: sugar, cotton fabrics, chess.
In 221 BC. this country was united by the ruler of the Qin kingdom.
In this country, many things were invented and discovered that are successfully used to this day: paper, silk, rice, tea, compass, porcelain, gunpowder.
The inhabitants of this country tamed elephants and worshiped snakes and monkeys.
To protect against enemy invasions, a wall about 5,000 km long was built on the border of this country.
In the 6th century BC. Buddha, the founder of a new religion, lived in this country.
The rules of behavior of people and government of the country were based on the teachings of the philosopher Confucius.
Card No. 3. Outline map “India and China in ancient times.”
Write the names of the main rivers of India and China.
Label and label the Himalayan mountains.
Circle the boundaries of the largest state in India (3rd century BC).
Outline the boundaries of the Chinese state under Qin Shihuang (3rd century BC).
Mark and write the name of the Great Wall of China on the map
Use the maps on pages 92 and 101 in your textbook for reference.
Literature:
- Supplement to the newspaper “First of September”. Story. - No. 39, 1997.
Araslanova O.V. Lesson developments on the history of the Ancient World. – M.: VAKO, 2007.
Goder G.I. Workbook on the history of the Ancient World. – M.: Education, 2002.
Vigasin A.A., Goder G.I., Sventsitskaya I.S. History of the Ancient World: textbook for 5th grade in general education institutions. – M.: Education, 2005.
Merzlova V.S. Quiz on the history of the ancient world and the Middle Ages. – Minsk: Narodnaya Asveta, 1969.
Nemirovsky A.I. A book to read on the history of the ancient world. – M.: Education, 1990.
Russian historical magazine "Rodina". - No. 10, 2004.
First overlord
united China

Show
on the map:
1.Country China
2. Two main rivers of China. Name them
3. Tell us about the climate in China

In China to this day they treat with great
Respect for the ancient sage
Named Confucius.
- What did he teach?
- Whom Confucius considered noble, i.e. a worthy person?
- What sayings of Confucius do you remember?
- What advice did Confucius give to rulers?

Why did the Chinese believe that Heaven fulfills the ruler's requests?
What were the religious beliefs of the Chinese?
Does this coincide with our ideas about a well-mannered person?
How should polite Chinese behave?


Egypt
China
Babylon
What did a book look like in Babylon?
And in Ancient Egypt?
Clay
Bamboo
Papyrus


Examination
historical

§ 23, paragraph 1
§ 23, paragraph 2 (map p. 101)
Find on the map:
Capital of united China
Coast of the South China Sea,
occupied by the Huns
Great Wall of China

Until 3rd century BC .existed in China 7 kingdoms
IN 221 g . after 200 years of wars, China was unified Qin Shihuang.
After the end of the internal wars, he began campaigns of conquest against his northern neighbors.
Qin Shihuan.
Ancient Chinese
drawing on silk.

The more lands the Qin state annexed to its territory, the more difficult it was to keep them under control.
? THINK - WHY?
Soon from the north China began to be raided Huns.

To protect against the Huns, the emperor ordered the construction THE GREAT WALL OF CHINA .
This is the only monument that can be seen from MOON !!!
Wall length 6500km.


1. Creation of a large army
TAXES collected from farmers increased sharply

Internal order in Ancient China
2. Thousands of youths ran away from their homes to hide from army recruitment
3. Severe punishments were used against those who were dissatisfied (beating with sticks, cutting off noses, etc.)
4. For the most insignificant act, not only the offender, but also his relatives and neighbors were fiercely punished

Internal order in Ancient China
5. By order of the ruler there were ancient books burned , hundreds were massacred who revered the teachings of Confucius
6. The ruler of China lived in constant fear for his life

After his death, the emperor was buried in a grandiose
tomb.
An entire army had to guard the posthumous peace of the first lord of Qin






What's good and what's bad
brought to the people
China's unification of the country?
Increased taxes, military service periods, loss of life, severe punishments
It became easier to fight the nomads

Chinese heritage
They made a number of inventions using 1000 years earlier than in Europe:
paper, typography, silk, powder,
compass ,
firearms, metal coins and porcelain.

Homework:
§ 23 , questions and tasks for the paragraph

D/Z check:
- Describe the geographical location of Ancient China, show the main objects on the map.
- Talk about Chinese writing. How do Chinese books differ from books of other ancient peoples?
- Talk about the beliefs of the ancient Chinese.
- What rules of decency should a well-bred Chinese man observe?

Exercise: fill in the gaps in the text.

First overlord
united China

Assignment: paragraph 2 “Wars of Conquest”
Question:
- What territories did Qin Shihuang's campaigns cover? What attracted the conqueror to these lands?
- Working with the atlas on page 16.

Exercise: Fill in the blanks in the text “The Great Wall of China”
__1__, __2__ and __3__. _4_, __5__. _6_ and _7_. ___8___. ___9___. __10__.

- Construction took 10 years.
- Approximately 2 million 300 thousand people were involved in construction.
- 400,000 people are buried here.
- The length of the wall with branches is more than 4000 km.

Exercise: paragraph 4 "Indignation of the people."
Questions:
1. Reasons for the people's indignation?
2. Think about whether Qin Shi Huang ruled as Confucius taught?
3. Why was the reign of Qin Shihuang’s heirs short-lived?

Working with a contour map:
- Circle the border of the ancient Chinese kingdoms of the 12th-6th centuries. BC.
- Label the largest kingdoms of Ancient China in the 6th - 3rd centuries. BC.
- Indicate with arrows the raids of the Huns.
- Highlight the Great Wall of China with a colored line.
- Show the borders and territories of the Qin and Han empires.



3. The first ruler of unified China was:
- a) Confucius;
- b) Qin Shihuang;
- c) Sun.

4. The name of the great Chinese sage who lived 5 centuries BC:
- a) Confucius;
- b) Qin Shihuang;
- c) Sun.

5. Select the concept that this definition corresponds to. Title of the first ruler of unified China:
- a) Qin Shihuang - Son of Heaven
- b) Qin Shihuang - First Lord of Qin
- c) Qin Shihuang - Eternal Lord of Qin

In 1974, Chinese peasant Yan Ji Wang
I decided to dig a well on my property.
At a depth of 5 meters, Yan Jiwan came across
on a full-length statue of an ancient warrior.
One of the Chinese states
called Qin. In 221
BC. its ruler
smashing your opponents
one by one, united
all of China under its control
power. He began to call
himself Qin Shihuang (
First Lord of Qin)
Qin Shihuang
Unification of China:
UNIFICATION OF CHINA:In his decree he
announced that his son
it will be
be called
" Second
Lord of Qin"
then the third, etc. Wars of conquest:
When the wars ended
inside China, Qin
Shihuang started
go hiking
against neighboring countries.
In the south he was attracted
lands on the coast
South China Sea. Wars of conquest:
The population, having learned about
invasion, went into
mountains, taking away their
belongings and livestock.
Cultivated land
the Chinese selected for
their warriors, creating
military settlements. Wars of conquest:
In the north by opponents
China had tribes
the Huns, who
wandered with their
in herds. They lived in
light felt
tents, ate
milk and boiled
meat.
The great Wall of China
THE GREAT WALL OF CHINA The great Wall of China:To hold
recaptured from the Huns
land and secure
trade routes from them
raids began
construction of the Great
Chinese wall. The great Wall of China:
Length –
5000 km
Height – 7 m
Width - close
could drive 5
riders and 10
foot soldiers, on
they could
separate 2
carts
The great Wall of China:
THE GREAT WALL OF CHINA:The height of the wall was as high as a 2-3 storey building. In the wall
there are viewing slots and
loopholes. In some places
towers rose.
They lived at the bottom of the tower
the soldiers guarding her,
and in the upper one they carried
service.
The great Wall of China:
THE GREAT WALL OF CHINA:If the warrior noticed
danger, he kindled
tower-mounted
brushwood. I saw him
another guard too
set fire to brushwood. Squad
warriors hurried to
help.
Formation of the Chinese Empire
FORMATION OF THE EMPIRE OF CHINATomb of Qin Shihuang
TOMB OF QIN SHIHUANGThe tomb is guarded by 8,000 thousand terracotta
warriors For some reason they don't have weapons in their hands
Construction of the Great Wall of China
CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREAT WALL OF CHINA During the reign of Qin Shihuang in China:-United
monetary
system.
-One system
measures and weights.
-Census
population.
-Good roads.
The people's discontent was caused by:
1. Burden of taxes
2.Cruel treatment by officials
towards the peasants
3.The death of many innocent people,
including those from the emperor's entourage
End of the Qin Empire
END OF THE QIN EMPIREQin Shihuang was buried in a huge underground tomb, killed and
They buried all his wives who did not bear him children with the deceased.
In the tomb, 6 thousand warriors were placed in a row, the height of a full man.
weapons - to protect the peace of their ruler.
- Perform testing
- 1-a 9-b
- 2-in 10-in
- 3- b 11 - b
- History of the Ancient World, 5th grade
- Lesson topic:
- How did the unification of China happen?
- What were the wars of conquest like?
- Find out what the Great Wall of China was and why it was built;
- How did the Chinese people live and why did they revolt?
- Today you will learn:
- Unification of China.
- Wars of conquest.
- The great Wall of China.
- People's outrage.
- Qin Shihuang
- Unification of China:
- One of the Chinese states was called Qin. In 221 BC. its ruler, having defeated his rivals one by one, united all of China under his rule. He began to call himself Qin Shihuang (First Lord of Qin)
- In his decree, he announced that his son would be called “Second Lord of Qin”, then the third, etc.
- When the wars within China ended, Qin Shihuang began campaigning against neighboring countries. In the south, he was attracted by the lands on the coast of the South China Sea.
- Wars of conquest:
- The population, having learned about the invasion, went to the mountains, taking away their belongings and livestock. The Chinese took the cultivated land for their warriors, creating military settlements.
- Wars of conquest:
- In the north, China's opponents were the Huns, who roamed with their herds. They lived in light felt tents and ate milk and boiled meat.
- Wars of conquest:
- In order to retain the lands conquered from the Huns and protect trade routes from their raids, the construction of the Great Wall of China began.
- The great Wall of China:
- Length – 5000 km
- Height – 7 m
- Width – 5 horsemen and 10 foot soldiers could ride side by side, 2 carts could pass each other on it
- The great Wall of China:
- The height of the wall was as high as a 2-3 storey building. There are viewing slots and loopholes in the wall. Towers rose in places. At the bottom of the tower lived the soldiers guarding it, and at the top they served.
- If a warrior noticed danger, he lit the brushwood on the tower. Another guard saw him and also set fire to the brushwood. A detachment of warriors rushed to the rescue.
- Read the material on pages 106-108 and answer the questions:
- 1) Why was the population dissatisfied with the policy?
- 2) What did they do to express their dissatisfaction?
- People's outrage:
- People's outrage:
- What did China give to the world?
- The ancient Chinese were very talented.
- They made a number of inventions using 1000 years earlier than in Europe:
- paper, printing, silk, gunpowder, compass, firearms, metal coins and porcelain.
- Questions on page 108
- Let's summarize the lesson:
- Paragraph 13 – 23, prepare for the test, questions on page 110.
- Homework:
- http://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D6%E8%ED%FC_%D8%E8%F5%F3%E0%ED%E4%E8
- http://images.rambler.ru/search?query=%D0%92%D0%B5%D0%BB%D0%B8%D0%BA%D0%B0%D1%8F+%D0%9A%D0%B8 %D1%82%D0%B0%D0%B9%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%B0%D1%8F+%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B0
- Antonenkova Anzhelika Viktorovna
- History teacher, Municipal Educational Institution Budinskaya Secondary School
- Tver region