The value of sound alarm in the life of birds. Acoustic alarm and bird behavior
In nature, everything is interconnected and therefore the behavior of some individuals directly depends on the behavior of others. So, for example, a flock of Kulikov, which feeds on shames, takes off immediately if one kulik rises into the air. And, the warning cry of one of the Guses of the Big Kosik will lead to all birds. Also, duck chasing can attract the spleen, which flies past at a distance. It turns out that the birds have its own language with which they communicate and understand each other. Continuing our cycle of articles about the life of birds (find out here about), we suggest you today just about it and talk ...
Bird language and its meaning for feathered
At the root, they do not correctly fall into the anthropomorphism and try to think the language of animals. Mechanisms of communication in birds are different from communication between people. And, about this difference should not forget. Therefore, it will not correctly think about the fact that the chicken that sees the flying aunt, publishes the threatening sounds because it wants to prevent other chicken chicken in this way. Rather, her cry is an unconscious answer, a natural reaction to the appearance of the enemy. Similar reaction launches the mechanisms of flight from this bird. But, other chicken, who do not see the hawk, but hear the cry of chicken, they still react to him and turn to flight. At the same time, the hawk himself acts as an irritant for them, but the behavior of the first chicken and her cry.
It is noteworthy that, when such a chicken will be shouting in such a situation, which will be in complete loneliness. It turns out that her behavior and screams is the manifestation of unconscious instincts? It is possible that they are unconscious instincts are one of the most important biological devices that allow us to quickly escape from enemies, find food and in general coordinate the actions of your avian community or flocks. This is the important task of the language of animals, which provides all the main parties and aspects of existence - the processes of nutrition, migration, reproduction ...
Therefore, the essence of the language of birds and animals can be explained very simple - this the reaction of one living organism to the stimulus, which is clear to another living organism. And, it is the demonstration of such an irritable that can cause the reaction of another animal. Thus, communication and communication between different animals of one species is formed. A, the stimulus itself, which serves as a binder, serves as a signal or a starting mechanism for such joint actions.
Types of bird sound signals
At the same time, signals that can be used by animals and birds for communication with each other can be the most different. These are trace tags, smells of females, poses, bright stains of coloring. And of course, various sounds that publish birds publish in such a general behavior are of great importance. So, a quiet whistle of the Ryabik (find out how to cook it - look for a recipe) can attract other ripples, and the voice of the fog of quail causes a response of the males of this species. The peak of chicks of Tetherov, who run in thick and high grass, allows their mother to find their own brood, and not get lost and not to disperse.
Tools of birds of birds
The senses that accept sound signals are served by the channels by which the connection between birds is directly communicated, and it is they are the main tools of the animal language.. As a rule, it is usually used those signals that are closely related to the senses and are most developed in this group of animals. For birds - this is vision and rumor, but for mammals - hearing and smell. At the same time, the nature of communication itself should strictly comply with the peculiarities of the biology of the species. So birds, like flying creatures, and the leading public lifestyle should be able to respond to extraneous irritants in a timely manner, which are from them at a high distance, long before the approach to such objects stimuli. Therefore, it is appropriate to assume that
the basis of bird communication is precisely visual stimuli, which are complemented by sound, in those situations where the possibility of visual perception is limited.
Sound reproduction mechanisms in birds
Birds have special sound reproduction mechanisms. They have a tool or mechanical voice, which is closely related to the structures that are on the surface of the body of the bird. Therefore, it is not surprising that often the fastening of birds participates in the production of sound. So Bekas, familiar with our hunters, are able to cause sound vibrations with their extreme tail feathers, which are somewhat narrowed and are tough appeal. At the same time, Bekas bleak can be safely regarded as its tok. A, some ornithologists think at all that those rattling sounds, which Bekas publishes during their flight, are caused by not steering feathers, but the feathers of his wings. Many chicken also possess their male caressing method for female. It is clearly visible on the example of home chickens. The rooster with force lowers the wings and holds a paw on fly hard feathers, as a result of his actions, characteristic cracks arise. A sharp and long thigh, which has roosters - it is called spur, also participates in the process of playing current sounds.

The science also has been proved that whistling sounds that occur during the flight of some duck (they arise as a result of friction of air flows about rigid duck feathers) also possess their signaling. These sounds are well audible even at a distance, and the human ear is able to catch them at a distance of 30 and more than meters. By the way, on such instrumental characteristic sounds a good hunter can easily distinguish which birds fly.
Often in spring in the forest can be heard as a drummer of the woodpecker, it produces this sound with the help of frequent and strong blows with its solid beak along dry wood. In a dry tree there is a resonance, and the sound is enhanced, and spread far through the forest. In order to strengthen such a drum fraction, the woodpecker can specifically choose separate sharp knots having a pointed peak. The latter serve as a kind of natural device for fixing and amplifying sound. Interestingly, the fact that different types of wood drums with different frequencies, regardless of their gender. And, their fraction serves for these birds way to know each other.
It has great importance in the signal language and flaking wings. It can be done both on Earth - when birds are current and in the air. Often, the knock of the beak or legs is also able to cause responses from other birds. You can check it out. Chickens run, having heard a slight tapping about the board, and it is perceived by them like a signal to get food. It is noteworthy that for adult chickens, the value of this signal remains the same.
Voice of birds
And, although instrumental sounds can be found in many groups of birds, their meaning, in fact, is not so big. All the same, the main burden of birds carry their real voice, in other words, these are the sounds that birds are produced using their larynx. The sound spectrum of these sounds is large enough and exceeds several times the spectrum of the human voice. So, for example, if you listen to the marriage scream of the eared owl, then it sounds at a frequency of 500 Hz, and the sounds that make small sparrows include ultrasound frequencies up to 48 thousand Hz, and their human ear naturally does not hear.
Bird sound signals
The very same set of bird sounds that a person can hear, there are up to hundreds of shouts, melodies, urges, stanza, which differ in the intensity, frequency, timbre, and so on. An American bird, close to our cranes, called Syria, has the ability to reproduce up to 170 different sounds, however, in patriot birds such a sound range of possibilities is even wider.
There are various living situations in which birds make certain identical sounds that are associated with nutrition, feeding chicks, reproduction, nesting, mating, and so on. Through the use of modern sound recording equipment and modern developed physiological methods, a person has a unique opportunity to finally decipher the semantic and biological meaning of some bird signals.
Dr. Sounds and England was spent a lot of time on such a decoding, and he managed to find out that chapters had 5 signals related to information evaluating the surrounding environment, 9 signals relate to relations inside the package and to the nesting period, 7 signals are identifying The meaning and 7 refer to oriented in space. And, here Mukholovka has a finger-up to 15 successful signals, while ordinary oatmeal - 14, as many signals managed to decipher from the black drosk language.
Value of bird signals
At the same time, decoding the biological value of bird signals allows you to count on the fact that in the case of accurate reproduction of such sounds, the nature of which can be predetermined in advance. So, for example, if you give to listen to the blue signal that stimulates it immediately takes, and then scroll signals to stop the flight, then you can control the movements of the bird in the air.
Whereas, the imitation of the cry of chicks, which beg for food, can cause movement in adult birds towards the sound source.
Below we bring a list of those signals in which you do not have to doubt the biological meaning.
Signal satisfaction
It is a long silent peak, which often publishes chicken chicks and other brood birds. So often peeped and fed chickens. Chickens, Kulikov and some types of ducks similarly manifest their satisfaction. The sign is the signal and small sparrows.
Signal of begging
It is published chicks pumped by parents - sparrow, seagulls, cleaners ... In this case, such a signal can be 2 types. The first one can attribute to the smallest chicks that publish it at the sight of feed and parents, the second is more characteristic of the stars and they publish it during the lack of parents. Make it chicks so that adult birds can find them. By the way, this signal allows the chicks to hold together.

- Go to Table of Contents section: * Opened secrets from the life of birds
Voice of birds. Birdsong.

V.D. Ilyichev, O.L. Silayova
Bird's voice is almost the same unique phenomenon as her flight. Both are provided by structures that are peculiar only to birds: Flying - feathers with their special microstructure, and a variety of sounds primarily with the lower larynx, where the voice-forming organ is located. This distinguishes the voice of birds from the voices of mammals, the source of which is the upper laryn, located on the border of the oral cavity and trachea.
For the vocal apparatus of mammals, reference cartilage, providing and supporting the pharyngeal gap, which, in fact, forms sound. It is limited to the sipsel gap with steam-haired cartilage. For the upper larynx mammals, the thyroid cartilage and the native is also characteristic.
Between the thyroid and silent cartilages inside the larynx there is a voice gap, limited by voice ligaments. Voice ligaments are the folds of the mucous membrane, inside of which the elastic fabric is located. Some species under these folds there are a couple of false voice ligaments, developed much weaker.
Some mammals have Morganev vitrors - pits located between the upper and lower voice ligaments. Unpaired bags between the thyroid and dignity cartilage were found from cloth monkeys, gazelles and reindeer. The resonance of these bags enhances the voice. Mammal lads are innervated by the upper and lower gentle nerves - the branches of the wandering nerve.
At the bottom of the trachea, pinned or fascinated cartilage rings form a drum. Between the trachea and bronchi there are enlarged bronchial semirings. Between the second and third half rings, the outer side forms a subtle mucosa membrane - an outer voice membrane (tympanal membrane). Elastic thickening on the inside of the third half-ring is called outdoor voice lip. The internal voice lip, attached between the free ends of the bronchial half-colt, is located on the opposite, facing the middle line of the body of the bronchi.
The compound of the inner walls of the bronchi provides cartilage kid with a semi-lobby. The inner surface of the bronchi below the internal lips is covered with an internal voice refill. At the same time, the internal voice metering of each of the bronchi is connected by an elastic ligament - Bortezmam. This type of lower trachea, combining the elements of the trachea and bronchi, is called tracheobrichial and characteristic, primarily for sparrows and parrots, as well as for wintering, curtains, fuddles and some other birds.
The tracheal and bronchial types of lower larynx are significantly less common, which, as clearly from the titles, the elements of the trachea and bronchi have predominant importance. Finally, there are troops of birds with a complete or partial reduction of the voice apparatus - they have no voice metering, konzelok, etc.
In the work of the lower larynx, the sternum-hyoid muscles are important, innervated by approximate and wandering nerves and ensure complex and varied movements of individual elements of the lower larynx.
The largest development of the sander-hyoid muscles reach representatives of the Sparrows detachment - in the pattering of birds, their number reaches 7-9 pairs. Parrots have 3 pairs of such muscles; At cranes, cuckoo, faddles, owls, goatoev, woodwoods, penguins, gagar, cakes, lamellaries, palaceda, chicken and pigeons and some others - 1 pair. Lower burning of Kazuar, African Ostrich and Kiwi generally devoid of muscles.
If the Gundan Musculature is poorly developed, the sounds are produced while reducing the sterno-trachy muscles, bringing clocking and pressing the trachea to bronchoms. At the same time, the goat presses on the ledge of the keyclosure bag that protrudes the inner voice reconciliation. When passing the air jet, the voice metering vibrate. Platechwater, chicken, ostriches and some other birds produce sounds in this way .....
The patterns of voice formation and sound communication in birds are one of the most important directions in modern ornithological bioacastics. The study of the issues of the functional physiology of the vocal apparatus of birds is associated with great difficulties, mainly due to the diversity of the morphological types of lower larynx in various systematic class groups (Teresa, 1930; Ames, 1971). Recently, the most promising method of studying the voization is the analysis with the help of special radio-electronic equipment of the acoustic structure of sounds emitted by birds. The use of this method in relation to early ontogenesis makes it possible to identify the age patterns of votes in birds.
The formation of acoustic alarm in birds in embryogenesis is highlighted in the literature extremely weakly. The focus of researchers have paid "Click" the sounds of embryosAs the most easily recorded immediately before hatching.
Sound communication, being a reliable communication mechanism, is widely used by brood birds, in which the development of the fluff system in embryogenesis is a leading pace compared with the development of vision. The microphone potential of the chicken embryo snail in response to low-frequency sounds is registered on the 11th day of incubation, and the electrical activity of the retina is only on the 18th day.
The setting of mutual communication contributes to the heterochronous development of an embryo hearing analyzer. It provides maximum auditory sensitivity before hatching in the frequency bands corresponding to the main energy maxima in the sounds of parents and their own vocalization. Acoustic afferentation at certain stages of early ontogenesis has a direct impact on the development of hearing, accelerates the process of mastering the high-frequency range characteristic of the eMbin's own vocalization. The range of the perceived frequencies of chicks, both in the brood, and in semi-power birds coincides with the spectral characteristics of the effect effective for appropriate forms of the behavior of the vocational signals of adult birds, which has an important adaptive value. It is that the species-specific sound alarm system between embryos and adult birds ensures synchronization of hatching hatching and maintaining the stability of its subsequent existence.
The development of acoustic alarm in birds in prenatal ontogenesis is mediated by the formation of pulmonary respiration. The first sound signals of embryos are formed before they are released into the air chamber of the egg. By the appearance of the appearance, they correspond to the "spontaneous" breathing, which is carried out due to the air of the Amnion cavity. In the same period, the mutual acoustic connection of embryos and the accidenting bird is established. Such a phenomenon is noted in Kulikov, on the example of the Bolshoi Veretnik, in chicken and lamellaries.
The beginning of the functioning of soundly freeing systems from representatives of various systematic groups varies significantly. The first sound signals of embryos are single pisks separated by durable time intervals - up to 30-60 minutes. After the embryo exit to the air chamber of the egg, its sound activity increases dramatically, which indicates the appearance of true pulmonary respiration. The intensity of the squearies increases, they can be heard even without opening the egg shell, but they are still separated by long pauses - 20-40 minutes. Problem - the appearance of the first cracks on the shell - is accompanied by a grouping of individual dyskits in a series of 2--3 pulses. The motor activity of embryos at this stage of development is accompanied by intensive scribes; The frequency of their radiation increases significantly with sharp movements and vibration of eggs.
Duration paranatal Period (from the probe shell shell before hatching) Correlated in birds with the total duration of the incubation period. Attention is drawn to the short paternal period of nANDU and chomgi.. This paradox is associated with the ecology of the nesting of the species. Reducing the duration of the paranatarian period in NAND to a minimum is a kind of adaptation of embryogenesis to arid conditions. The shell shell cakes with an embryo before hatching leads to intense evaporation of moisture, which, with a long paranitious period of development, in conditions of savannah and semi-desert, can achieve a critical value and entail the death of masonry. In the nests of the loading, on the contrary, high humidity, due to the well-known features of their "floating" design, were noted. Prolonged stay of embryos at the Problev stage of the shell in conditions of increased (excessive) humidity may also be destructive for them. In this regard, despite the early inclusion of the sound-proof system of embryos, the duration of the paranatarian development of CHOMGA is reduced to a minimum.
The "clicking" sounds occupy a special position in the development of voices in birds. They accompany pulmonary respiration and are characteristic of embryos. There is an opinion that "clicking" sounds arise as a result of mobility of the cartilage trachea, bronchi or larynx. As studies have shown, "Clicks" are the second type of sound signals in chronological order in the development of voting in birds in embryogenesis. The first "clicks" - irregular and low-intensity - are recorded in embryos a few hours before the clerk shell. Their rhythm does not exceed 10 per minute. Series, including from 10 to 50 pulses, alternate with pauses with a duration of up to 5-15 minutes.
Problem shells and subsequent stabilization of pulmonary respiration lead to the establishment of regular and more intensely "clicking" activity in embryos. Since "clicking sounds accompany the respiratory acts, their rhythm increases until hatching, being an indicator of development and stabilization of breathing. According to spectral-temporal parameters, they are short (10-30 ms), rhythmic broadband pulses. Viospecific characteristics of "clicking" sounds are not detected. The rhythm "click" in addition to the age characteristics of the embryos is directly dependent on the external temperature, which is caused by the intensification of respiratory movements. At brood and semi-consuming birds, the "clicking" sounds serve as the basis for acoustic stimulation of embryos, leading to the acceleration of embryonic development and synchronizing the hatching of chicks in the masonry.
The transition of embryos to breathing with atmospheric air is accompanied by a rhythmic organization of emitted sound signals. Certain categories of them ("discomfort" signals, "comfort") are functional significance in the process of sound communication of embryos and a rapid bird. A number of groups of the shell shell and stabilization of the pulmonary respiration of embryos change dramatically the spectral structure of the emitted signals. In general, the transition to the radiation of "noise", or broadband signals, practically no pronounced frequency modulation, takes place in birds with a "primitive" type of structure of the lower larynx. Primitive type of structure of the lower larynxit is characterized by one pair of muscles, and in some species of the delicate (storks) and Bulk Birds (EMU, NANDU, African Ostrich) and it is exposed to considerable reduction. Developed lower lads (for example, in the singers of sparrow) determines the complexity of voice muscles (8-12 pairs); It is characterized by a strong modification of the dumping tracheal rings.
Different and structurally dynamic organization of signals. Thick Cair embryos are capable of radiating both separate pulses and trolping sound signals. The trolshide structure of the signals is not characteristic of the prenatal ontogenesis of fine-oxid kair. Such an early and strong difference in acoustic signal systems in close types of Kair is due, apparently, the sinister nesting in the colonies. High-level in the nesting colonies of Kair reaches not only interspecific, but also an individual recognition in families.
The maturity and complexity of the acoustic signal system in birds by the time of hatching are determined by the type of development and species environmental features. In the prenatal ontogenesis of brood and semi-high-consuming birds, all major categories of signals are formed: the sounds of "discomfort", "comfort", "facing feed", etc. Not registered in embryos only alarms.

Embos of Sulishary (Fulmarus GlacLalis)and Stercorariidae (semcorariidae) (semcorariidae) are capable of publishing all sound signals characteristic of adult birds. A comparative analysis of juvenile and definitive acoustic signal systems in these species indicates that age changes are mainly expressed in the expansion of spectral boundaries and increasing the duration of the signals. The structural organization of sound signals in embryos and adult birds is almost identical. Thus, in tube and perisons, the type of development of the acoustic signaling system is rigidly determined. All categories of sound signals are formed in prenatal ontogenesis and by structural organization are as if copies of definitive signals. Further functional differentiation and structural complication of signals does not occur.
Before hatching embryos actively correspond to the signals of "discomfort" to certain external influences: cooling, sharp coupling eggs, shaking, etc. The number of pulses in the series and the rhythm of their radiation are not strictly fixed and are determined, apparently, the physiological state of embryos and external factors. . Signals "Comfort" are easily distinguishable for rumor from "uncomfortable" signals and perceived as quiet chirping or disintegration. The intensity of their empty empty is significantly lower than the "discomfort" signals. Signals of "Comfort" are usually recorded at the end of "outbreaks" of motor activity in embryos, during heating cooled eggs, their vibrations.
To one of the varieties of sounds of "comfort" belongs to "comfortable" trill. Trells are published embryos at the stages directly preceding hatching. Trells follow, as a rule, inthe end of the series "Comfortable" sounds and complete it. For the embryos of plate-fuel, chicken, shepherd and some other species of birds are characteristic of the sleepy trills as one of the options for trilting sounds. They differ from the usual "comfortable" trails of narrow band in spectrally, and a smaller pulse duration. Sleepy trills are common when heating cooled eggs, the motor activity of embryos in this case is significantly reduced.
Immediately before hatching embryos "Wear" the shell shell of the egg: This process is accompanied by specific "Instrumental" soundsarising from the friction of the egg "tooth" about the shell. The intensity of these sounds is extremely low.
The yield of chicks from the shell is accompanied by the signals of "hatching". Their radiation is caused by painful sensations, because at this moment the chicks occur at the pumped "stem". The spectral-temporal parameters of the "hatching" signals are close to the sounds of "discomfort"
Sound alarm at the stages of pre-deposition at brood and semi-power birds ensures communication between embryos in the masonry, on the one hand, and between the embryos and the starting bird - on the other. Sound communication during this period coordinates the behavior of embryos and leads to the establishment of primary acoustic contact with parents, on the basis of which a stable connection of an adult bird with a brood is formed after hatching. The rhythm of the signals of "discomfort" in embryos increases when the birds from the nest occur (kill). In this case, they stimulate the return of the causening bird. Magnetic recording of the sounds published by embryo in the natural incubation, allowed to identify some of the features of their sound communication with a crucible bird. Thus, the radiation of the chicken-zing of the alarms led to the termination of the sound activity of embryos. The gathering of the jacks from the nest caused the embryos after 5-8 min intense signals "discomfort", and the return of the bird and its call sounds were activated "Comfortable « alarm. Reproduction for the sounds of sounds "discomfort" with the help of a tape recorder led to the fact that it actively emptied the call signals, moved to the socket tapping the beak along the eggshell. The "comfortable" signal of embryos did not cause special changes in its behavior.
In this way, formation of the main types of acoustic signals It is completed before hatching, which subsequently provides a successful acoustic orientation of the entire brood transition from the acoustic perception of the outer environment, characteristic of embryos, to the perception of complex afferentation after the output is accompanied by chicks by the further development of alarm. New categories of acoustic signals appear, which were not observed in embryos: anxious and alarming-defensive and alarming. Together with this, there is a further development of "discomfort" and "comfort" signals.
, Head organs, sound characteristics
The purpose of the lesson: to introduce students with a new science for them - bioacastics; consider ways to reproduce sounds in the animal world; identify the feasibility of the structure of hearing organs in various animals; Repeat knowledge on the topic "Sound Waves"
Preparation for a lesson: the topic of the lesson, a lesson plan, expressing-epigraphs to the lesson is recorded on the board.
"Putting the language of animals is ancient, like humanity itself, dream" K. Fabry
"The task of conservation of animals requires their understanding" N. Tinbergen
Lesson plan:
- Introduction
- Practical work "Sound alarm value"
- History of bioacastics
- Sound and its characteristics
- Who says?
- Who does it hear?
- Conclusion by lesson.
1. The introductory word of the teacher.
(Teacher of Physics) Theme of today's lesson "Sound alarm in the life of animals." The lesson is integrated, because Today we will talk about bioacastics, and this is a comprehensive science that combines knowledge of biology and physics. We will work according to plan shown on the board.
In fairy tales, animals are talking. Remember, at least "Mowgli" kipling or "a fairy tale about the Golden Fish" Pushkin. And the kids do not seem strange that the goldfish, fox, the bear or frog can speak. In fairy tales and himself speaks animals. This manifests a century-old dream of a person learn to understand the language of animals.
The reason for these dreams is understandable. Million years, a person is very closely in contact with animals, his dependence on them is too large: because animals are tasty and nutritious food, and clothing, and all kinds of household items, finally, animals are deadly enemies.
Decay and get the beast on the hunt, to avoid his fangs, make the assistants from the beasts, taking them, - all this requires a deep understanding of animal behavior.
Today, when civilization is increasingly separates us from wildlife, when "nature becomes less and more environment," we are somehow especially starting to feel its lack, we strive to study the signs of the living.
The term "animal language" Biologists have been written in quotes for a long time in quotes, but now recognized the legality of this concept to designate animal ability to communicate with each other.
Animal language is a complex concept. An important role in the exchange of information between animals is played by language poses and televitations. Remember the dumbfounded mouth of the predator or, on the contrary, the marriage dance of the crane. It is important for them and the language of odors. But the sound language has a completely particular importance for animals, because it allows animals to communicate without seeing each other (for example, in complete darkness) and on distant distance.
Sound - besides the "long-range weapon". The screams of the vanes are heard in a kilometer from them, crocodiles hear each other at a distance of 1.5 km, lions - 2.5 km. But the range of the distance was given humpback whales: they hear each other at a distance of several hundred miles.
2. "Sound alarm value." Practical work with the design of the table in the notebook.
(Biology teacher) And now we invite you to listen to the voices of animals recorded in different parts of our planet. Maybe someone learn? And think about how to have sound signals. ( Sounds recording)The results of the work are made in the table:
Conclusion: So, let's summarize. Sound alarm value for animals:
1. Intravidal communication:
a) between representatives of different floors of one species during the reproduction period (search for a sexual partner or the fight against the opponent for the possibility of pairing);
b) care for offspring (search for food, danger signals);
Example with chickens: With its offspring, the chicken communicates mainly using sound signals. For example, in one of the experiments it was found that the chicken does not come to the rescue of chicken, seeing it in a difficult position if he is under the soundproof glass cap. Both chickens and adult birds make about 20 different sound signals and can express pleasure, fear, fright, threat, celebration using sounds. In this case, from 20 signals that enjoy chickens, 7 signals refine the nature of the danger.
c) Public Animals Joint Food Search, Collective Protection;
d) the label of the territory.
2. Intervidal communication:
a) the victims make it possible to avoid the attack of a predator, and predator - to detect it;
b) interaction between competing species.
3. The history of bioacastics
(Teacher tells biology) Two and a half thousand years ago, the Greek thinker and mathematician Pythagoras (you know his theorem) started the first acoustic experience in the world. Pythagoras died. It was century for a century, and the science of sound, the beginning of which he laid down, stopped. Not a single experiment until 1638, when Pythagora's case continued Galileo Galilee. And now it came to the nineteenth century. Classic work on the acoustics of the German scientist Hermann Helmholts are published.
It is unlikely that there are many sciences in the world that could boast of your day and the place of birth. The emergence of most sciences is lost in the depths of the centuries. Another thing is bioacaby. We can accurately say that she was born in 1956 in Pennsylvania (USA), it was there that scientists from different countries came to the first bioacuistic congress, where the official passport of this new science was issued.
Today we are talking about bioacastics, and this is a comprehensive science that unites knowledge of biology and physics. Acoustics- Science of sounds, and bioacoust - studies all sorts of existing methods of sound communication between alive creatures. Bioakousty is interested in and unites not only biologists and physicists, but also linguists, psychologists, engineers and many other specialists.
The phonotheki of many bioacastic scientific centers contain tens of thousands of records of various animal votes. Collecting animal votes has a large scientific and practical importance. For example, many birds and insects, not distinguishable externally, differ well in votes, and on this basis they can be allocated to independent biological species.
By broadcasting the call signals, you can make fish or insects in traps, and if you turn on the threat signals, then scare animals from unwanted places of their presence.
For example: N. and the north in the village is often visiting bears to rummage in trash rooms in search of food. To get rid of the unreasonable guests, the ferocious growl of two breeding bears recorded a tape recorder and played through loudspeakers in one of the villages. Cheeky guests in fear were retracted and forgot the way for a long time.
The feature of birds react to sounds are used when the airfields are protected. After all, Pernaya became a real disaster for them. Birds often fall into the air intakes of engines of jet aircraft, hit the windshields and cause accidents. Therefore, they are trying to be expelled with airfields by any ways. And the easiest way to do this, turning on the alarming signals of the birds themselves recorded on the tape recorder. True, it must be borne in mind that in different places the birds are "talking" on different "languages \u200b\u200band dialects." The case is known when the alarms of the French Raven recorded the film and gave them to listen to American. However, they did not understand the screams of their overseas relatives and did not respond to them. [ one]
4. Sound and its characteristics
(Physics teacher) living organisms are able to publish a wide variety of sounds, unlike each other. Let's remember the physics lessons, what is the sound, and how can the sounds differ from each other? (Frontal conversation survey with students)
Question: What is the sound?
Answer: Sound is an elastic compression wave and praise, propagating in a solid, liquid, gaseous medium.
Those. Sound is an ordinary mechanical wave, which is a replacement area of \u200b\u200bthickening and vacuum.
But each sound has its own characteristics, i.e. Your characteristics.
Question: What sound characteristics do you know?
Answer: Height, volume, timbre.
Question: What is the height or tone of the sound?
Answer: This is a characteristic that is determined by the frequency of oscillations in the sound wave. Large frequency correspond to high sounds, less frequency - low sounds.
Question: Sounds What frequency does a person perceive?
Answer: From 20 to 20,000 Hz (experience with the sound generator)
Question: What sounds are behind these limits?
Answer: Infrasounds (frequency less than 20 Hz) and ultrasound (frequency greater than 20 kHz)
Question: What is the volume of sound?
Answer: This is a characteristic that is determined by the amplitude of oscillations in the sound wave. The greater the amplitude, the volume is greater.
Question: What units is measured?
Answer: Measured in dB.
Question: What is the characteristic called timber?
Answer: Sound color arising from overlaying several overtones on each other.
It is thanks to Tembre that we can distinguish the sounds of various musical instruments, voices of different people, animals, birds.
One of the characteristics of any wave is the speed of distribution.
Question: What can be said about this characteristic. What does it depend on?
Answer: The speed of sound is different in different environments. More in solids, less in gases, because The interaction of particles in the gaseous substance is the weakest.
It is not by chance that in the distant times of the warrior, the ear was attached to the Earth and thus found the enemy to the Connection much earlier than it appeared in sight. Because Sound in a solid-land - spreads faster than in the air.
If we summarize the foregoing, it can be noted that all the variety of sounds is explained by their various characteristics.
5. Who says as.
(Physics teacher) The sound has an important meaning in animal life. This is a means of transmitting information. Animals are capable of sharing sounds, for example, a person can speak. How does the sound occur? Turn to the experience. I will hit the hammer on the feet of the camera and hear the sound. Why does the sound occur?
Answer: When hitting the hammer about the legs of the tuning, they begin to fluctuate, which causes air fluctuations that distribute in space, i.e. There is a sound wave.
So, the source of sound is the oscillating body.
Why do you use a stand in the form of a wooden drawer?
Answer: To enhance sound. It is selected in such a way that its own oscillation frequency is equal to the sound frequency of the camera, i.e. In order to observe the phenomenon of resonance, as a result of which the amplitude of oscillations increases, and we hear a loud sound.
The stand is called the resonator.
What way the animals make sounds? Consider this issue on the example of a person. (Tag of the teacher of biology about voice ligaments).
And what other ways to create sounds exist in animals? (student message)You have in my notebook in the course of the report, mark the name of the animal and "what it says":
| Animal name | Sounds reproducing organs |
| 1 | |
| 2 |
The report "How are the sounds formed?"
(The report is accompanied by a photograph of the corresponding animals)
As with a person, all mammal organs, specially intended to create sound oscillations, is the larynx. Parts constituting its bimnery. The thyroid cartilage resembles a revealed book whose root is vertically. What is the first-shaped cartilage, it is clear from his name, and the sneak-shaped cartilage - triangular pyramids. Just between these pyramids and thyroid cartilage, voice ligaments are elastic folds of the mucous membrane. Many sounds of the beasts depend on breathing, and almost all animals arise when they break out of the light air. It is they forced to fluctuate the vocal ligaments of the larynx, and they make a weak sound, and the pot of the cavity plays the role of a resonator that enhances the sound. If the air leaves the lungs more or less smoothly, then it turns out howl. In some animals, sounds can both form in breathe and in exhalation (for example, the maral and donkey). Tiger and the rest of his counterparts when they are well-friendly, snort. And they snort peculiar: two different sounds are collapsed, because at that moment they use not only larynx, but also the nose. And dogs, waterproofs and wombat so breathe and exhale air through the nose that it turns out the whistle. Dolphins know how to whistle. And they can click. With the air here, it is not necessary here, as the source of sounds is not to fluctuate the voice ligaments, but the vibration of the sneak-shaped cartilage driven by the muscles of the larynx. It is easy to do it yourself (suggest try).
Lanes of birds are similar to Mammal's larynx, but the birds are little use. It is called "Upper Lane". Why top? Yes, because there is also lower or sirinx.Sirinx - the organ is special. It is only in birds. In the depths of the chest, where the trachea is divided into bronchi, the camera is located. If you look inside this chamber, we will see voice metering in each bronch. Although the anatomy of Sirinx has been studied very well, it is so complex system that there is still no single theory explaining how the sounds of birds are formed. Speed, from which bird to extract their sounds, extraordinary. Garden Kamyshevka managed to die 250 sounds in 1 minute, and the marsh blame - exactly twice as much.
However, is there always to let something to each other, you need to use the larynx? Not at all. And these special sounds that arise without the participation of the larynx are given a special name: "Instrumental". But the tools used by animals are very different. Click the beak owl. They clap the wings of pigeons, the ducks whistling them. Galapagos shepherd is in paws. Cockroaches, sindes, ants knock on what: who head, who is the tip of the abdomen, and who are jaws. Termites, finding a danger, friendly beat the heads about the substrate (metering material), notifying about the alarm of all the inhabitants. Punny pigs and sony-shelters are knocking. The grasshopper shifts and spreads the wings, yes so that the rope on one wing is touched to a writing with ribs on the second wing. Some beetles (elephant, water-cut, native) are shifted, rubbing the abdomen about the pulp, and the deer beetles make sounds with hollows and feet feet.
Lowering the hydrophones into the water, the researchers found that both "fish are not dead." Sea cock, for example, "bitch and quoucht". Studum "bakes". The drummer fish makes sounds, indeed, resembling a drum fight, and Marine Plisch expressively urchit and "grunt." The power of the sound of some sea fish is so great that they caused the explosions of the acoustic mines who were distributed during the Second World War, and intended, naturally, to defeat the enemy's ships. One of Somoms living in Amazon - Pirarar (not to be confused with bloodthirsty pirani), reaching a meter in length and weighing up to 100 kilograms, makes pipe sounds similar to the roar of the elephant and audible up to 100 meters. These sounds are published by COM by pushing the mixture of water and air through tightly closed gill gaps and serve, most likely, to scare away predators. Haraki is the main fishing fish of the Amazon - during spawning, it makes a strongest sound with a swimming bubble, resembling a motorcycle sound. You can imagine when hundreds of macaics males during a spawning roll their motorcycles. The causes of abundance and diversity on the Amazon of "singing fish" scientists see that the water of this river is very muddy due to the impurities of limestone and humus. The visual communication of the fish is almost impossible, so nature and went on the way of developing a variety of acoustic alarm. [2]
6. Who as hears.
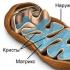
(Physics teacher) to communicate animals should not only make sounds, but also take them, i.e. hear. Sound receiver is an ear. Animals are heard, because their ears react to sound waves. We will analyze the structure of the ear of mammals on the example of the human ear. (story on the table "The internal structure of the ear") The ear can be divided into three parts: outdoor, secondary, internal. The outdoor ear consists of ear shell and auditory passage. The middle ear: here there is a drum membrane and three bones of characteristic shape: hammer, anvil and rapidly. In addition, the average ear is connected to the nod to the narrow tube, which is necessary for aligning the air pressure in the middle ear with respect to the external environment. In the inner ear, there are three tubes filled with liquid (semicircular channels), which belong to the vestibular apparatus, snail is a miniature spiral tube and a hearing nerve.
So, the ear shell takes a sound wave. Moreover, the surface area of \u200b\u200bthe auricle has an important meaning. Let's spend experience: stick your hand to the ear shell and listen. Hearing increases. The larger the surface area, the most of the sound waves we perceive.
Next, the auditory pass guides the wave to the eardrum. The eardrum under the action of the sound wave begins to fluctuate, and these oscillations are transmitted to the hammer, anvil and the shirling, which work as small levers, amplifying oscillations. The bones are connected to the snail filled with a special fluid, and the transmitted oscillations cause the movement of fluid back and forth to the tact with oscillations in the sound wave. In this case, sensitive hair cells located inside the snail are deformed and sent an electrical signal through the hearing nerve into the brain. The brain decrypts signals and perceives them as sounds.
Why a person two ears? It turns out that, thanks to this, we can determine where the sound source is. The ear, the nearest source hears him a little louder and a little earlier than the other ear. It is these two sounds and make it possible to determine where the sound comes from.
If the source is strictly in front of you, the sound reaches each ear at the same time, and we cannot determine the desired direction. So, if we want to determine where the sound comes from, you must not turn to the sound, but on the contrary, turn away from it.
The ear is arranged in such a way that it reacts in different ways to loud and quiet sounds. The smallest pressure on which the ear reacts, calls the threshold of hearingness. Each body has its own. For example, a person is able to hear such weak sounds as a rustle of 10 dB leaves or clock ticking at a distance of 1 m - 30 dB.
In the case of high-profile sounds, the two muscles of the middle ear and the eardrum, the hammer, anvil, and rapidly fluctuate the amplitude, are additionally reduced. In this case, the pressure transmitted by the inner ear - snail decreases. But too loud sounds are harmful to hearing, and the sounds equal to 140 dB cause pain, and equal 160 dB - the destruction of the eardrum. How to protect the hearing body: close your ears and open your mouth.
Despite the fundamental similarity in the structure of the ears, different mammals have their own characteristics. Individual features of hearing organs allow different animals to perceive different sounds. So, a person hears sounds from 20 to 20,000 Hz, and with age, the limits of hearingness change. Children can hear up to 40 kHz, i.e. ultrasound. With age, this ability decreases. It has been established that after 40 years five years in a row every six months, the upper limit of the frequency scale falls at 80 Hz.
Many animals throughout their lives perceive ultrasound, for example, dogs - up to 60 kHz; Lisens up to 65 kHz; Bats up to 250 kHz, cetaceans also communicate with ultrasound. And some marine animals (squid, cuttlefish, octopuses) perceive infrasound.
(Biology teacher) You know that the animals live who where. Depending on the habitat and ears, they are arranged in different ways. Let's try together with you on the example of some animals to explain the biological feasibility of the structure of their ears. I will call animals, and you try to determine the biological feasibility of the structure of their ears: (The conversation on issues is accompanied by a display of photographs of the corresponding animals)
Question 1: Music whales, ordinary dolphins, moles do not have ear shell at all, why? Answer:In the water and in the ground, where these animals live, the ear shell only interfered. CROT, so that the Earth did not hit the auditory passage, there is a special valve that can open and close as needed.
Question 2: The nutria ears are small, rounded, and the upper edges are turned toward the inlet, downstairs a bunch of hard and long hair, why? Answer:Nutria lives in water and on land, therefore must hear in both media. A bunch of hard hair does not give water to get into the auditory passage.
Question 3: African Fenneke Fenil Same (30-40CM), and her ears are up to 15 cm. How can you explain it? Answer:Fenca's ears are not only an hearing body, but also participate in thermoregulation. In animals of hot climate, all protruding parts of the body (ears, tail, limbs) are much longer than those of the species in the cold edges (Alena rule). These features of the structure increase the overall surface of the body, and, therefore, its heat transfer. The same can be said about the big ears of elephants, which, moreover, you can still handle the annoying insects perfectly.
7. The results of the lesson.
(Students are summarized) So, summarize today's lesson. Sound alarm is of great importance in the life of animals. The study of the methods of sound alarm existing in nature between animals, that is, what bioacaby is engaged in, it is important for scientific and practical activity of a person.
Bibliography
- Morozov V.P. Entertaining bioacaby. Ed. 2nd, add., Pererab. - M.: Knowledge, 1987.
- Eschkovskaya L.L. And said the Golden Fish. Scientific and fiction / artist V. Levinson. - M.: Dets., 1989.
- CD. 1C: School. Biology (man and his health), 9 CL. Publishing center "Ventana Graph", textbook text with illustrations, 2006.
- CD. 1C: School. Biology (animals), 7 CL. Publishing center "Ventana Graph", textbook text with illustrations, 2006.