The overall characteristic of single-celled animals or simplest. Overall characteristic of unicellular
To fabrication Simplestapply unicellular animals. Some species form colonies.
The cells of the simplest has the same structure of the structure as a cell of a multicellular animal: is limited to the shell, the inner space is filled with cytoplasm, in which the kernel (kernel), organoids and inclusions are located.
The cell shell in one species is represented by an outer (cytoplasmic) membrane, in the other - membrane and pellicula. Some groups of simplest form a shell around them. The membrane has a typical structure for eukaryotic cell: consists of two layers of phospholipids, in which the proteins are "immersed" into different depths.
The number of nuclei is one, two or more. The shape of the core is usually rounded. The kernel is limited to two membranes, these membranes are permeated by pores. The internal content of the nucleus is nuclear juice (karyoplasm) in which chromatin and nuclei are located. Chromatin consists of DNA and proteins and is an interphase form of chromosomes (decondested chromosomes). The nuclei consist of RRNA and proteins and are a place in which the ribosomes subunits are formed.
The outer layer of cytoplasm is usually brighter and dense - ectoplasm, internal - endoplasm.
In the cytoplasm there are organides, characteristic of both multicellular animal cells and organoids, characteristic of only this group of animals. Organoations of the simplest, common with organoid cells of a multicellular animal: mitochondria (Synthesis of ATP, oxidation of organic substances), an endoplasmic network (transport substances, synthesis of various organic substances, compartmentalization), a complex of the Golges (accumulation, modification, secretion of various organic substances, carbohydrate and lipid synthesis , the place of formation of primary lysosomes), lysosomes (splitting of organic substances), ribosomes (protein synthesis), a cell center with centrioles (the formation of microtubules, in particular, microtubules of the separation of division), microtubule and microfilaments (cytosketee). Organoations of the simplest, characteristic only for this group of animals: stigma (light perception), tricotters (protection), accosateness (support), contracting vacuoles (osmor regulation) and other photosynthesis organides that are available in vegetable flagellations are called chromatophores. Organo motion of the simplest are represented by pseudopodies, cilia, flavors.
Food - heterotrophic; In vegetable harness, the autotrophic may be mixotrophic.
Gas exchange takes place through a cellular shell, the overwhelming majority of the simplest - aerobic organisms.
The response to the effects of the external environment (irritable) is manifested in the form of taxis.
Upon the occurrence of adverse conditions, most of the simplest form cysts. Insisting is a way to experience adverse conditions.
The main method of reproduction of the simplest - the most powerful reproduction: a) the division of the mother's cell into two subsidiaries, b) the division of the mother's cell to the set of subsidiaries (schistonium), c) boring. The basis of the most powerful reproduction is mitosis. A number of species has a sexual process - conjugation (infusoria) and sexual reproduction (disputes).
Habitat environment: marine and fresh reservoirs, soil, plant, animal and human organisms.
Classification of simplest
- Fitness simplest, or unicellular (Protozoa)
- Sarcomastigophora type (Saromastigophora)
- Mastigophora Zatigophora
- Class of vegetable harness (phytomastigophorea)
- Class Animals Zoomastigophorea
- Subtype of fallen (OPALINATA)
- Sarcodina subtype (Sarcodina)
- Class of Cartoon (Rhizopoda)
- Radiolarian class, or Radiolaria (Radiolaria)
- Solnezhnik class (Heliozoa)
- Mastigophora Zatigophora
- Type of Apicplexa (Apicomplexa)
- Perkinsey class (Perkinsea)
- Sporozoea class (Sporozoea)
- MIXOPRIROIDI TYPE (MYXOZOA)
- MIXOSPOREY Class (Myxosporea)
- Actinosporea class (Actinosporea)
- Microspora type type
- Infusoria type (Ciliophora)
- Class Classified Infusoria (Ciliata)
- Class Suspending Infusoria (Suctoria)
- Labyrinthly Type (Labirinthomorpha)
- Ascetosporah type type (Ascetospora)
- Sarcomastigophora type (Saromastigophora)
The simplest appeared about 1.5 billion years ago.
The simplest belongs to primitive unicellular eukaryotas (Eucariota's talent). Currently is considered to be generally recognized that eukaryotes occurred from prokaryotes. There are two hypotheses of the origin of eukaryotes from prokaryotes: a) subtestic, b) symbiotic. According to the succesive hypothesis, membrane organoids arise gradually from the plasmalemma of prokaryotes. According to a symbiotic hypothesis (endosimbiotic hypothesis, symbiogenesis hypothesis), the eukaryotic cell occurs as a result of a series of symbiosis of several ancient prokaryotic cells.
This reference book contains all theoretical material at the rate of biology required for the delivery of the USE. It includes all the elements of the content being checked by control and measuring materials, and helps to summarize and systematize knowledge and skills for the course of the average (full) school.
Theoretical material is set out in a brief, accessible form. Each section is accompanied by examples of test tasks, allowing you to test your knowledge and degree of preparedness to the attestation exam. Practical tasks comply with the format of the USE. At the end of the allowance, answers are answered to tests that will help schoolchildren and applicants check themselves and fill the existing gaps.
The manual is addressed to schoolchildren, applicants and teachers.
Reproduction of infusoria It happens both cans with dolls and fellow ways. Under the bunch of reproduction there is a longitudinal division of the cell. With a sexual process between two infusories, a cytoplasmic bridge is formed. Polyploid (large) kernels are destroyed, and diploid (small) kernels are divided by meyosis with the formation of four haploid cores, three of which perishes, and the fourth is divided by half, but already mitosis. Two cores are formed. One is stationary and more - migrating. Then there is an exchange of migrating nuclei between infusories. Then the stationary and migrated kernel merge, the individuals are diverged and a large and small kernel are formed in them.
A1. Taxon, which combines all the simplest, called
1) Kingdom
2) Preciousness
A2. NO protozoa
2) organoids 4) sexual reproduction
A3. With full oxidation of 1 glucose molecule, Ameba produces ATP in quantity
1) 18 g / mol 3) 9 g / mol
2) 2 g / mol 4) 38 g / mol
1) Ameba protea 3) trypanosoma
2) Evglen green 4) radolar
A5. Through the contractive vacuole in the infusoria occurs
1) Deleting Solid Vital Products
2) Isolation of liquid products of life
3) removal of genital cells - Games
4) Gas exchange
1) blood mosquito 3) mosquito larva
2) saliva mosquito 5) eggs mosquito
A7. Mascular multiplication of malaria plasmodium occurs in
1) human erythrocytes
2) Erythrocytes and Komara's stomach
3) man leukocytes
4) Erythrocytes and human liver cells
A8. Which of the organoids is absent in cages of infusories?
1) kernel 3) mitochondria
2) Chloroplasts 4) Golgi Device
A9. What is common between Evglen and Chlorella?
1) presence in glycogen cells
2) the ability to photosynthesis
3) anaerobic breathing
4) the presence of flagella
A10. Among the infusories are not found
1) heterotrophic organisms
2) aerobic organisms
3) autotrophic organisms
A11. Most hardly arranged
ameba ordinary 3) malaria plasmodium
evglen green 4) infusor-shill
A12. When cooling, other unfavorable conditions freely living simplest
1) form colonies 3) form disputes
2) Actively move 4) form cysts
Part B.
IN 1. Choose the simplest leading free lifestyle
1) Infusoria Stacker 4) Giardia
2) Amebe Prota 5) Stylonichia
3) Tripanosoma 6) BALANDIDY
AT 2. Relate the representative of the simplest with a sign that he has
Unicellular or simplest. General characteristic "class \u003d" img-responsive img-thumbnail "\u003e
Part FROM
C1. Why do the aquarists grow the culture of infusories on milk?
C2. Find the errors in the text given, correct them, specify the number of the offers in which they are made. 1. The simplest (unicellular) organisms dwell only in fresh waters. 2. The cell of the simplest is an independent organism, with all the functions of the living system. 3. Unlike cells of multicellular organisms, the cells of all the simplests have the same form. 4. The simplest feed on solid food particles, bacteria. 5. Imaginary food residues are removed through contractile vacuoles. 6. Some simplest chromatophores containing chlorophyll, and are capable of photosynthesis.
| <<< Назад
|
Forward \u003e\u003e\u003e |
Class of badge
Structure. The flagellas have flagellas who serve as organoids of movement and contributing to the seizure of food. There may be one, two or many. The movement of the burning burning in the surrounding water is caused by a whirlpool, thanks to which small particles weighted in water are keen on the base of the flavor, where there is a small hole - a cell mouth leading to a deep-sided channel.
Almost all flagellas are covered with a dense elastic shell, which, along with the developed elements of the cytoskeleton, determines the constant body shape.
Genetic apparatus
Most of the flagellas are represented by one core, but there are also duid (for example, giardia) and multi-core (for example, opalin).
Cytoplasm
It is clearly divided into a thin outer layer - a transparent ectoplasm and a deeper endoplasm.
Method of nutrition. By the method of nutrition, flagellas are divided into three groups. Avtrophic organisms as an exception in the kingdom of animals synthesize organic matter (carbohydrates) from carbon dioxide and water with chlorophyll and solar radiation energy. Chlorophyll is located in chromatophoras similar to the organization with plants plates. Many flagendrians with vegetable food type have special devices that perceive light irritation, - stigma.
Heterotrophic organisms (tribanosoma - the causative agent of a sleepy disease) do not have chlorophyll and therefore can not be synthesized carbohydrates from inorganic substances. Mixotrophic organisms are capable of photosynthesis, but also feed on mineral and organic substances created by other organisms (green enevlen).
Osicore regulatory
And partly the excretory functions are performed in flagella, like sarcodic, contractile vacuoles that are available at free-lived freshwater forms.
Reproduction. The flagellas have sexual and powerful reproduction. The usual shape of the crucible reproduction is a longitudinal division.
Habitat. The flagellas are widespread in fresh water bodies, especially small and contaminated by organic residues, as well as in the seas. Many species parasitize among various animals and humans and thereby bring great damage (triponosomes, intestinal parasites, etc.).
For single-cell, or simplest animals, the body of which morphologically corresponds to one cell, while being with the independent holistic organism with all the inherent functions. The total number of types of simplest exceeds 30 thousand.
Appearance Unicellular animals were accompanied by aromorphosis: 1. Diploidity (double chromosoma set) appeared in a core-bounded core as a structure separating the cells of the cytoplasm cell and creating a specific medium to interact in the diploid chromosome set. 2. An organides that are capable of self-reproduction occurred. 3. Internal membranes were formed. 4. A highly specialized and dynamic internal skeleton appeared - cytoskeleton. b. A sexual process arose as a form of sharing genetic information between two individuals.
Structure. The plan of the structure of the simplest corresponds to the general features of the organization of the eukaryotic cell.
Genetic alpathic Unicellites is represented by one or more nuclei. If there are two cores, then, as a rule, one of them, diploid, is a generative, and the other, polyploid, is vegetative. The generative kernel performs functions related to reproduction. Vegetative kernel provides all the processes of the body's life activity.
Cytoplasm Consideration of light source, devoid of organoids, - extoplasma and the darker inner part containing the main organides - endoplasm.In the endoplasm there are general applications.
Unlike the cells of the multicellular organism, unicellites have special purpose organo. These are organides of motion - falconed - pseudopod; flagella, cilia. There are organo-osmoregulation organides - contractile vacuoles. There are specialized organs providing irritability.
Unicellular with a permanent form of body have permanent digestive organoids: cell funnel, cellular mouth, throat, as well as organoid selection of undigested residues - poroshires.
INunfavorable The conditions of the existence of a core with a small amount of cytoplasm containing the necessary organides are surrounded by a thick multi-layer capsule - a cystic and transitions from the active state to the rest. If you get into favorable conditions, the cysts are "revealed", and the simplest in the form of active and moving individuals.
Reproduction. The main form of reproduction "of the simplest - the most powerful reproduction by mitotic division of the cell. However, the sexual process is often found.
Sarcodic class. or root.
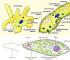
Amoeba
The class includes a detachment of amoeba. A characteristic feature is the ability to form cytoplasmic grown - pseudopodia (falsecakes), thanks to which they move.
Amoeba:1 - core, 2 - cytoplasm, 3 - pseudopodia, 4 - contracting vacuole, 5 - formed digestive vacuol
Structure. Body shape is inconsistent. The hereditary apparatus is represented by one, as a rule, polyploid core. The cytoplasm has a distinct unit on an ecoto and endoplasm, in which general purpose organides are located. Free-lived freshwater forms have simply arranged contracting vacuol.
Method of nutrition. All feeding feeds by phagocytosis, capturing food with false peasants.
Reproduction. For the most primitive representatives of the groups of the AmeB and the shell, AmeB are characterized by only the useless reproduction by mitotic cell division.
Class of badge
Structure. The flagellas have flagellas who serve as organoids of movement and contributing to the seizure of food. There may be one, two or many. The movement of the burning burning in the surrounding water is caused by a whirlpool, thanks to which small particles weighted in water are keen on the base of the flavor, where there is a small hole - a cell mouth leading to a deep-sided channel.
Evglen green:1 - Zhgutichka, 2 - contractile vacuole, 3 - chloroplasts, 4 - core, 5 - contracting vacuol
Almost all flagellas are covered with a dense elastic shell, which, along with the developed elements of the cytoskeleton, determines the constant body shape.
Genetic apparatus Most of the flagellas are represented by one core, but there are also duid (for example, giardia) and multi-core (for example, opalin).
Cytoplasm It is clearly divided into a thin outer layer - a transparent ectoplasm and a deeper endoplasm.
Method of nutrition. By the method of nutrition, flagellas are divided into three groups. Avtotrophny Organisms as an exception in the kingdom of animals synthesize organic substances (carbohydrates) from carbon dioxide and water with chlorophyll and solar radiation energy. Chlorophyll is located in chromatophoras similar to the organization with plants plates. Many flagendrians with vegetable food type have special devices that perceive light irritation - stigma.
Heterotrophic Organisms (tribanosoma - the causative agent of the sleepy disease) do not have chlorophyll and therefore cannot be synthesized carbohydrates from inorganic substances. Mixotrophic Organisms are capable of photosynthesis, but also feed on mineral and organic substances created by other organisms (green eurlen).
Osicore regulatory and Partly excretory functions are performed in flagella, like sarcodic, contractile vacuoles, which are available at free-lived freshwater forms.
Reproduction. The flagellas have sexual and powerful reproduction. The usual shape of the crucible reproduction is a longitudinal division.
Infusoria type, or wilderness
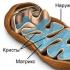
General characteristics. TO The type of infusories includes more than 7 thousand species. Equipment of motion serve cilia. There are two cores: large polyploid - vegetative kernel (macronucleus) and petty diploid - generative kernel (Micronuclease).
Structure. Infusoria can be a variety of shape, in most commonly oval, as a shower infusorium. They are achieved in length 1mm . Outside the body is covered with pellicula. Cytoplasm It is always clearly divided into ecto- and entoderm. In the ectoplasma there are basal cilia tales. Elements of the cytoskeleton are closely connected with basal bodies.
Method of feeding infusoria. IN The front half of the body is a longitudinal excavation - Okamot Vpadina. In the depths of it, an oval hole is a cellular mouth leading to a curved throat, which is supported by a skeletal piping yard system. The throat is opened directly in the endoplasm.
Osorgulatory. Free-lived infusorium-mixed vacuoles.
Infusorian shoe:1 - Cilia, 2 - digestive vacuoles, 3 - small kernel, 4 - large kernel, 5 - cellular, in - cell pharynx, 7 - Poroshitz, 8 - contractive vacuol<
Reproduction. For infusories, the alternation of sexual and powerful reproduction is characteristic. With a bunch of reproduction, the transverse division of infusories takes place.
Habitat. Free-lived infusories are found in fresh waters, and in the seas. A few of them are diverse.
The simplest type includes approximately 25 thousand species of single-cell animals living in water, soil or organisms of other animals and humans. Having morphological similarity in the structure of cells with multicellular organisms, the simplest differs significantly from them in a functionality.
If the cells of the multicellular animal perform special functions, the cell of the simplest is an independent organism capable of exchanging substances, irritability, movement and reproduction.
The simplest are organisms at the cellular level of the organization. In the morphological terms, the protozoa is equal to the cell, but in the physiological represents a whole independent organism. The overwhelming majority of their microscopically small sizes (from 2 to 150 microns). However, some of the now living simplest reaches reach 1cm, and the sinks of a number of fossil cornnels have in diameter up to 5-6 cm. The total number of known species exceeds 25 thousand.
The structure of the simplest is extremely varied, but they all have features characteristic of the organization and function of the cell. The general in the structure of the simplest is the two main components of the body - cytoplasm and the kernel.

Citaplasm
The cytoplasm is limited to the outer membrane, which regulates the flow of substances into the cell. In many simplest, it is complicated by additional structures that increase the thickness and mechanical strength of the outer layer. Thus, the formations of the type of pellicula and shell occur.
The cytoplasm of the simplest usually disintegrates 2 layers - outdoor lighter and tight - ektoplasm and internal, equipped with numerous inclusions - endoplasm.
In the cytoplasm localized organo organides are localized. In addition, a variety of special organelles may be present in the cytoplasm of many simplest. Various fibrillar formations are especially widespread - support and reduced fibers, contracting vacuoles, digestive vacuoles, etc.
Core
The simplest possesses a typical cellular core, one or more. The core of the simplest has a typical two-layer nuclear sheath. The kernel is distributed chromatine material and nucleists. The cores of the simplest are characterized by an exceptional morphological manifold in size, the number of nucleols, the number of nuclear juice, etc.
Features of the variety of simplest
In contrast to somatic cells, multicellular protozoa is characterized by the presence of a life cycle. It is composed of a number of steps next to each other, which in the existence of each species is repeated with a certain pattern.
Most often, the cycle begins the stage of the zygote, which corresponds to the fertilized egg cell. Behind this stage, repeated non-reproduction, carried out by cellular division, follows or repeatedly repeated. Then the sex cells are formed (gemnets), the pair merging of which again gives the zygot.
An important biological feature of many simplest is the ability to incisions. At the same time, the animals are rounded, dumped or draw the organelles of motion, isolated on its surface a dense shell and fall into the state of rest. In the incidental state, the simplest can carry sharp changes in the environment, while maintaining vitality. Upon returning conversational conditions, the conditions of cysts are revealed and the simplest exit of them in the form of active, moving individuals.
According to the structure of organoids of movement and the features of reproduction, the type of simplest is divided into 6 classes. Basic 4 classes: sarcodic, flagella, disputes and infusories.