Find the square of the right hexagon with the side a. How to find a hexagon area by the formula? From theory to practice
Do you know what the right hexagon looks like?
This question is not as chance. Most grade students are not a response to it.
The correct hexagon is such that all parties are equal and all the angles are also equal.
Iron nut. Snowflake. The cell cell in which bees live. Benzol molecule. What is common to these objects? - The fact that they all have the right hexagonal shape.

Many schoolchildren are lost, seeing the tasks on the right hexagon, and believe that they need some special formulas to solve them. Is it so?
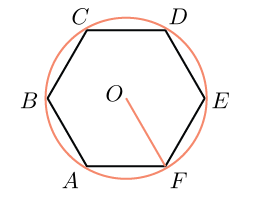
We carry out the diagonal of the correct hexagon. We received six equilateral triangles. 
We know that the area of \u200b\u200bthe right triangle :.
Then the area of \u200b\u200bthe right hexagon is six times more.
Where is the side of the right hexagon.
Please note that in the right hexagonal distance from its center to any of the vertices equally and equals the side of the right hexagon.
So, the radius of the circle described around the correct hexagon is equal to its side.
The radius of the circle inscribed in the correct hexagon, it is not difficult to find.
It is equal.
Now you can easily decide any tasks of the EGEin which the correct hexagon appears.
Find the radius of the circle, inscribed in the correct hexagon of the side.

The radius of such a circle is equal.
Answer:.
What is the side of the right hexagon, inscribed in a circle, the radius of which is 6?
We know that the side of the right hexagon is equal to the radius of the circumference described around it.
Do you know what the right hexagon looks like?
This question is not as chance. Most grade students are not a response to it.
The correct hexagon is such that all parties are equal and all the angles are also equal.
Iron nut. Snowflake. The cell cell in which bees live. Benzol molecule. What is common to these objects? - The fact that they all have the right hexagonal shape.

Many schoolchildren are lost, seeing the tasks on the right hexagon, and believe that they need some special formulas to solve them. Is it so?
We carry out the diagonal of the correct hexagon. We received six equilateral triangles. 
We know that the area of \u200b\u200bthe right triangle :.
Then the area of \u200b\u200bthe right hexagon is six times more.
Where is the side of the right hexagon.
Please note that in the right hexagonal distance from its center to any of the vertices equally and equals the side of the right hexagon.
So, the radius of the circle described around the correct hexagon is equal to its side.
The radius of the circle inscribed in the correct hexagon, it is not difficult to find.
It is equal.
Now you can easily solve any tasks of the EGE, in which the correct hexagon appears.
Find the radius of the circle, inscribed in the correct hexagon of the side.

The radius of such a circle is equal.
Answer:.
What is the side of the right hexagon, inscribed in a circle, the radius of which is 6?

We know that the side of the right hexagon is equal to the radius of the circumference described around it.
Converter Units Distance and Length Converter Units Square Join © 2011-2017 True Mikhail Copying Materials is prohibited. In the online calculating, you can use values \u200b\u200bin the same measurement units! If you have faced difficulties with the conversion of the measurement unit, use the range of distance units and length converter. Additional features of the calculator calculating the area of \u200b\u200bthe quadrangle
- Between the fields for entering, you can move by pressing the "Right" and "Left" keys on the keyboard.
Theory. Quadrangle Square Quadril - geometric figure, consisting of four points (vertices), no three of which do not lie on one straight line, and four segments (sides), in pairwise connect these points. The quadril is called convex if the segment connects any two points of this quadrangle will be inside it.
How to find out the area of \u200b\u200bthe polygon?
The formula for determining the area is determined by taking each edge of the polygon AB, and calculating the area of \u200b\u200bthe AVO triangle with the vertex at the beginning of the coordinates about the coordinates of the vertices. Upon bypass around the polygon, triangles are formed, including the inner of the polygon and located outside it. The difference between the sum of these areas is the area of \u200b\u200bthe polygon itself.
Therefore, the formula is called a geodesist formula, since "Cartographer" is at the beginning of the coordinates; If he bypasses the area counterclockwise, the area is added if it is left and deducted if it is on the right from the point of view from the start of the coordinates. The field formula is valid for any self-appropriate (simple) polygon, which can be convex or concave. Content
- 1 definition
- 2 examples
- 3 more complex example
- 4 Explanation of the name
- 5 cm.
Polygon area
Attention
It can be:
- triangle;
- quadrangle;
- five- or hexagon and so on.
Such a figure will certainly be characterized by two provisions:
- Related side does not belong to one straight line.
- Non-negative dots missing, that is, they do not intersect.
To understand what vertices are neighboring, you will need to see if they belong to one side. If so, then neighboring. Otherwise, they can be connected to the segment to be called a diagonal. They can be carried out only in polygons who have more than three vertices.
What kind of types are there? A polygon, which has more than four angles, can be convex or concave. The difference between the latter is that some of its vertices can lie on different directions from a straight line conducted through an arbitrary side of the polygon.
How to find the area of \u200b\u200bthe right and wrong hexagon?
- Knowing the length of the side, I multiply it by 6 and we get the perimeter of the hexagon: 10 cm x 6 \u003d 60 cm
- We substitute the results obtained in our formula: Area \u003d 1/2 * Perimeter * Appeamp Square \u003d ½ * 60cm * 5√3 We decide: now it remains to simplify the answer to get rid of square roots, And we point out the result in square centimeters: ½ * 60 cm * 5√3 cm \u003d 30 * 5√3 cm \u003d 150 √3 cm \u003d 259.8 cm² video about how to find the square of the right hexagon there are several options for determining the area of \u200b\u200bthe wrong hexagon:
- Trapezing method.
- The method of calculating the area of \u200b\u200bincorrect polygons with the axis of coordinates.
- The method of breaking the hexagon to other figures.
Depending on the source data that you will be known, the appropriate method is selected.
Important
Some irregular hexagons consist of two parallelograms. To determine the area, the parallelogram should multiply its length to the width and then fold the two already known areas. Video on how to find the area of \u200b\u200bthe polygon equilateral hexagon has six equal side And is the right hexagon.
The equilateral hexagon area is equal to 6 triangles area, which is broken by the correct hexagonal figure. All triangles in the hexagon of the correct form are equal, so it will be enough to know the area of \u200b\u200bat least one triangle to find the area of \u200b\u200bsuch a hexagon. To find the equilateral hexagon area, it is used, of course, the formula of the area of \u200b\u200bthe correct hexagon described above.
404 NOT FOUND.
Decoration of housing, clothes, drawing paintings contributed to the process of formation and accumulation of information in the field of geometry, which people of those times mined an experimental way, and transmitted from generation to generation. Today, knowledge of geometry is also necessary for the creation engineer, the builder, and the architect and everyone simple man at home. Therefore, it is necessary to learn to count the area of \u200b\u200bvarious figures, and remember that each of the formulas can be useful in practice, including the formula of the correct hexagon.
The hexagon is called such a polygonal figure, the total number of corners of which is six. The correct hexagon is called a hexagonal figure, which has equal side. The corners of the correct hexagon also equal among themselves.
IN everyday life We can often meet the items that have the form of the right hexagon.
Calculator of the area of \u200b\u200ban irregular polygon around
You will need
- - roulette;
- - electronic rangefinder;
- - sheet of paper and pencil;
- - Calculator.
Instruction 1 If you need total area Apartments or a separate room, just read the technical passport for an apartment or a house, there is a metrar of each room and a common foundation. 2 To measure the area of \u200b\u200bthe rectangular or square room, take a roulette or electronic rangefinder and measure the length of the walls. When measuring distances, the rangefinder must necessarily follow the perpendicularity of the beam direction, otherwise the results of measurements can be distorted. 3 Then the resulting length (in meters) multiply the width (in meters). The resulting value and will be the floor area, it is measured in square meters.
Gauss Square formula
If you need to calculate the floor area of \u200b\u200ba more complex design, for example, a pentagonal room or a round arch room, schematically draw a sketch on a piece of paper. Then divide complicated form A few simple, for example, on a square and a triangle or a rectangle and semicircle. Measure with the help of a roulette or rangefinder the value of all sides of the resulting figures (for the circle you need to know the diameter) and bring the results to your drawing.
5 Now consider the area of \u200b\u200beach figure separately. The area of \u200b\u200brectangles and squares calculate the parties to multiply. To calculate the area of \u200b\u200bthe circle diameter, divide in half and take into a square (multiply it to itself), then multiply the value obtained by 3.14.
If you need only half a circle, divide the resulting area in half. To calculate the triangle area, find the p, for this, share all sides to 2.
Formula for calculating the area of \u200b\u200ban incorrect polygon
If points are numbered consistently in the direction counterclockwise, the determinants in the formula above are positive and the module can be omitted in it; If they are numbered in the direction clockwise, determinants will be negative. This is because the formula can be considered as a special case of the Green Theorem. For the application of the formula, it is necessary to know the coordinates of the vertices of the polygon in the Cartesian plane.
For example, take a triangle with coordinates ((2, 1), (4, 5), (7, 8)). Take the first X-coordinate of the first top and multiply it on Y -Kordinate the second vertex, and then multiply x the second vertex on the Y third. Repeat this procedure for all vertices. The result can be determined by the following formula: A TRI.
Formula for calculating the area of \u200b\u200ban incorrect quadrangle
A) _ (\\ Text (Tri)) \u003d (1 \\ OVER 2) | x_ (1) y_ (2) + x_ (2) y_ (3) + x_ (3) y_ (1) -x_ (2) y_ (1) -x_ (3) y_ (2) -x_ (1) y_ (3) |) where xi and yi denote the corresponding coordinate. This formula can be obtained by opening brackets in general formula For the case of n \u003d 3. According to this formula, it can be found that the area of \u200b\u200bthe triangle is equal to half the amount of 10 + 32 + 7 - 4 - 35 - 16, which gives 3. The number of variables in the formula depends on the number of the parties of the polygon. For example, in a formula for a pentagon area will be used to x5 and y5: a Pent. \u003d 1 2 | x 1 y 2 + x 2 y 3 + x 3 y 4 + x 4 y 5 + x 5 y 1 - x 2 y 1 - x 3 y 2 - x 4 y 3 - x 5 y 4 - x 1 y 5 | (\\ DisplayStyle \\ MathBF (A) _ (\\ Text (Pent.)) \u003d (1 \\ OVER 2) | x_ (1) y_ (2) + x_ (2) y_ (3) + x_ (3) y_ (4 ) + x_ (4) y_ (5) + x_ (5) y_ (1) -x_ (2) y_ (1) -x_ (3) y_ (2) -x_ (4) y_ (3) -x_ (5 ) y_ (4) -x_ (1) y_ (5) |) A for a quadrilateral - variables to x4 and y4: a quad.
Are there any pencil from you? Take a look at its cross section - it is the right hexagon or, as it is also called hexagon. Such a form also has a cross section of nut, a field of hexagonal chess, some complex carbon molecules (for example, graphite), snowflake, bee honeycombs and other objects. A giant correct hexagon was recently discovered in not it seems strange so frequent use by nature for their creations of the structures of this form? Let's look more in more detail.
The correct hexagon is a polygon with six identical sides and equal corners. From the school courage, we know that it has the following properties:
- The length of its sides corresponds to the radius of the circle described. Of all this property has only the right hexagon.
- The angles are equal to each other, and the value of each is 120 °.
- The perimeter of hexagon can be found according to the formula P \u003d 6 * R, if the radius is known for the circle described around it, or p \u003d 4 * √ (3) * R, if the circle is inscribed in it. R and R radius described and inscribed circle.
- The area that the correct hexagon occupies is defined as follows: S \u003d (3 * √ (3) * R 2) / 2. If the radius is unknown, instead we substitute the length of one of the parties - as is known, it corresponds to the length of the radius of the described circle.

The right hexagon has one interesting feature, thanks to which he received such widespread in nature, it is able to fill any surface of the plane without overlaps and spaces. There is even a so-called lemma of the failed, according to which the correct hexagon, the side of which is equal to 1 / √ (3), is a universal tire, that is, any set with a diameter into one unit can be coated.
Now consider the construction of the right hexagon. There are several ways, the easiest of which involves the use of a circulation, pencil and ruler. Initially, we draw a circular an arbitrary circle, then in an arbitrary location on this circle we make a point. Without changing the solution of the circula, we put the tip at this point, mark the next notch on the circle, we continue until we get all 6 points. Now it remains only to connect them between themselves straight segments, and the desired figure will be.

In practice, there are cases when it is required to draw a large hexagon. For example, on a two-level plasterboard ceiling, around the place of attachment of the central chandelier, you need to install six small lamps at the lower level. The circuit of such sizes will be very and very difficult to find. What to do in this case? How to draw a big circle? Very simple. You need to take a strong thread of the desired length and tie one of its ends opposite the pencil. Now it remains only to find an assistant who would prescribe to the ceiling at the desired point the second end of the thread. Of course, in this case, minor errors are possible, but they are unlikely to be noticeable to a stranger.
With a question: "How to find a hexagon area?", It is possible to encounter not only on the geometry exam, etc., these knowledge will be useful and in everyday life, for example, to properly and accurately calculate the area of \u200b\u200bthe room during the repair process. Substituting the required values \u200b\u200bin the formula, it will be possible to determine the desired number of wall rolls, tiles in the bathroom or in the kitchen, etc.
Few facts from history
Geometry was used in ancient Babylon and other states that existed at one time with him. Calculations helped in the construction of significant structures, since thanks to her, the architects knew how to withstand the vertical, correctly make a plan, determine the height.
Aesthetics also had great importanceAnd here she went into the course of geometry. Today this science is needed by the builder, the crew, architect, and not a specialist too.
Therefore, it is better to be able to count s figures, to understand that formulas can be useful in practice.
Square of the right 6 square
So we have hexagonal figure with equal sides and corners. In everyday life, we often have the opportunity to meet the items of the right hexagonal form.
For instance:
- nut;
- bee honeycombs;
- snowflake.
Hexagonal figure most economically fills the space on the plane. Take a look at the paving slabs, one is adjacent to the other so that the gaps do not remain.
Each angle is 120˚. The side of the figure is equal to the radius of the described circle.

Payment
The required value can be calculated by splitting the figure for six triangles with equal parties.

Calculating s one of the triangles, it is not difficult to determine and general. Simple formula, since the correct hexagon, in fact, is six equal triangles. Thus, for its calculation, the found area of \u200b\u200bone triangle is multiplied by 6.
If the hexagon center to any side is carried out perpendicular, it turns out a segment - apothem.
Let's see how to find a hexagon s if the apophem is known:
- S \u003d 1/2 × perimeter × apophem.
- Take an aponema equal to 5√3 cm.
- We find the perimeter using apophem: since the apophem is perpendicular to the side of the 6-square, the corners of the triangle formed by the aponemy are 30˚-60˚-90˚. Each side of the triangle corresponds to: X-x√3-2x, where short, against an angle of 30˚, is X; A long side against an angle of 60˚ - x√3, and hypotenuse - 2x.
- Appeam X√3 can be substituted in the formula a \u003d x√3. If the apophem is equal to 5√3, substituting this value, we get: 5√3cm \u003d x√3, or x \u003d 5 cm.
- The short side of the triangle is 5cm, since this value is half the length of the side of the 6-square side. Multiplying 5 to 2, we get 10cm that is the value of the length.
- The resulting value of multiply by 6 and obtain perimeter value - 60cm.
We substitute the results obtained in the formula: S \u003d 1/2 × perimeter × apofem
S \u003d ½ × 60 cm × 5√3
We consider:
We simplify the response received to get rid of the roots. The result will be expressed in square centimeters: ½ × 60cm × 5√3cm \u003d 30 × 5√3cm \u003d 150 √3cm \u003d 259.8C m².
How to find an incorrect hexagon area
There are several options:
- Breakdown of a 6-coal to other figures.
- Trapezing method.
- The calculation of the incorrect polygons using the coordinate axes.
The choice of method is dictated by the source data.
Trapezium method
The hexagon is divided into separate trapets, after which the area of \u200b\u200beach obtained figure is calculated.

Use axes of coordinates
We use the coordinates of the vertices of the polygon:
- In the table, write the coordinates of the vertices x and y. Sequentially select the vertices, "moving" counterclockwise, completing the list by re-record the coordinates of the first vertex.
- Multiply the coordinate values \u200b\u200bof the 1st vertex to the value of Y 2nd vertices, and continue to multiply so. We fold the results.
- The coordinate values \u200b\u200bof the y1-th vertex multiply on the coordinate values \u200b\u200bof the X 2nd vertex. We fold the results.
- We subtract the amount obtained at the 4th stage of the amount received at the third stage.
- We divide the result obtained at the previous stage, and find what they were looking for.
Drinking a hexagon on other figures
Polygons are broken into other figures: trapezoids, triangles, rectangles. Using formulas for calculating the areas of listed figures, the required values \u200b\u200bare calculated and folded.
Incorrect hexagon can consist of two parallelograms. To calculate the parallelogram area, its length is multiplied by its width, and then the already known two areas are folded.
Square of equilateral hexagon
The right hexagon has six equal sides. The area of \u200b\u200bthe equilateral figure is 6s the triangles to which the correct hexagon is broken. Each triangle in the correct hexagon is equal, therefore, to calculate the area of \u200b\u200bsuch a figure, the area is rather known although B one triangle.

To find the desired value of the area of \u200b\u200bthe right figure described above.